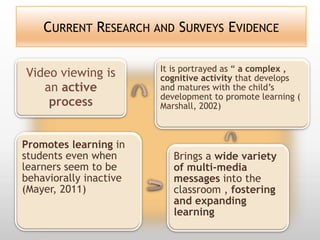
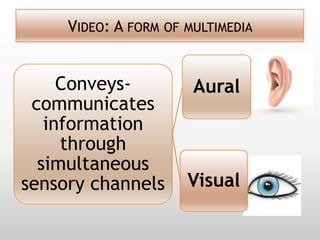
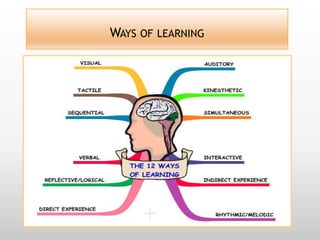
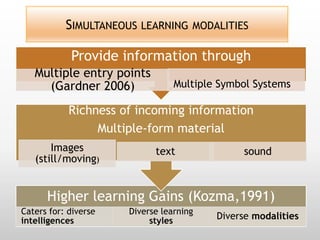
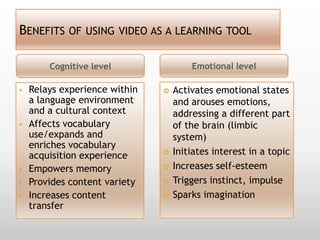
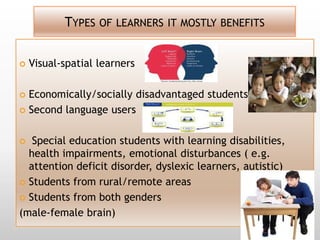
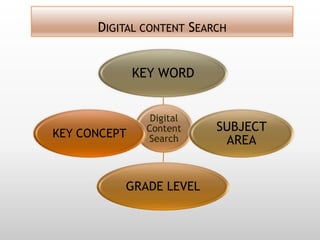
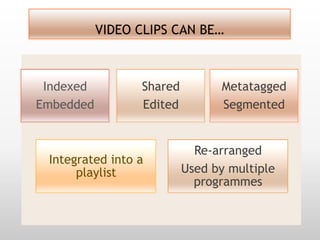
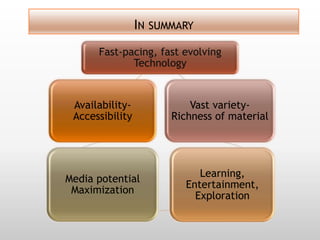
This document discusses using video in the English as a Foreign Language (EFL) classroom. It outlines how today's students are digital natives who learn differently than previous generations. Research shows that video viewing is an active process that can promote learning. When used appropriately, video can benefit different types of learners by appealing to multiple senses and providing information through various channels. The document provides suggestions for effective pre, during, and post viewing activities to maximize learning when incorporating video into EFL lessons.