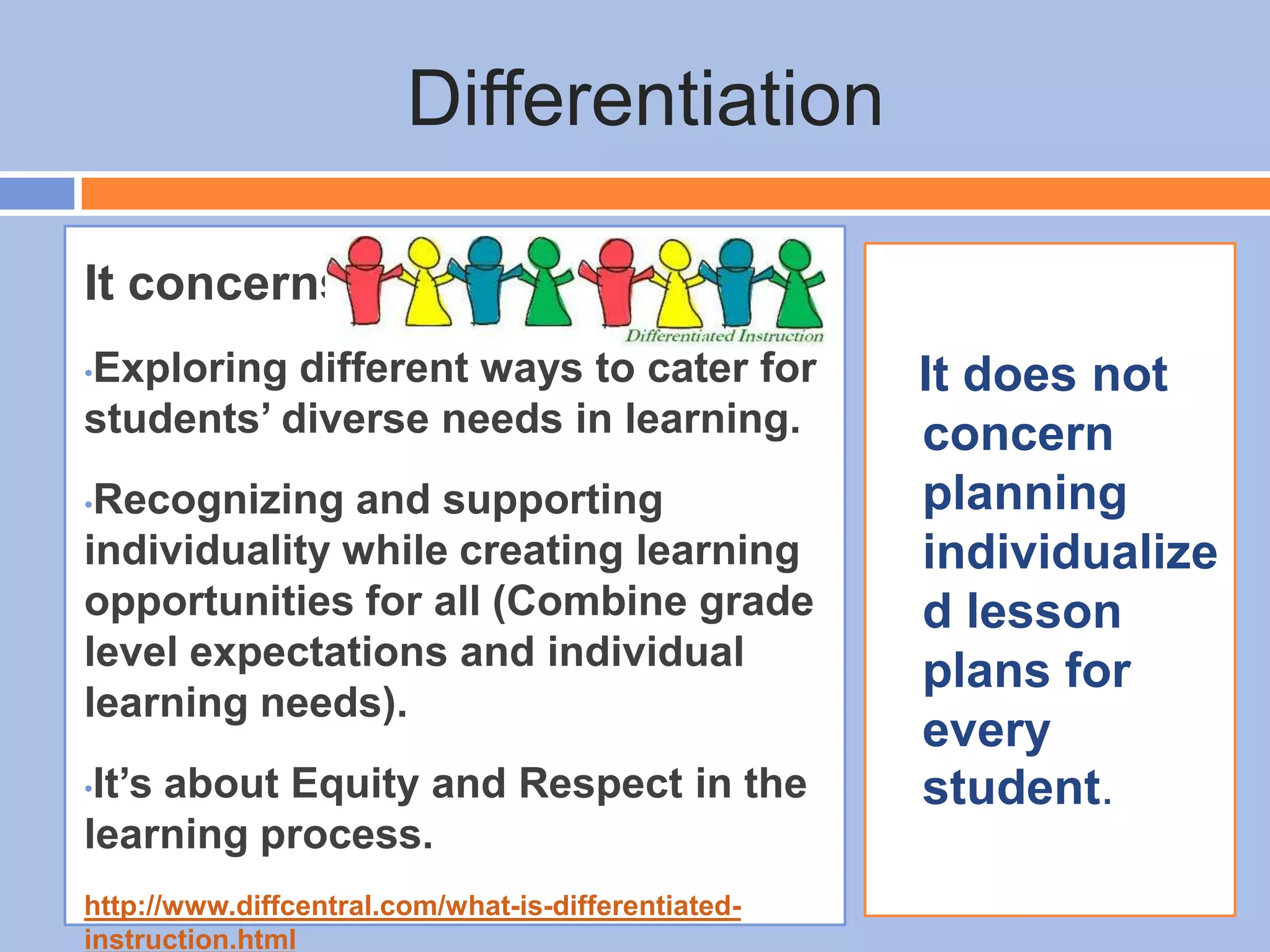
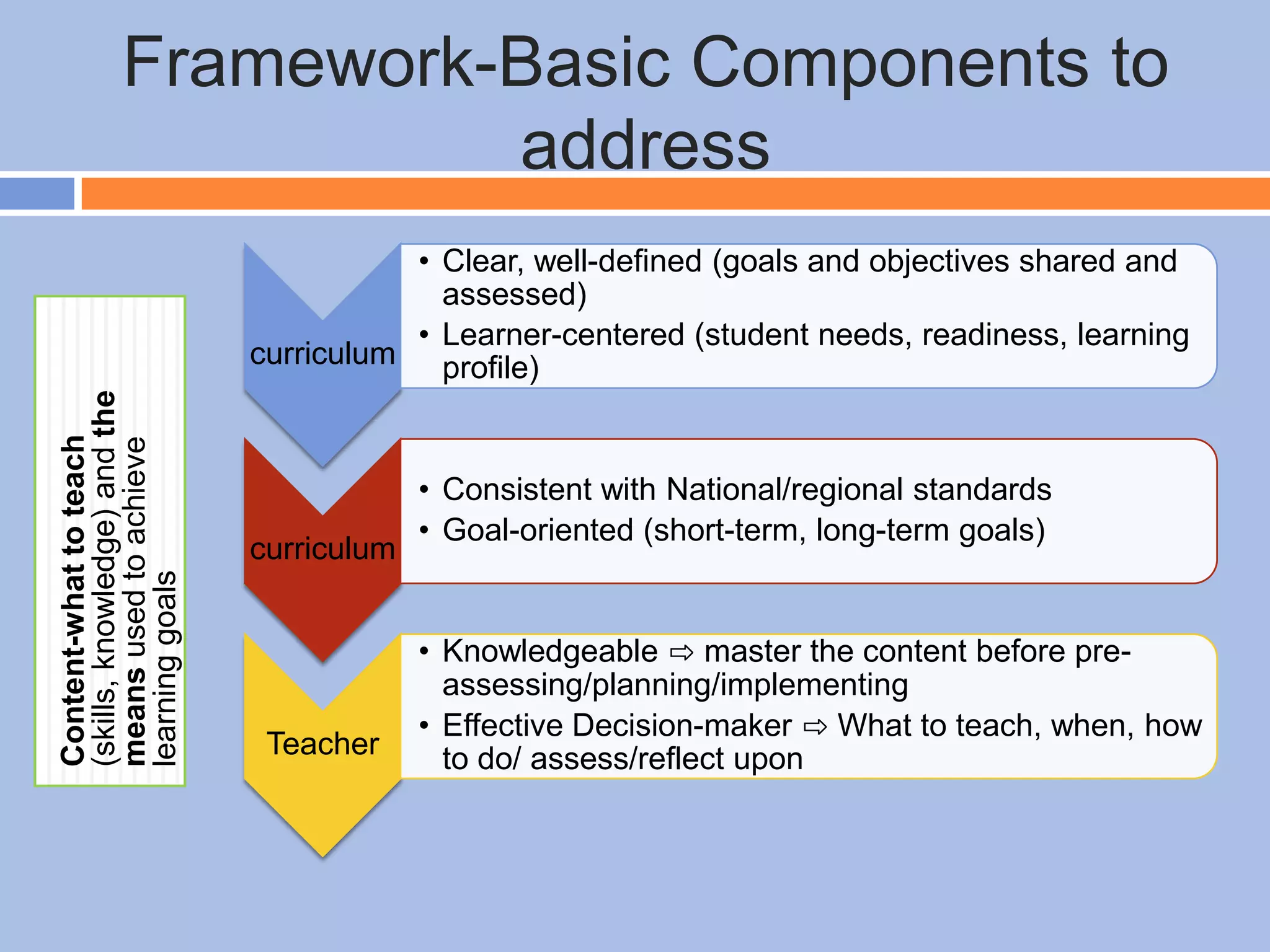
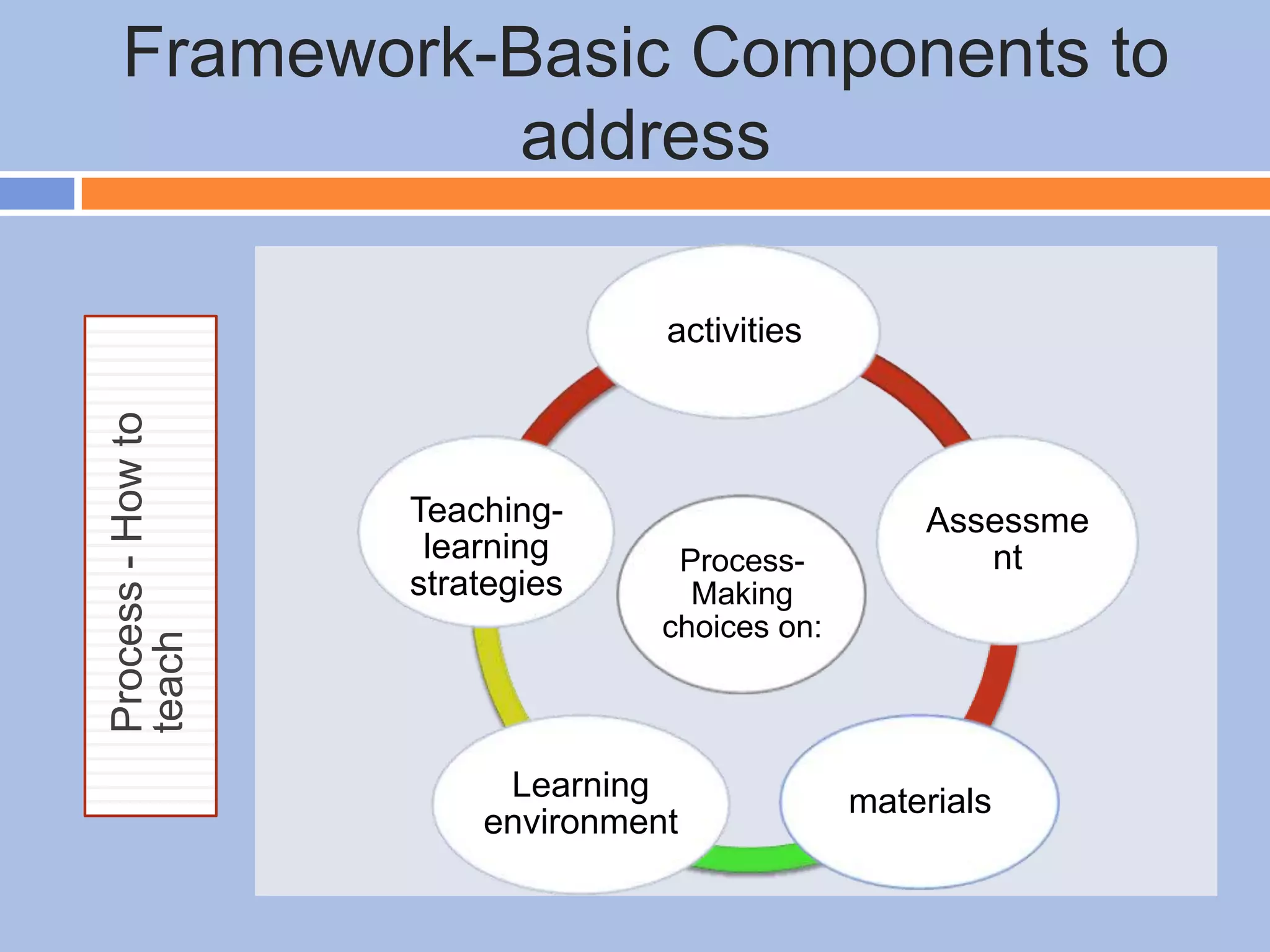
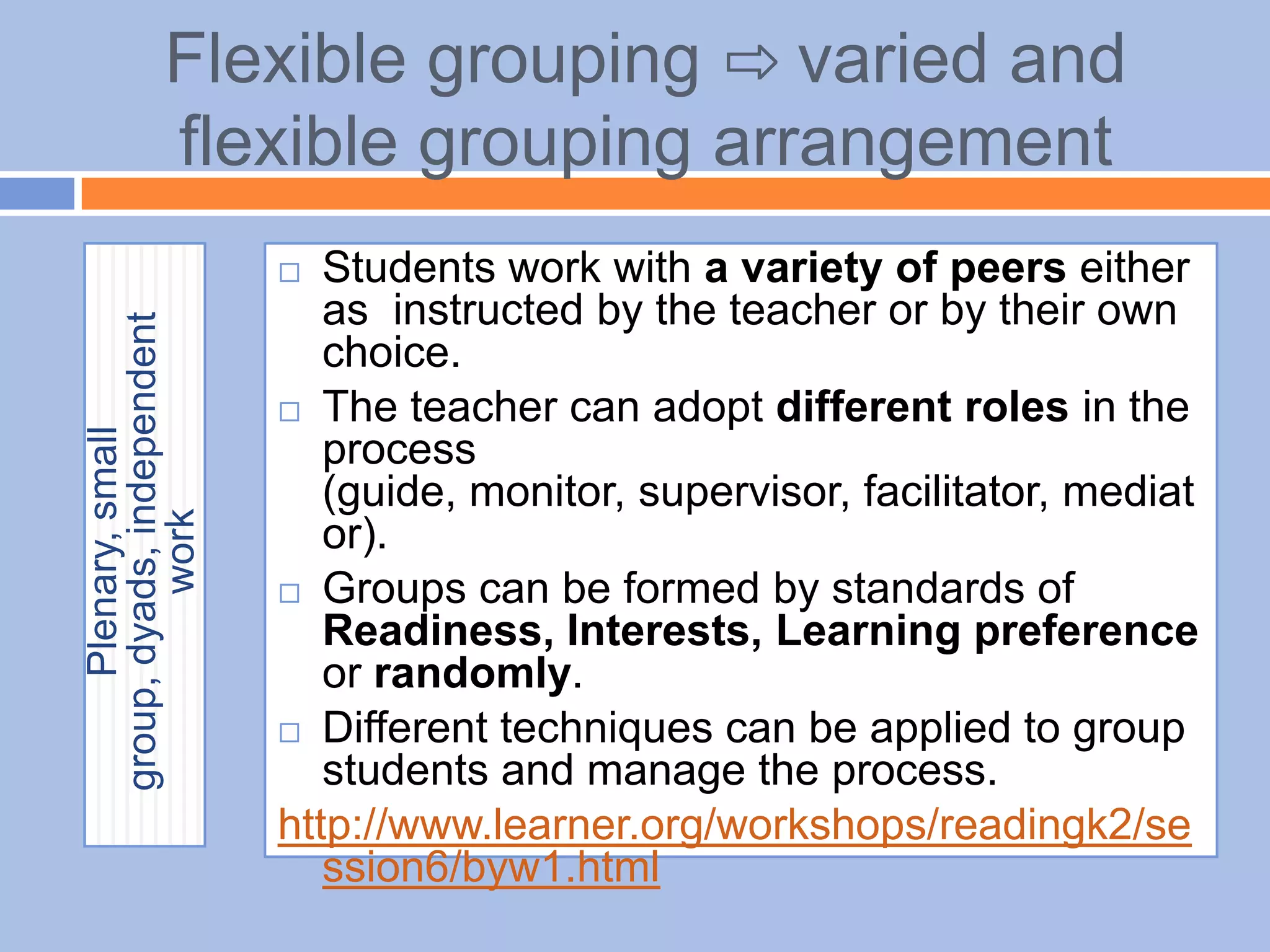
