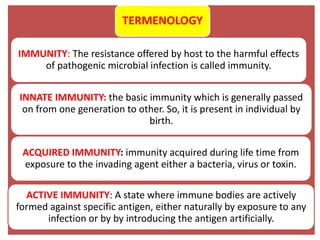
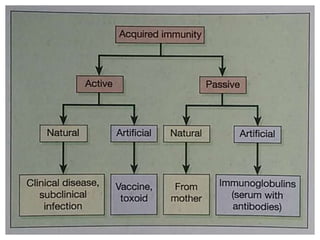
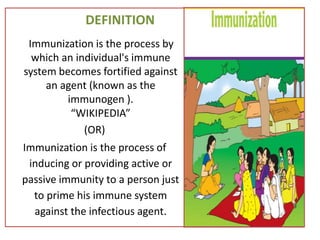
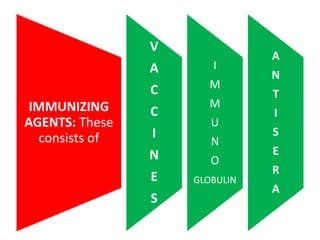
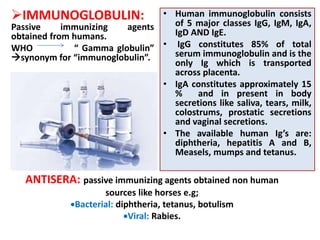
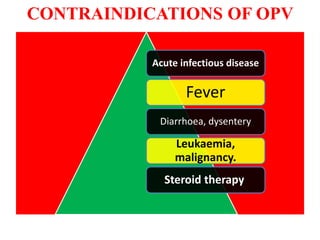
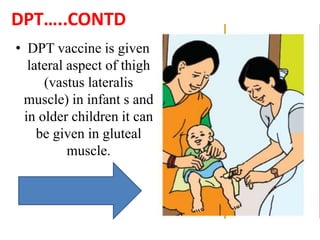
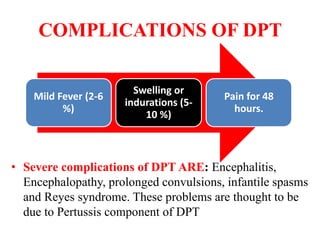
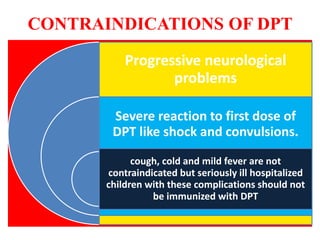
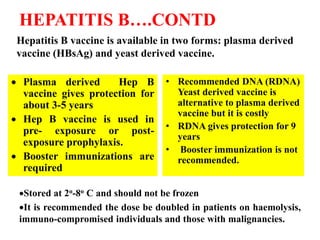
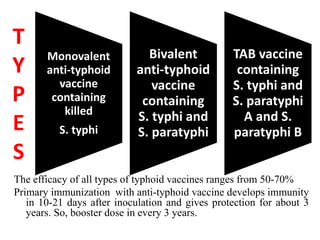
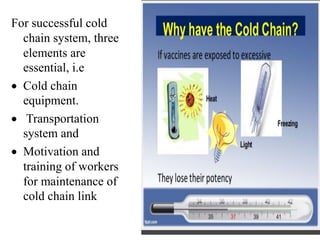
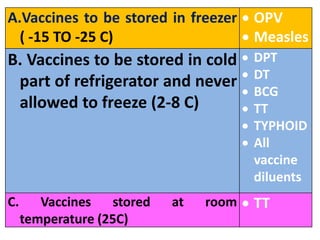
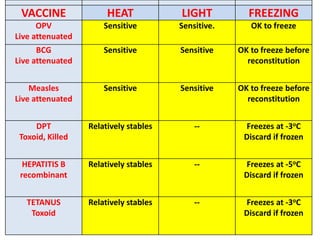
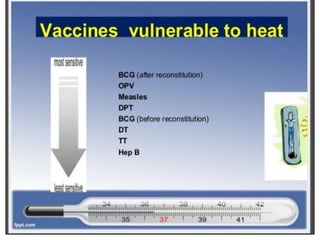
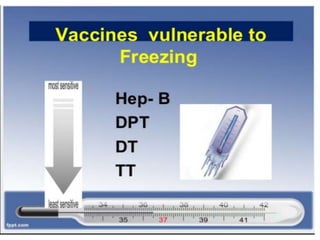
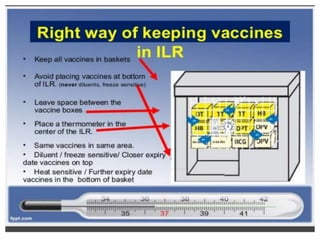
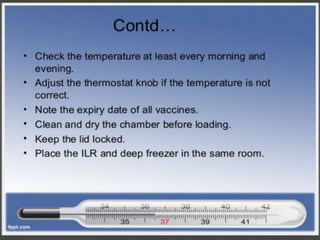
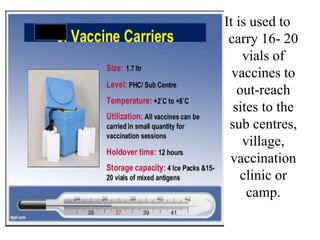
- Immunization is the process of protecting an individual from a disease through introduction of live, killed or attenuated organisms. It stimulates the immune system and produces antibodies to prevent disease.
