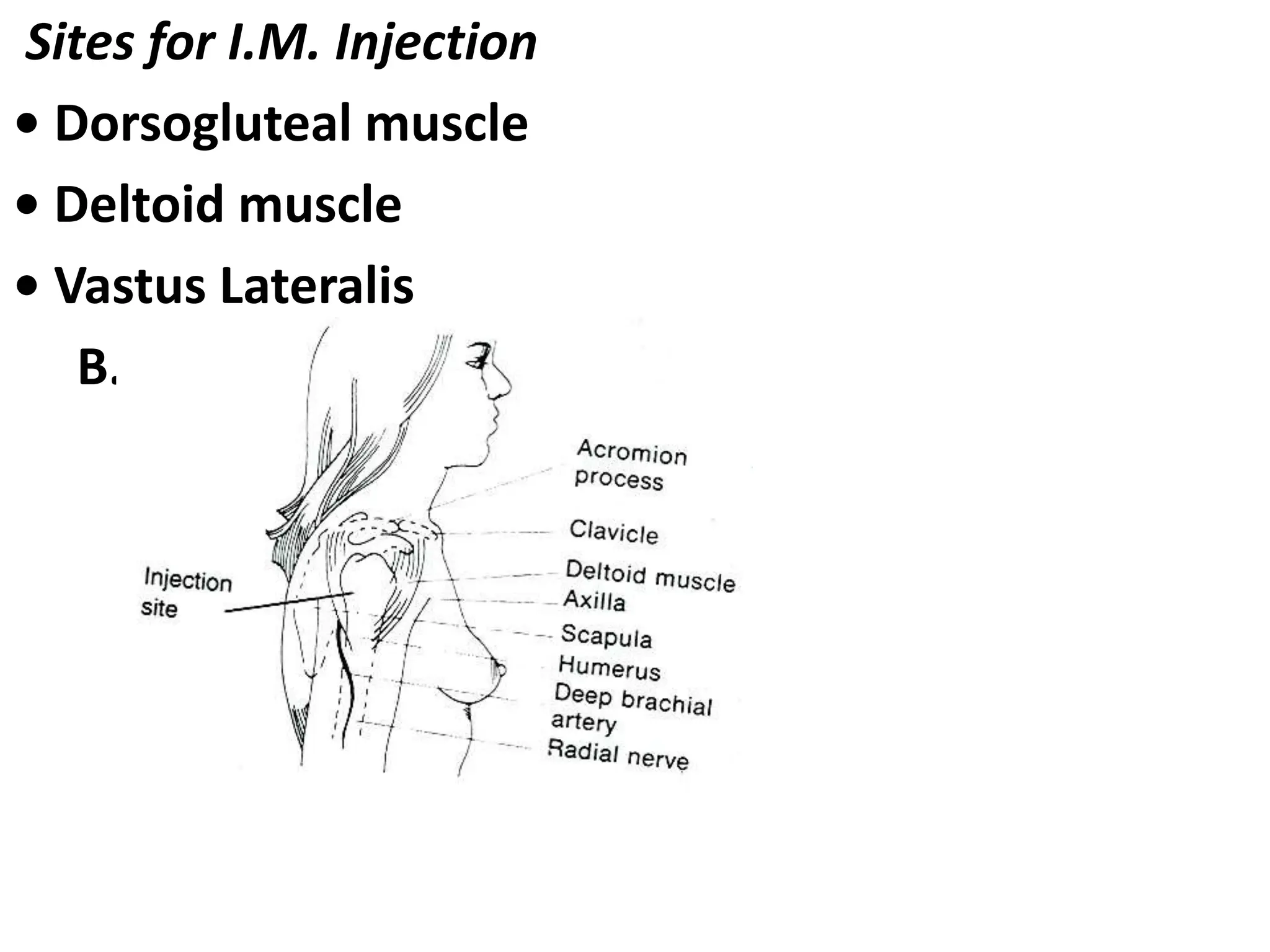
This document outlines medication administration via various routes. It discusses oral administration as well as parenteral routes like intradermal, subcutaneous, intramuscular, and intravenous injection. For each route, it describes the purpose, necessary equipment, appropriate sites on the body, and step-by-step procedures for safe and proper administration of medications. Safety is emphasized, including following the "Five Rights" and taking proper precautions.