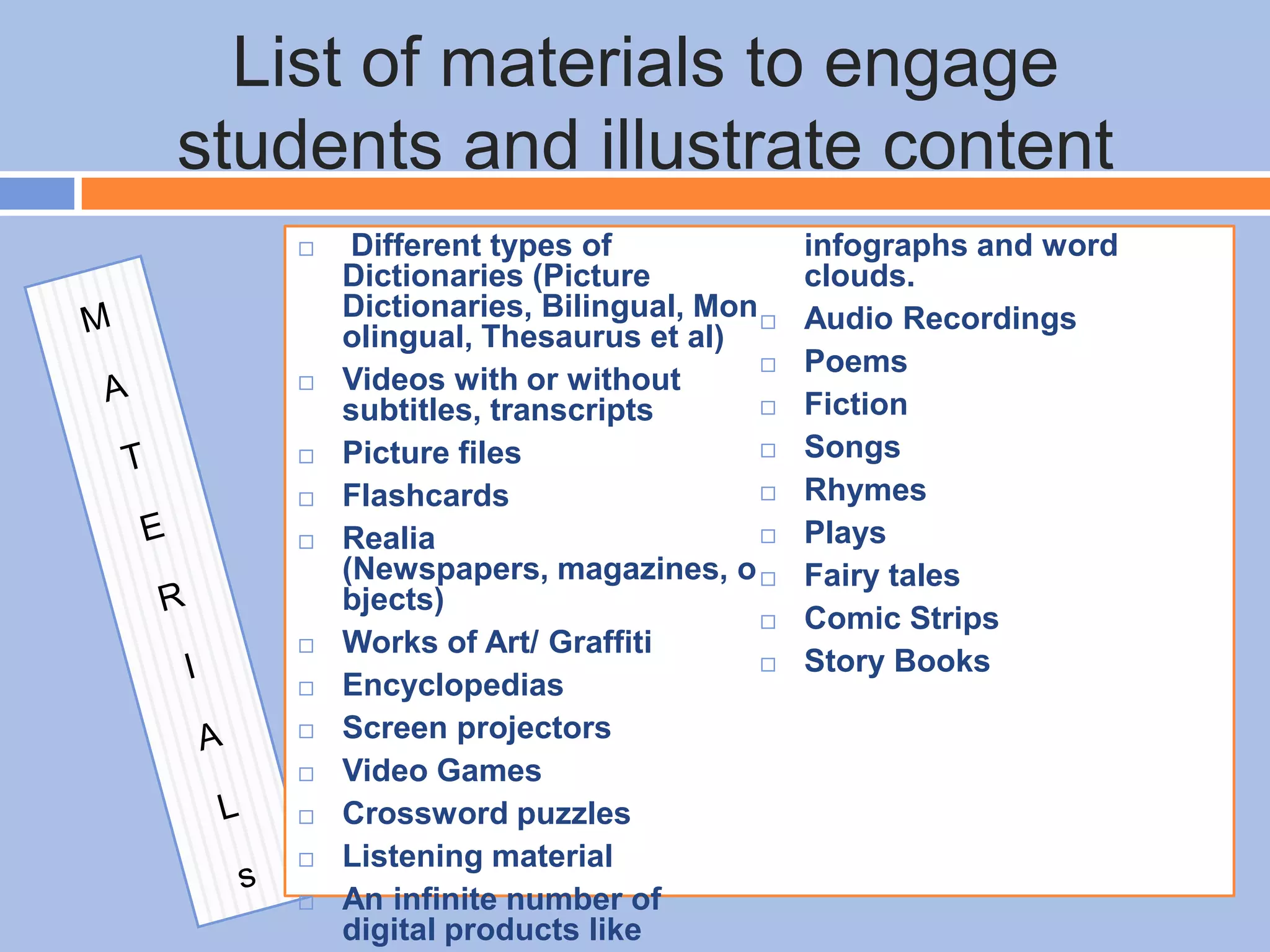
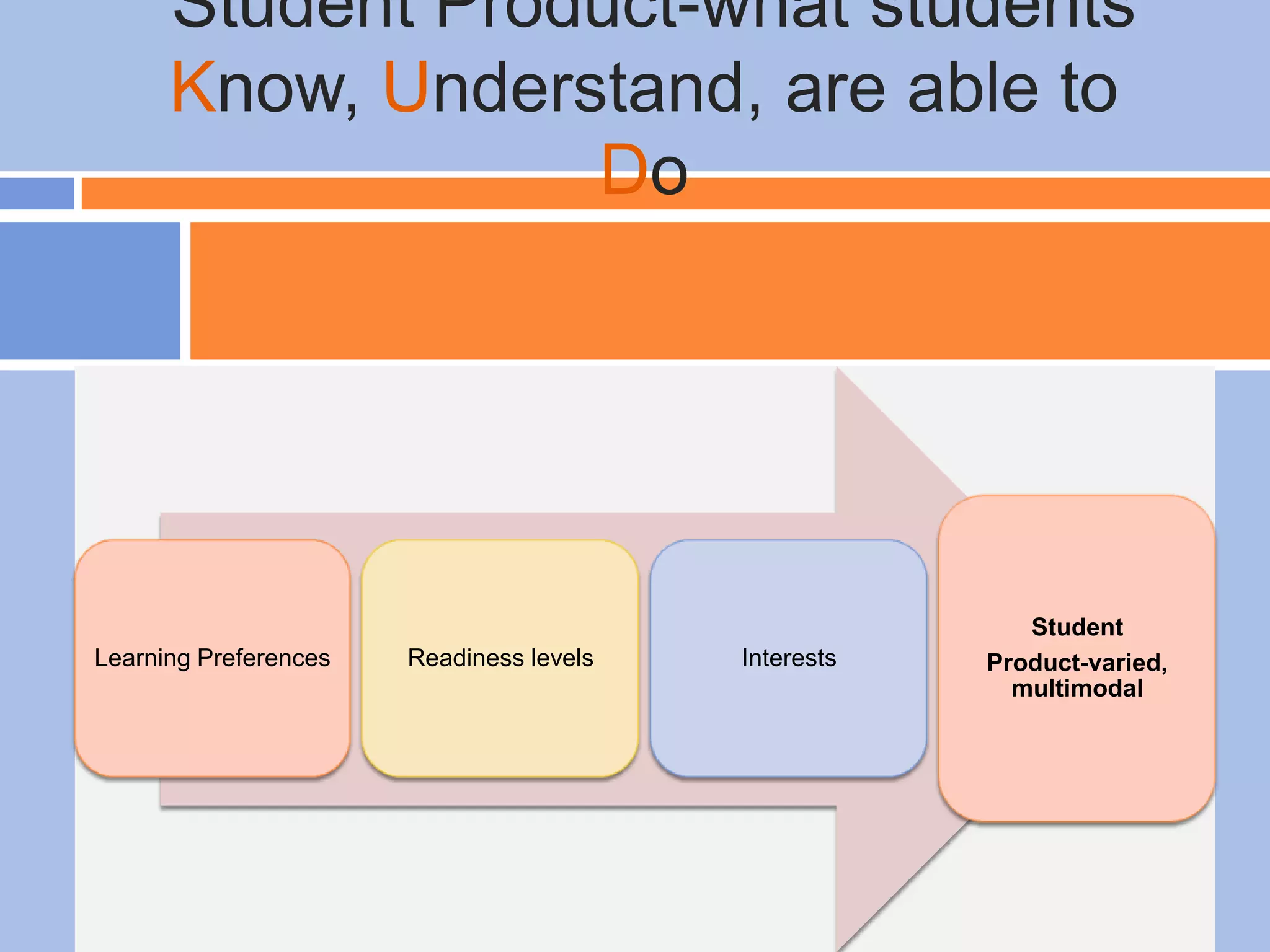
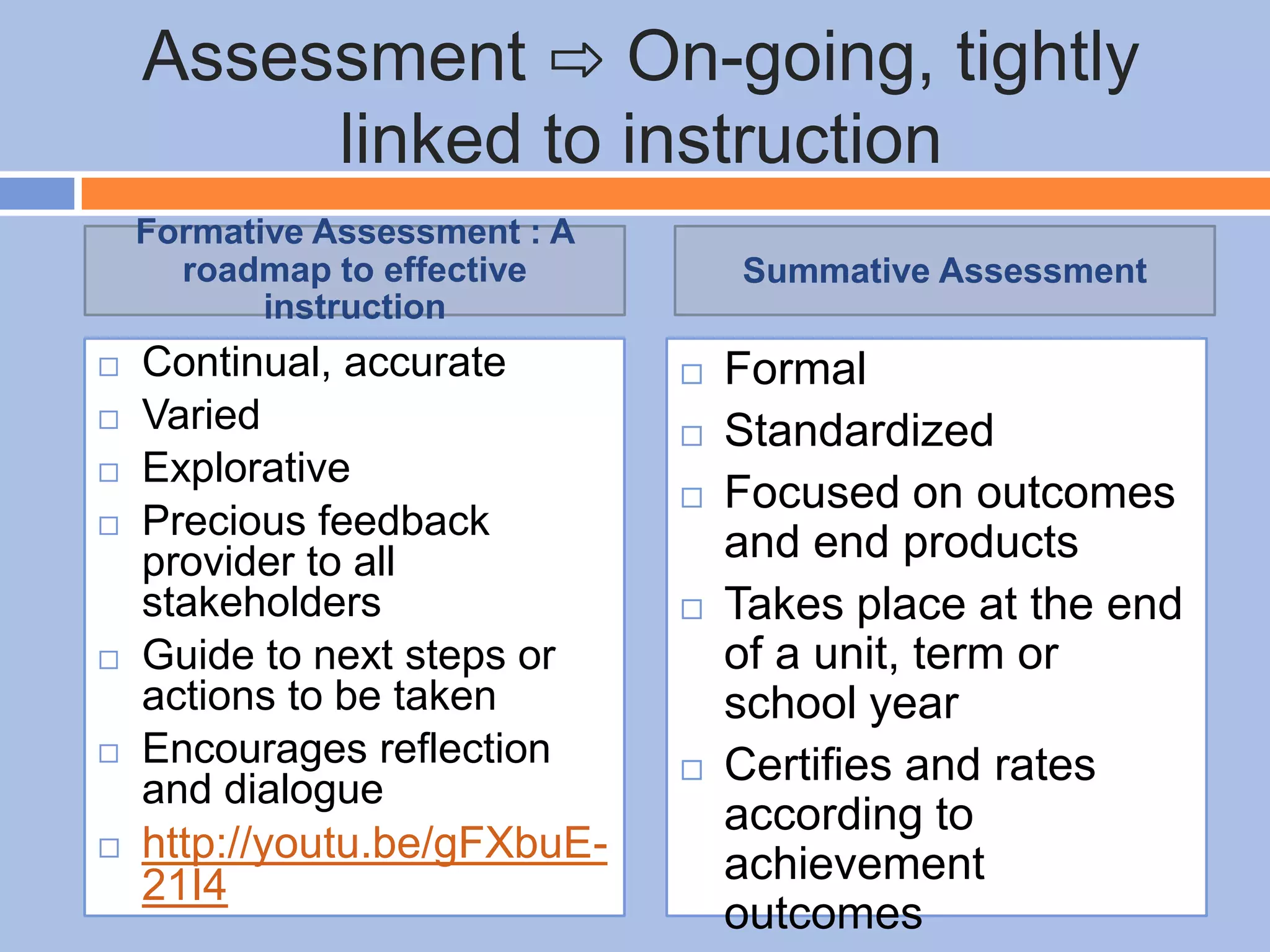
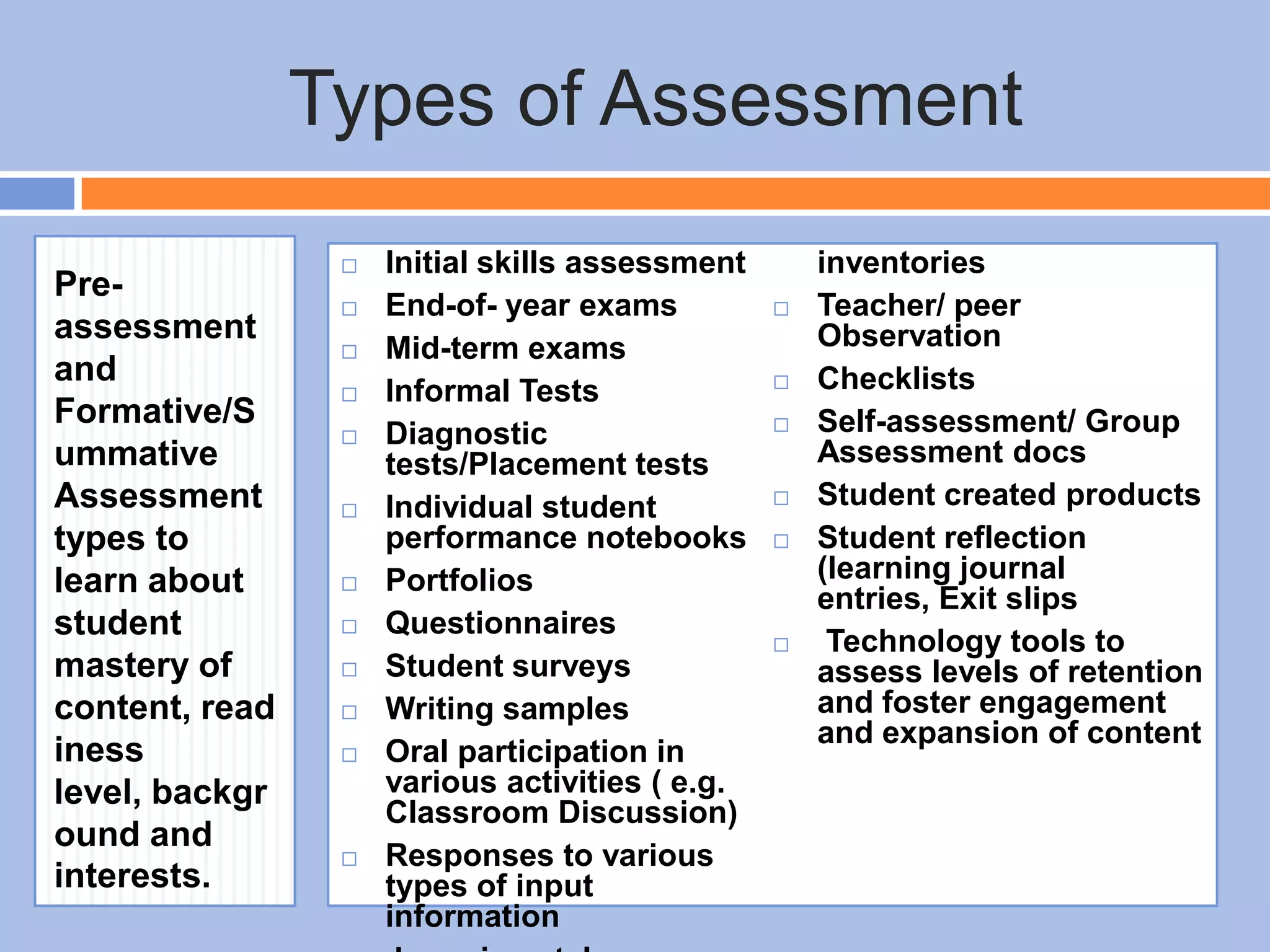