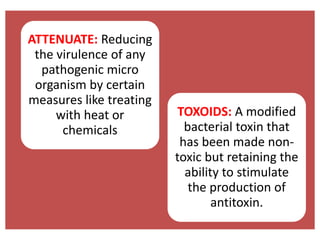
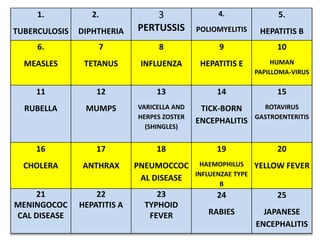
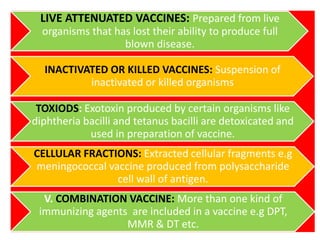
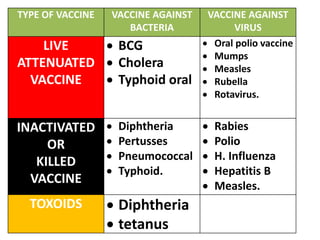
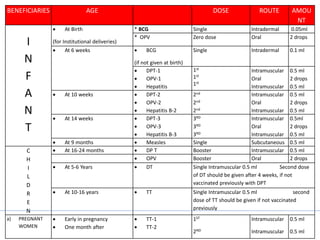
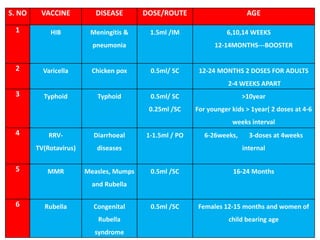
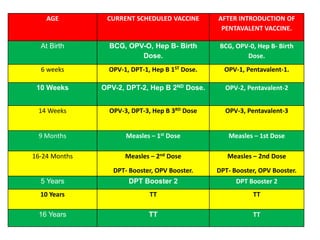
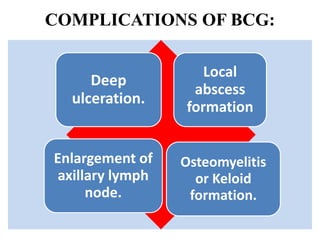
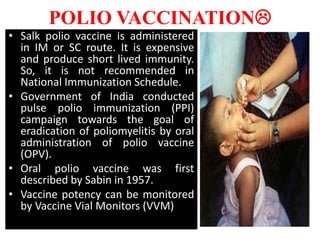
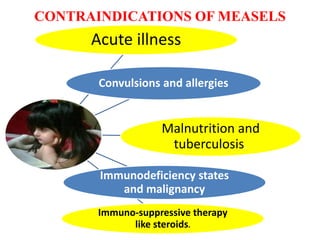
- There are various types of vaccines including live attenuated, inactivated/killed, and toxoids. National immunization schedules provide recommended ages and doses of vaccines like BCG, DPT, polio, hepatitis B, and measles.
- Immunization is essential to reduce child mortality and is one of the most effective public health interventions. Ensuring all children are fully immunized is important to protect both individuals and communities.