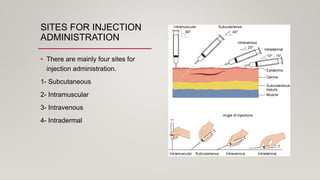
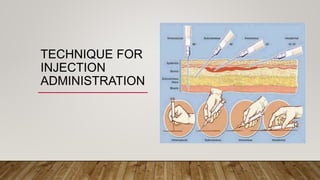
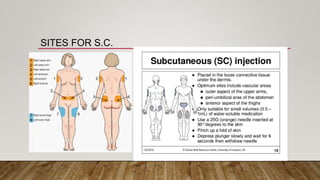
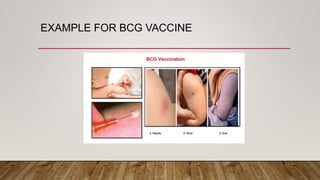
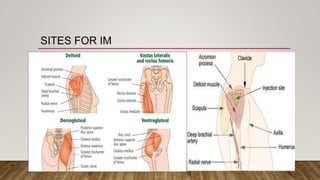
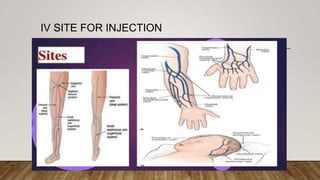
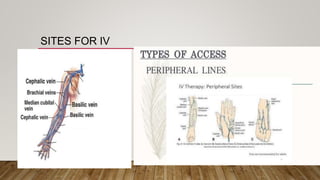
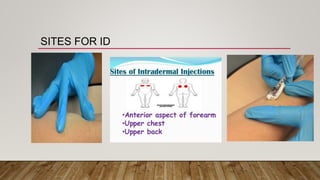
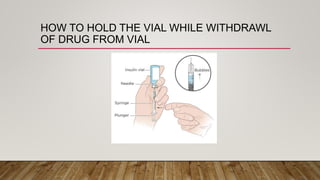
The document discusses the administration of injections, detailing four main injection sites: subcutaneous, intramuscular, intravenous, and intradermal. It outlines the techniques for each type, providing examples and emphasizing the importance of aseptic procedures and proper documentation post-administration. Key aspects include the required materials and procedural steps to ensure safe and effective injection practices.