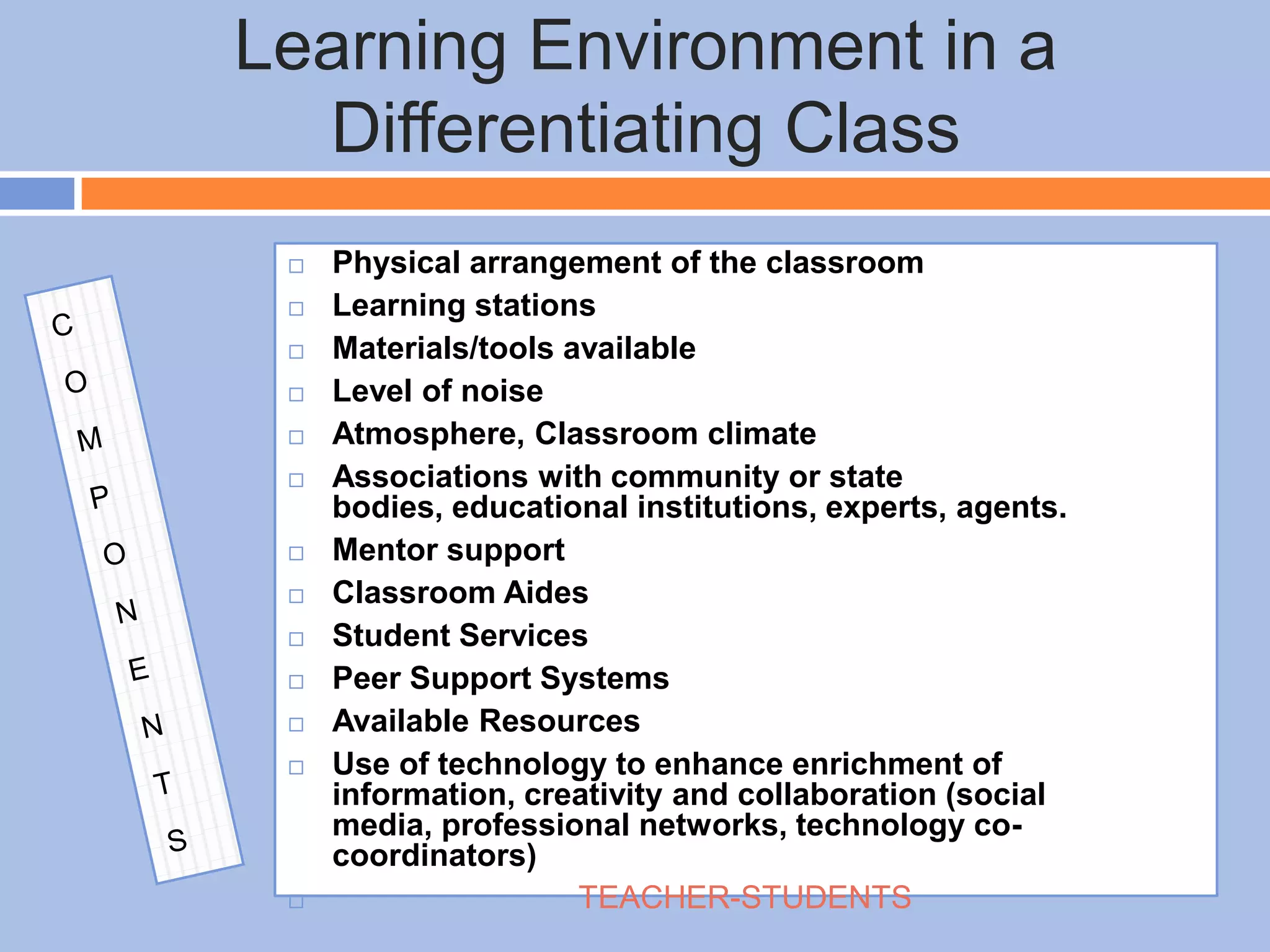
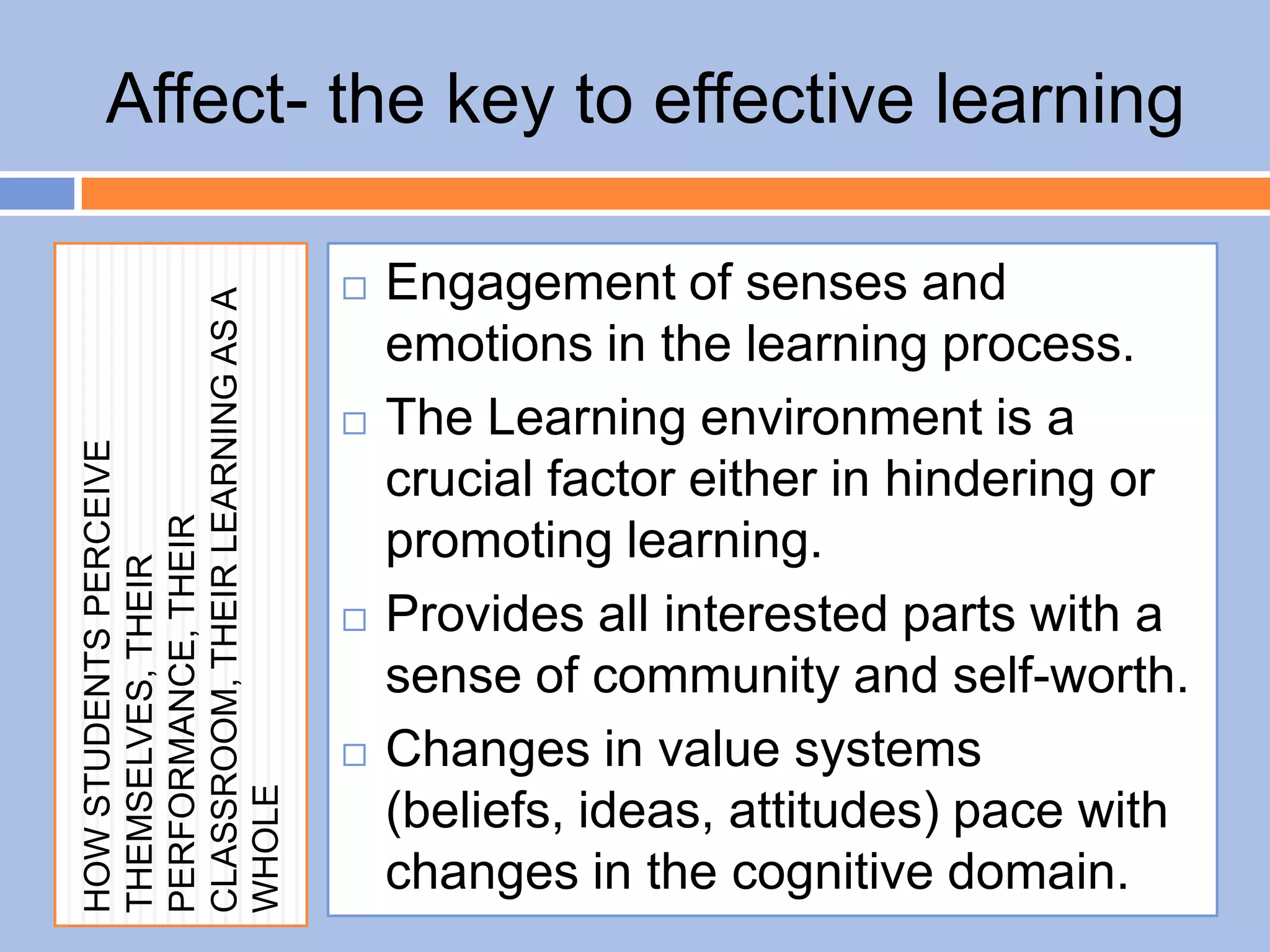
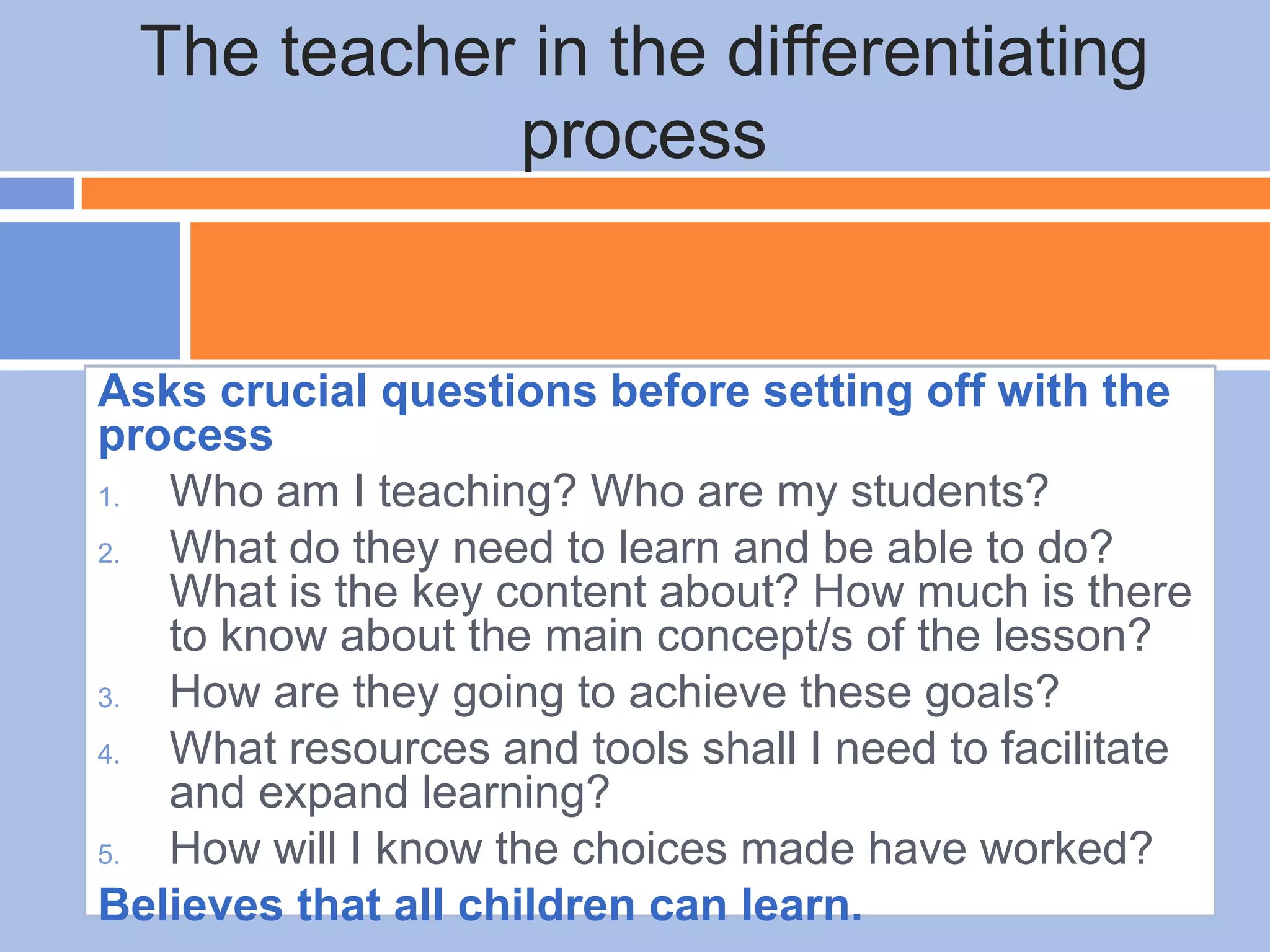
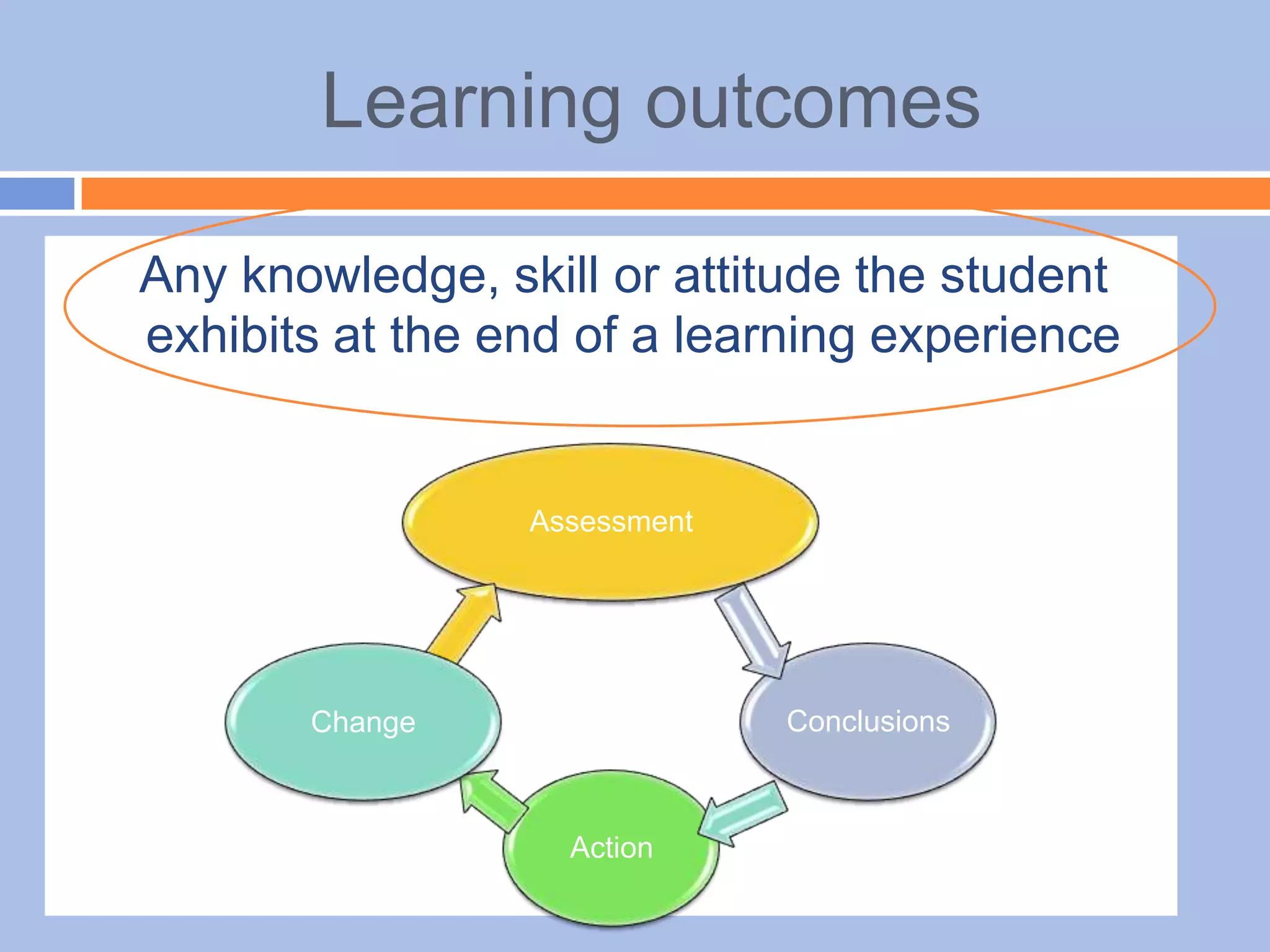
