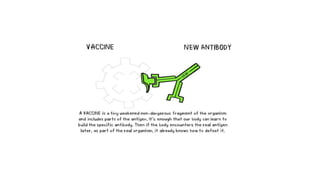
Vaccines work by exposing the body to antigens from pathogens to trigger an immune response. When first exposed, it takes time for the body to produce antibodies, but memory cells remain to allow faster response to future exposure. Vaccines introduce antigens to stimulate this immune response, protecting against disease. Major types include inactivated, live-attenuated, mRNA, and subunit/toxoid vaccines. Vaccination has helped reduce disease and mortality worldwide through innovations since Jenner's smallpox vaccine and ongoing efforts like polio and COVID-19 vaccine development.