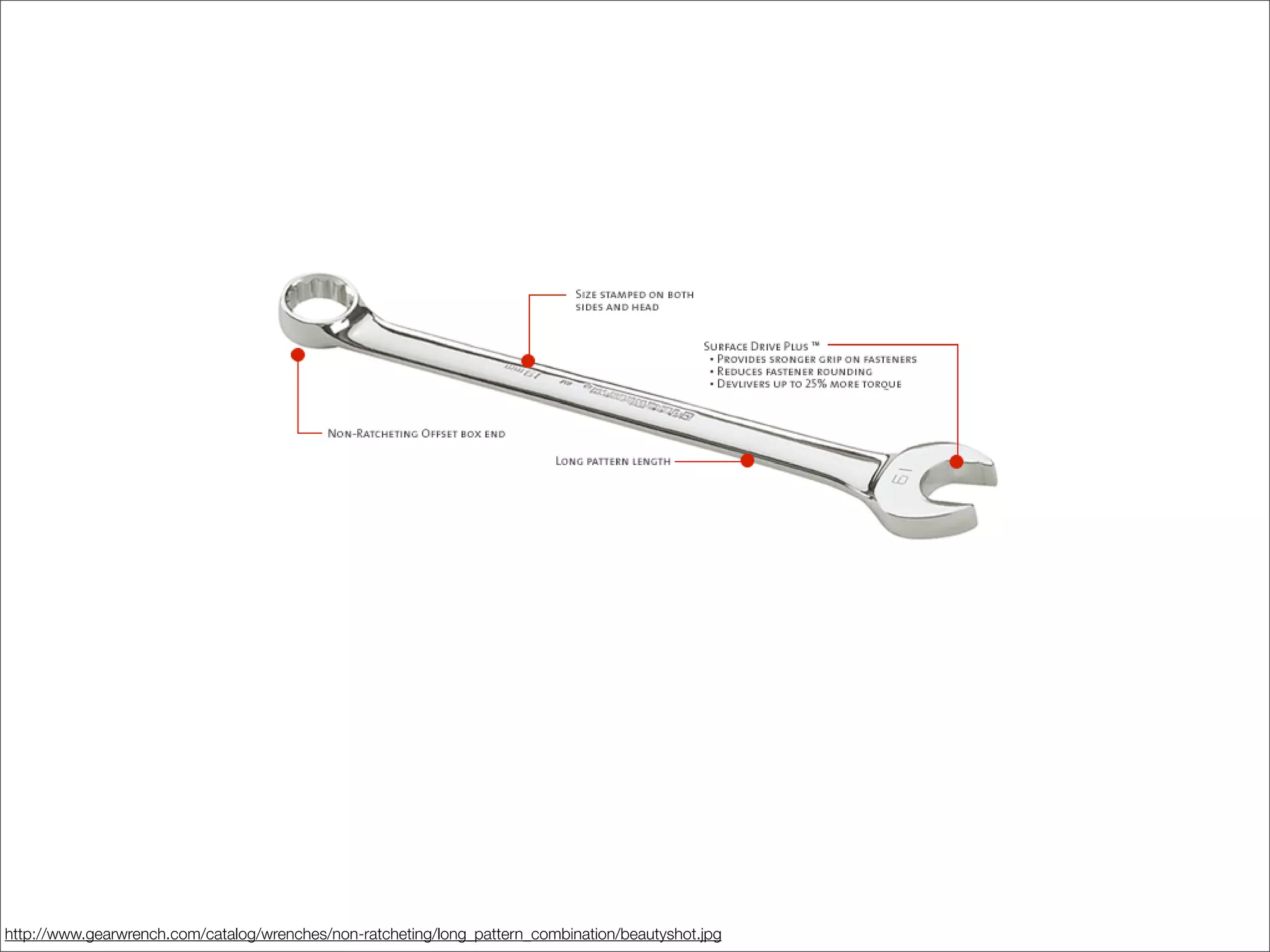
