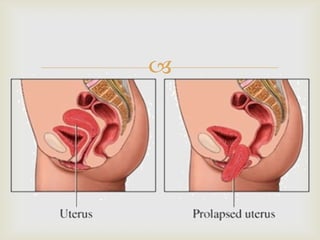
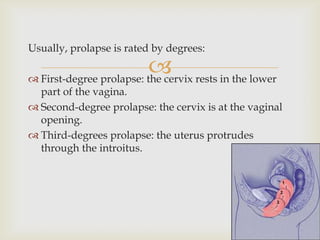
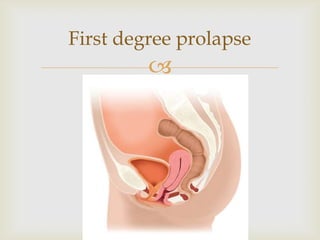
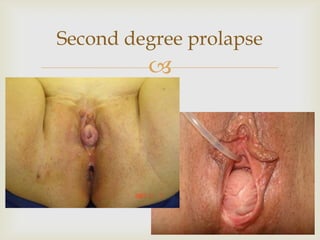
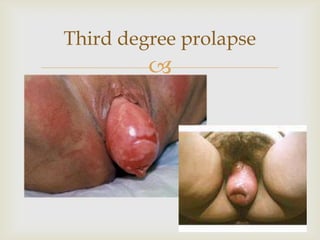
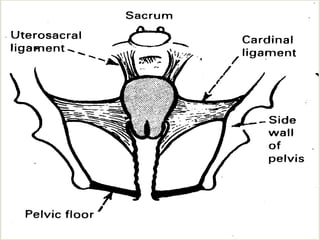
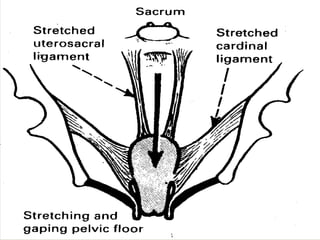
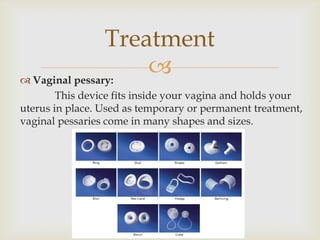
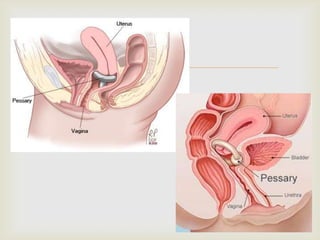
Uterine prolapse is the downward displacement of the uterus into the vaginal canal. It is usually rated by degree depending on how far the uterus has descended. Risk factors include pregnancy, childbirth, obesity, chronic coughing, and menopause. Symptoms include pressure or heaviness in the pelvis, urinary problems, and painful sex. Treatment options include the use of a vaginal pessary or various surgical procedures to repair tissues. Nursing care focuses on preventive measures like Kegel exercises and helping patients before and after surgery.