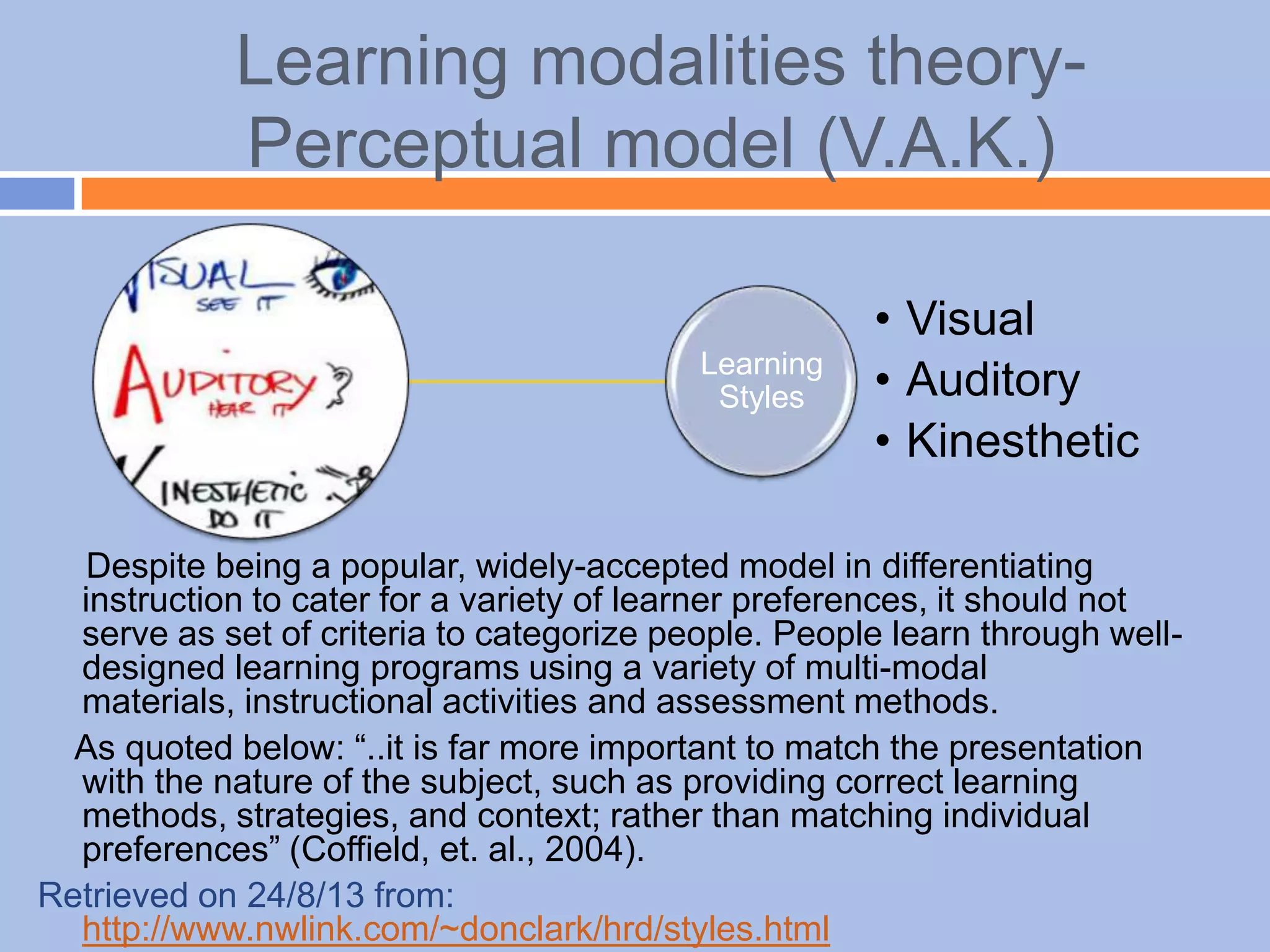
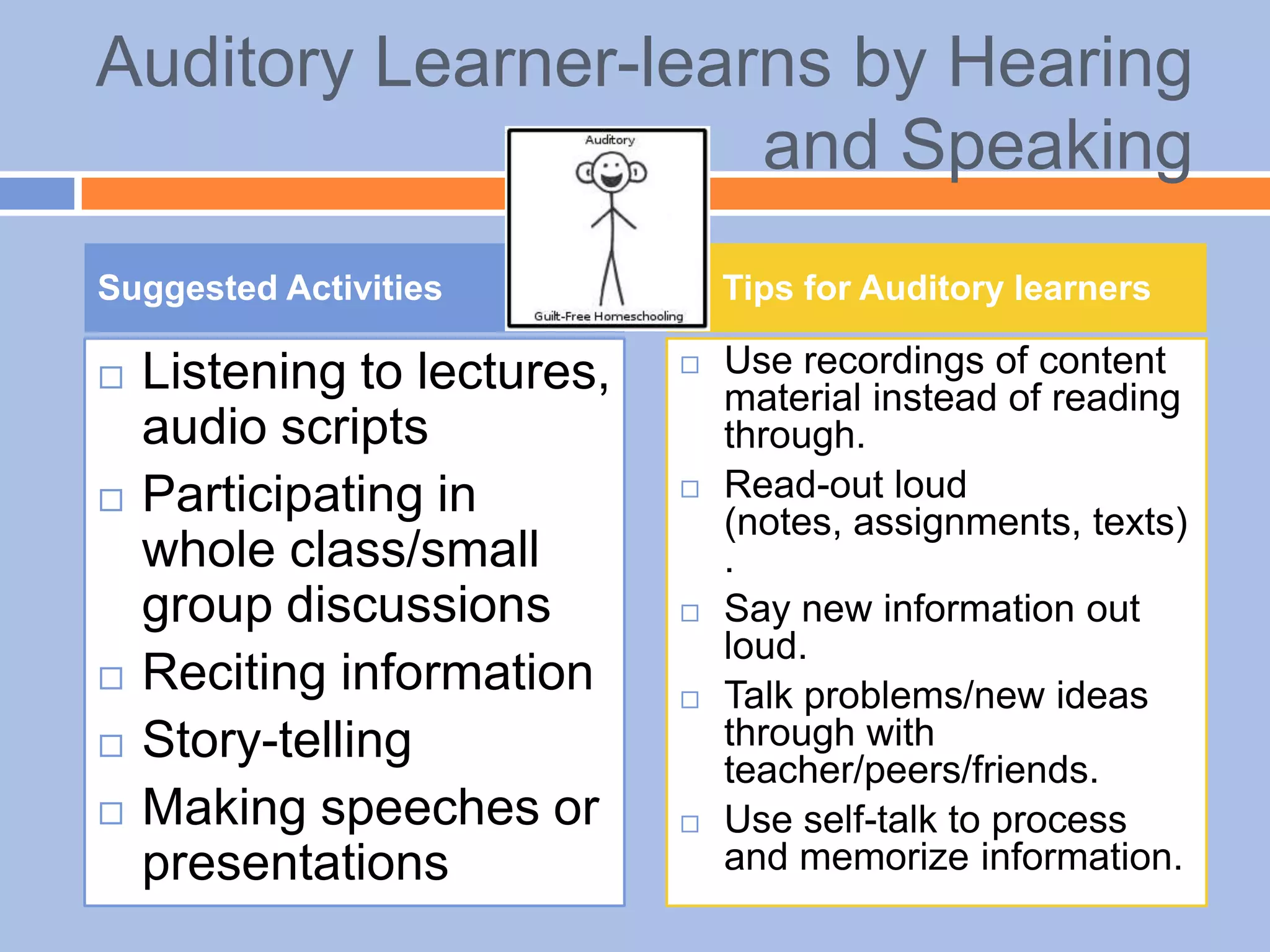
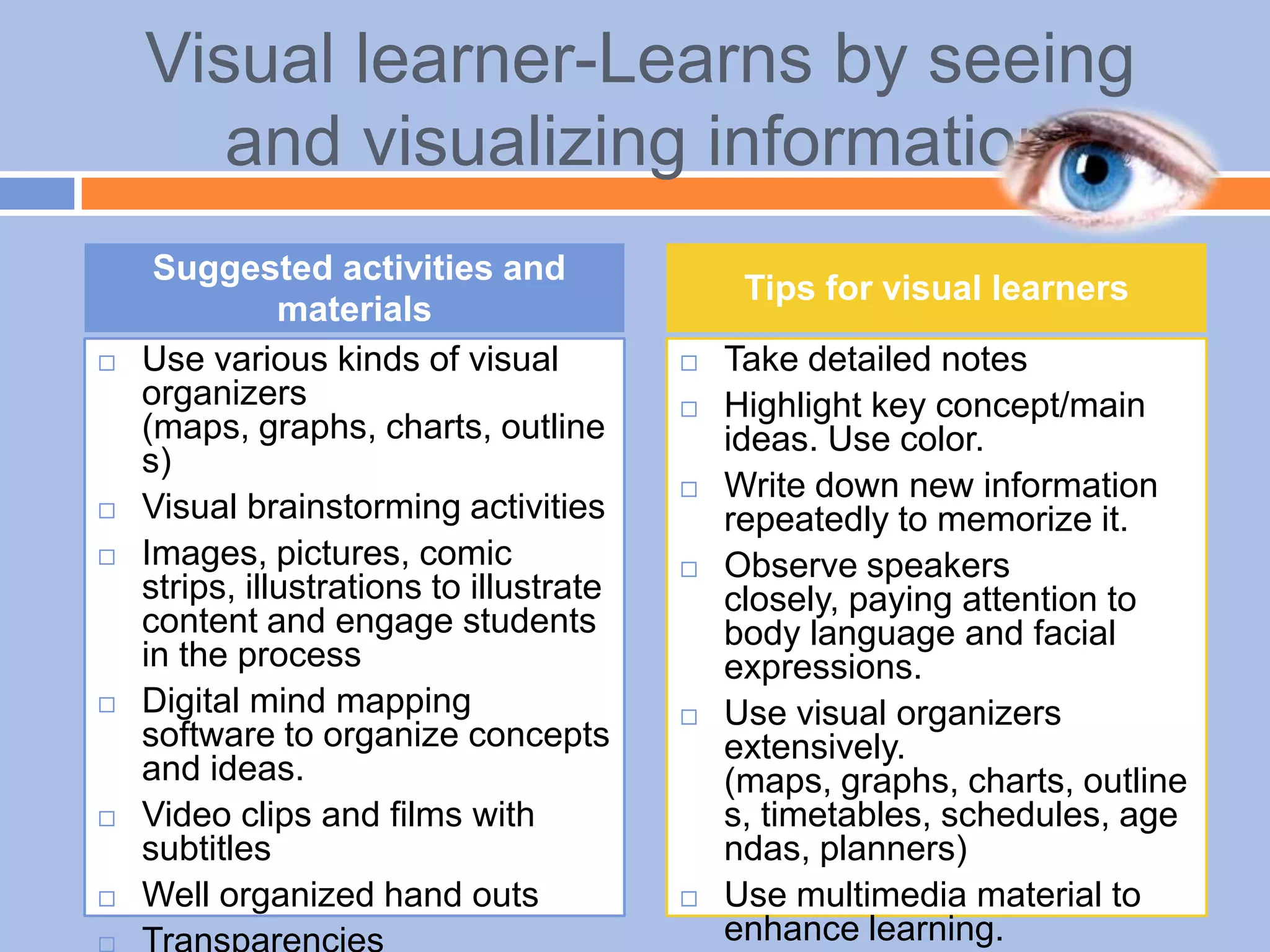
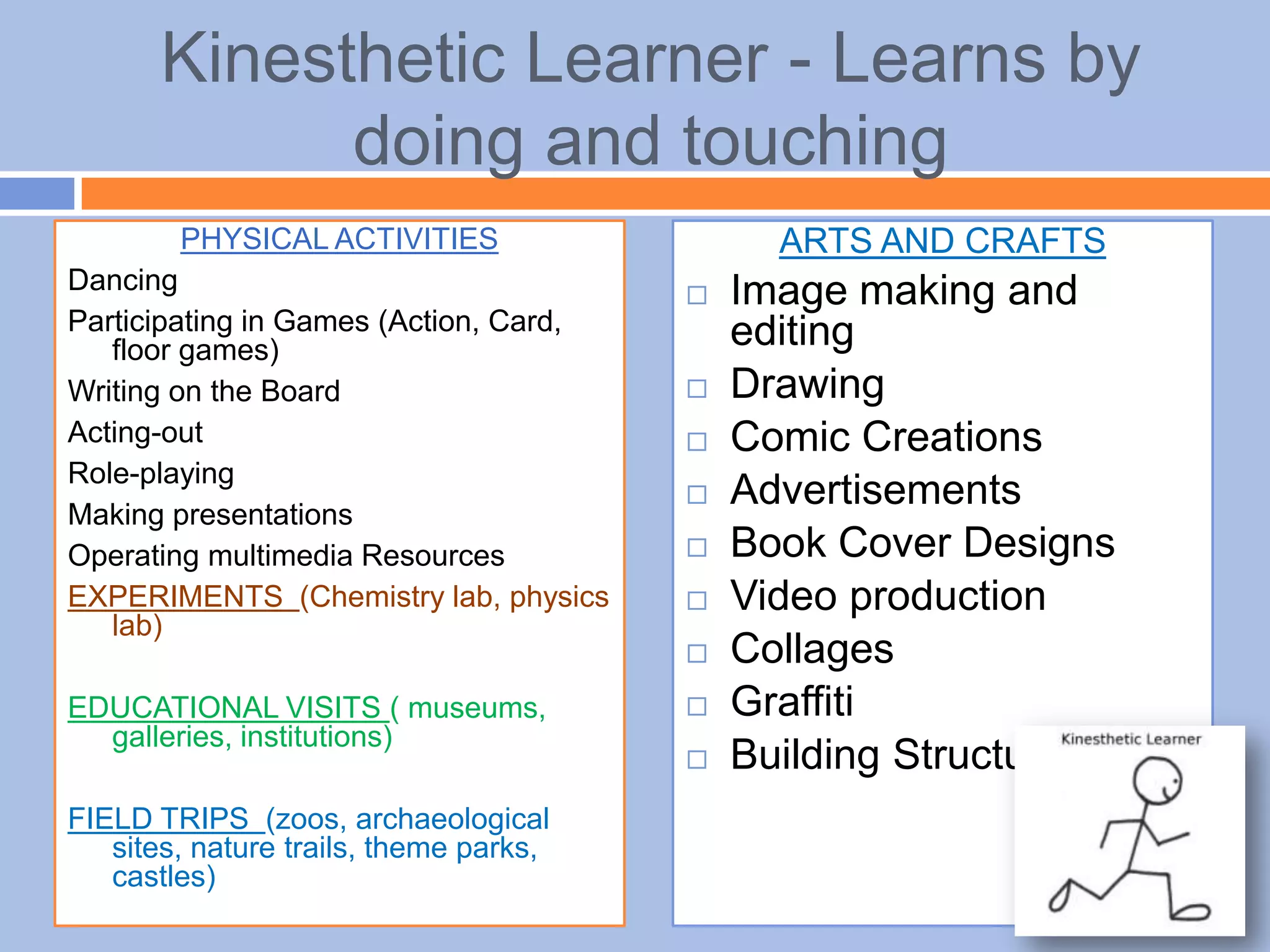
