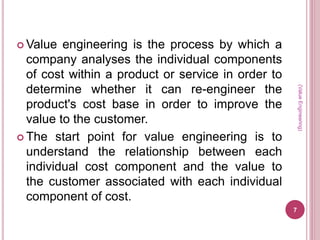
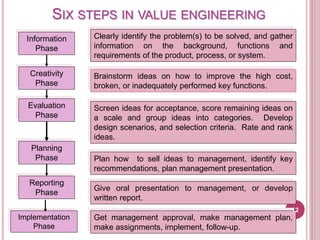
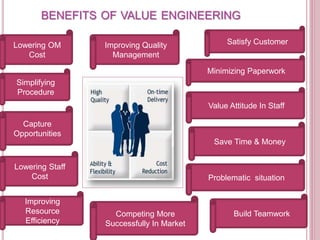
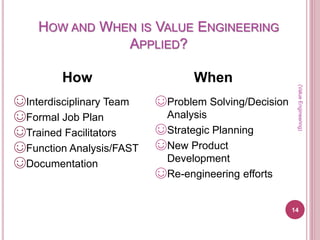
Value analysis and value engineering aim to reduce unnecessary costs through a systematic, creative approach. Value analysis focuses on identifying value as the relationship between function and cost, while value engineering takes a problem-solving perspective to improve value. The value methodology involves analyzing functions, determining functional worth, and providing necessary functions at lowest cost. Value engineering is applied through interdisciplinary teams using techniques like function analysis to develop cost-saving solutions.