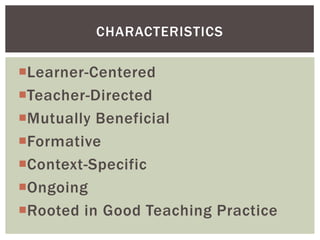
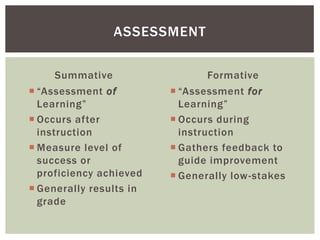
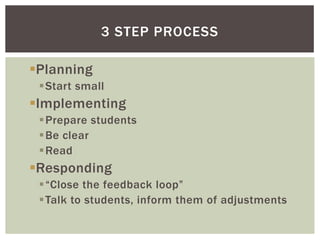
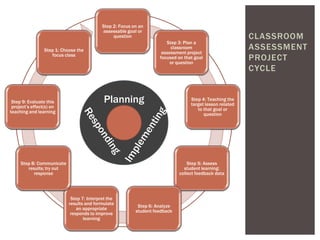
The document outlines classroom assessment techniques (CATs) aimed at enhancing formative assessment through active learning in education. It details a three-step process for implementing CATs, emphasizing planning, assessing goals, and gathering feedback to improve student learning. Additionally, it highlights the benefits of classroom assessment, including increased student involvement and satisfaction.