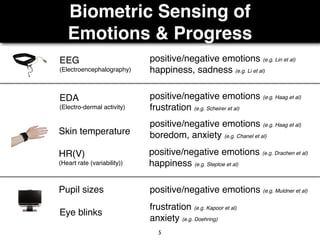
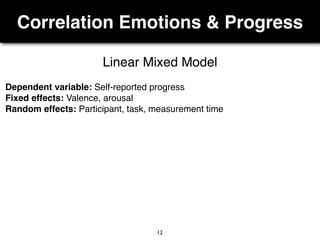
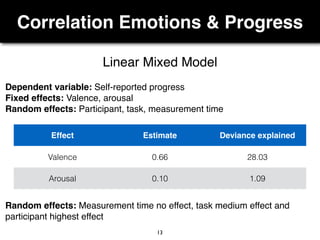
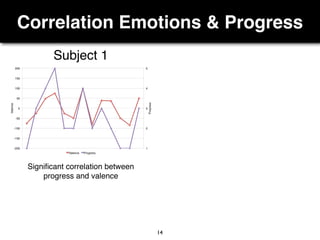
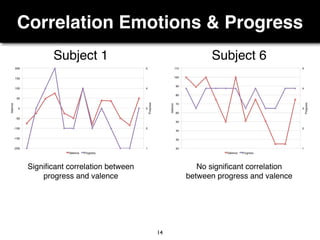
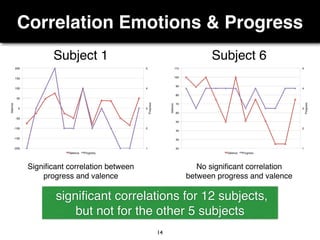
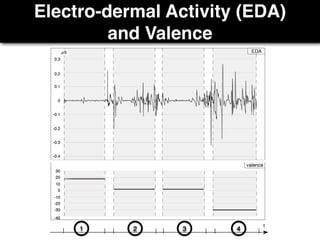
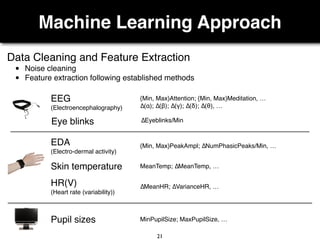
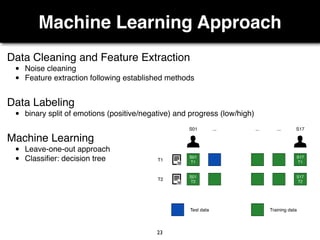
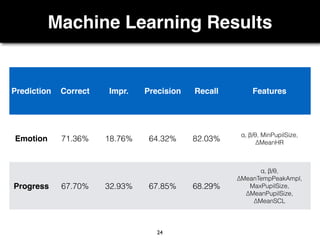
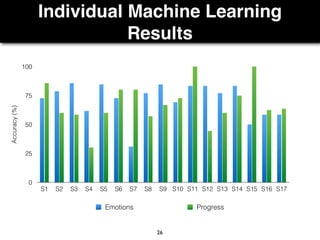
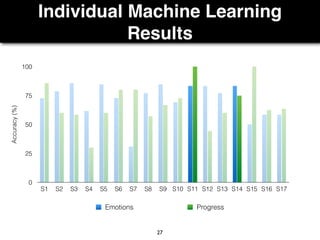
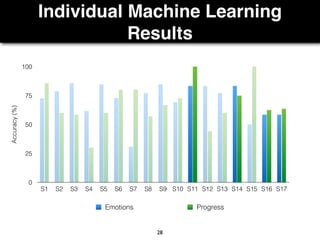
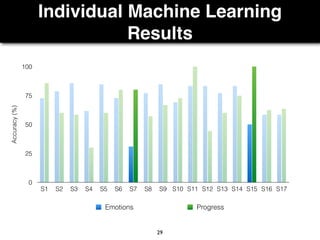
The document presents a study on the relationship between developers' emotions and their progress, using biometric sensors to track emotional states and performance during coding tasks. Key findings indicate that positive emotions correlate with perceived progress, while feelings of frustration hinder it, suggesting the importance of emotional awareness in developer productivity. The study discusses methods for leveraging biometric data to support developers effectively, especially when they are either stuck or in a productive flow state.