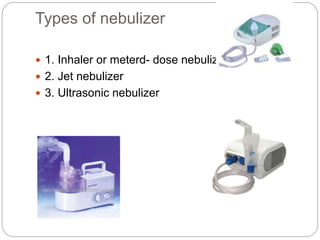
The document outlines the nebulization procedure, detailing its definition, purpose, types of nebulizers, and required equipment. It provides a comprehensive step-by-step guide on administering nebulizer therapy, emphasizing patient comfort, medication administration rights, and proper cleaning protocols. Additionally, it addresses troubleshooting and documentation requirements to ensure effective treatment and patient safety.