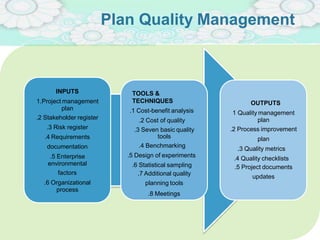
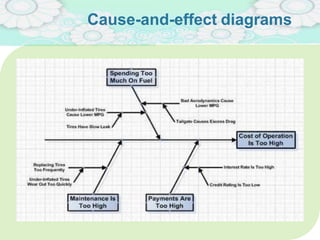
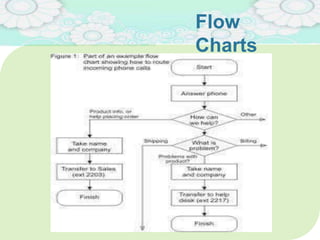
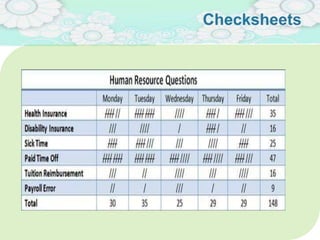
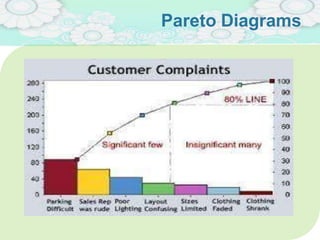
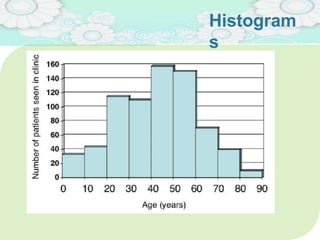
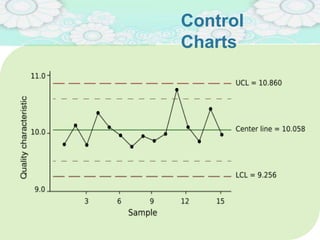
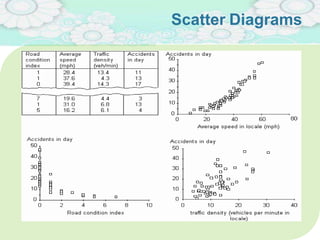
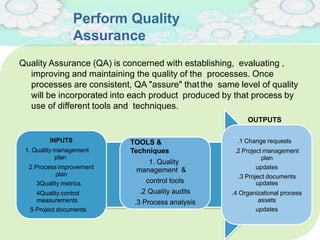
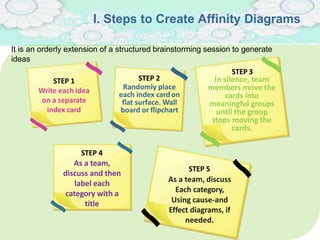
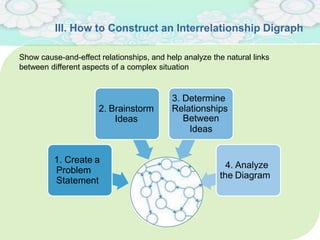
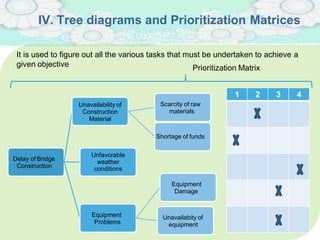
El manejo de la calidad del proyecto se centra en asegurar que productos y servicios cumplan con estándares específicos mediante la documentación de requisitos y la implementación de procesos de aseguramiento y control de calidad. El plan de gestión de calidad incluye métodos como el análisis de costo-beneficio y herramientas básicas como diagramas de causa-efecto y gráficos de control. Las actividades de aseguramiento y control de calidad permiten monitorear el desempeño y realizar ajustes necesarios para cumplir con los objetivos del proyecto.