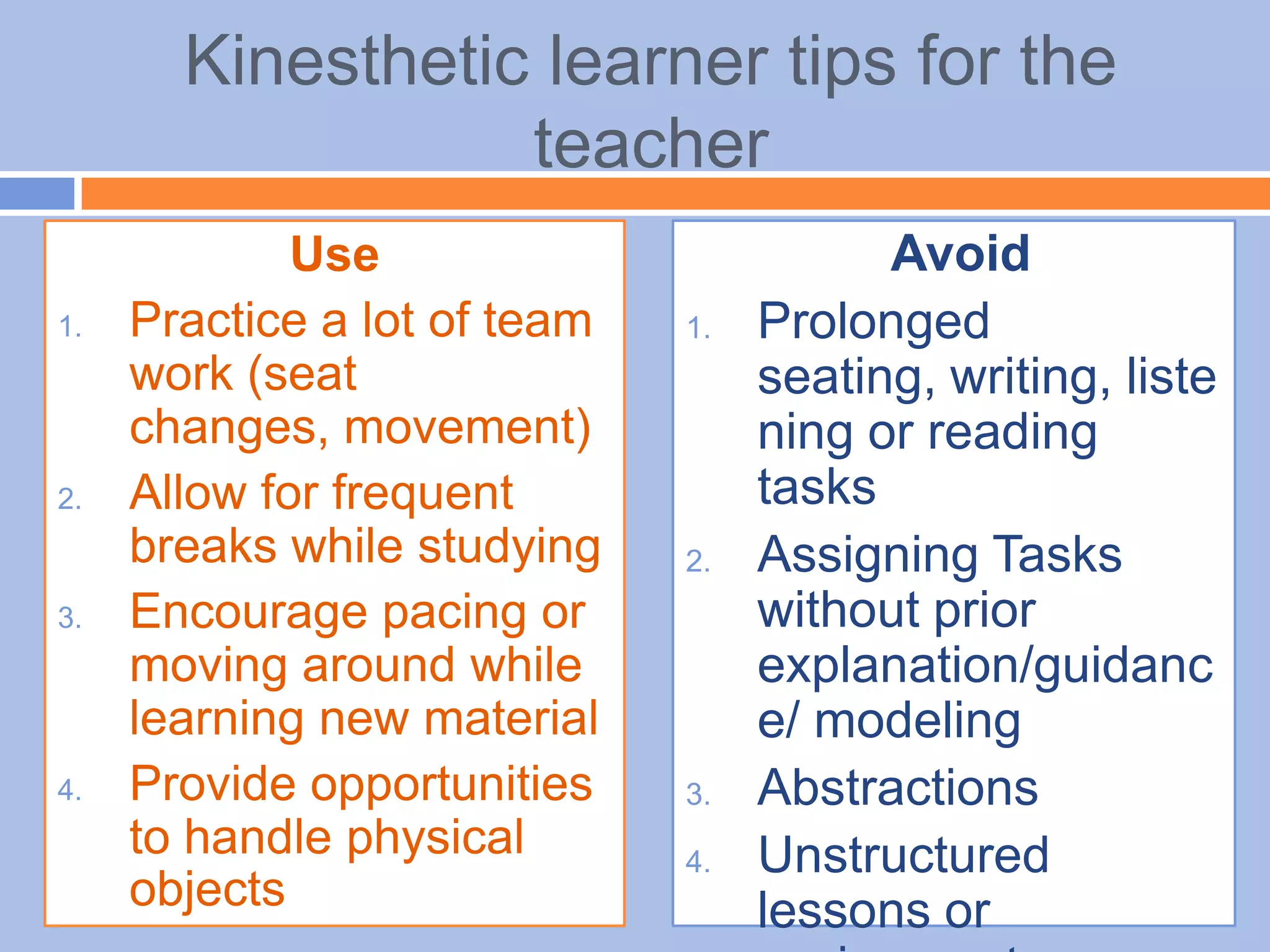
The document provides an overview of differentiated instruction in education, emphasizing the need to cater to diverse student needs based on their prior knowledge, experiences, and learning preferences. It outlines essential components such as learner-centered curriculum design, various teaching strategies, and assessment methods to foster strong teacher-student connections and promote equity in the classroom. The document concludes that successful differentiation requires combining effective instructional strategies with a high-quality curriculum and active learning opportunities.