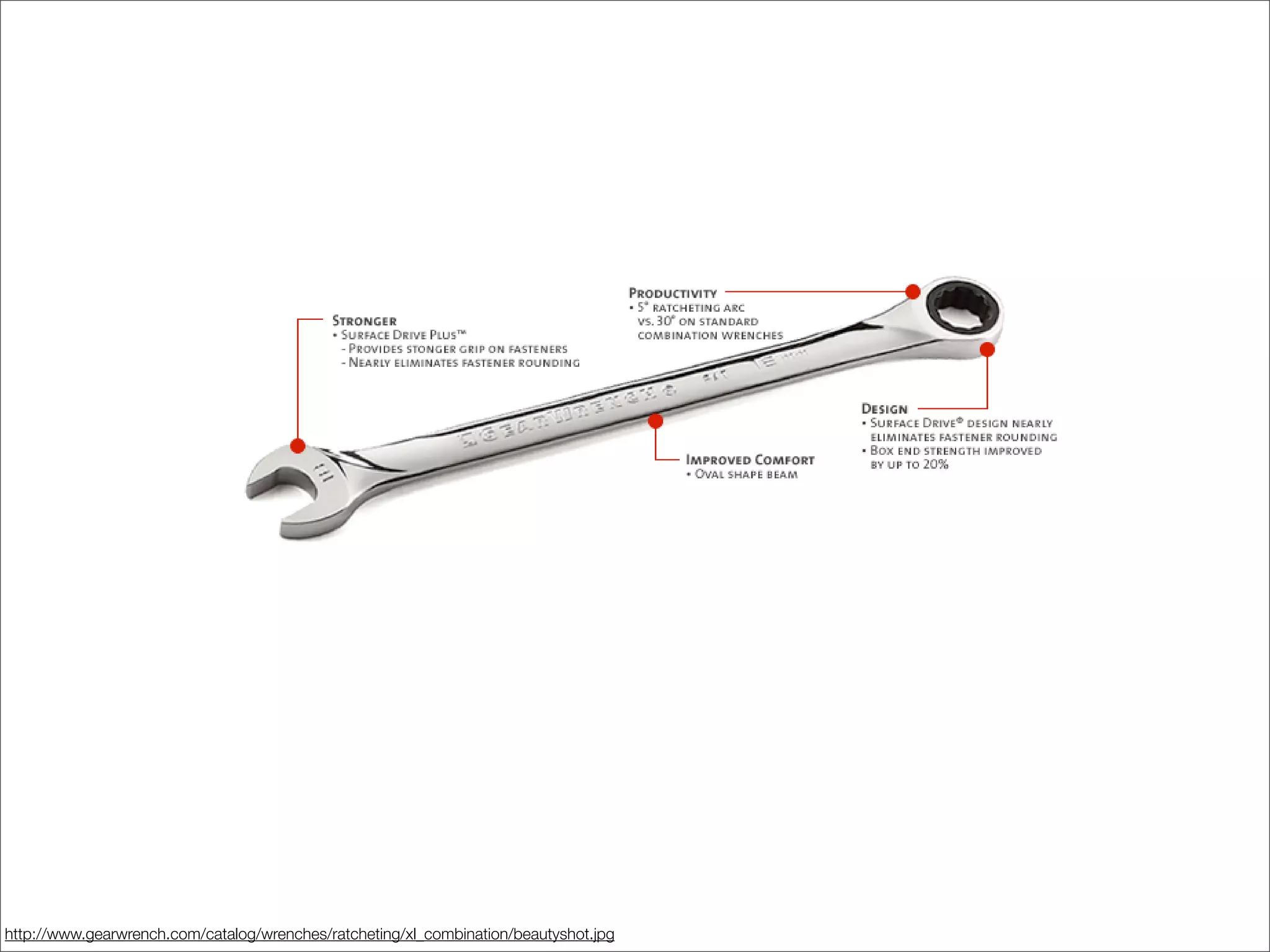
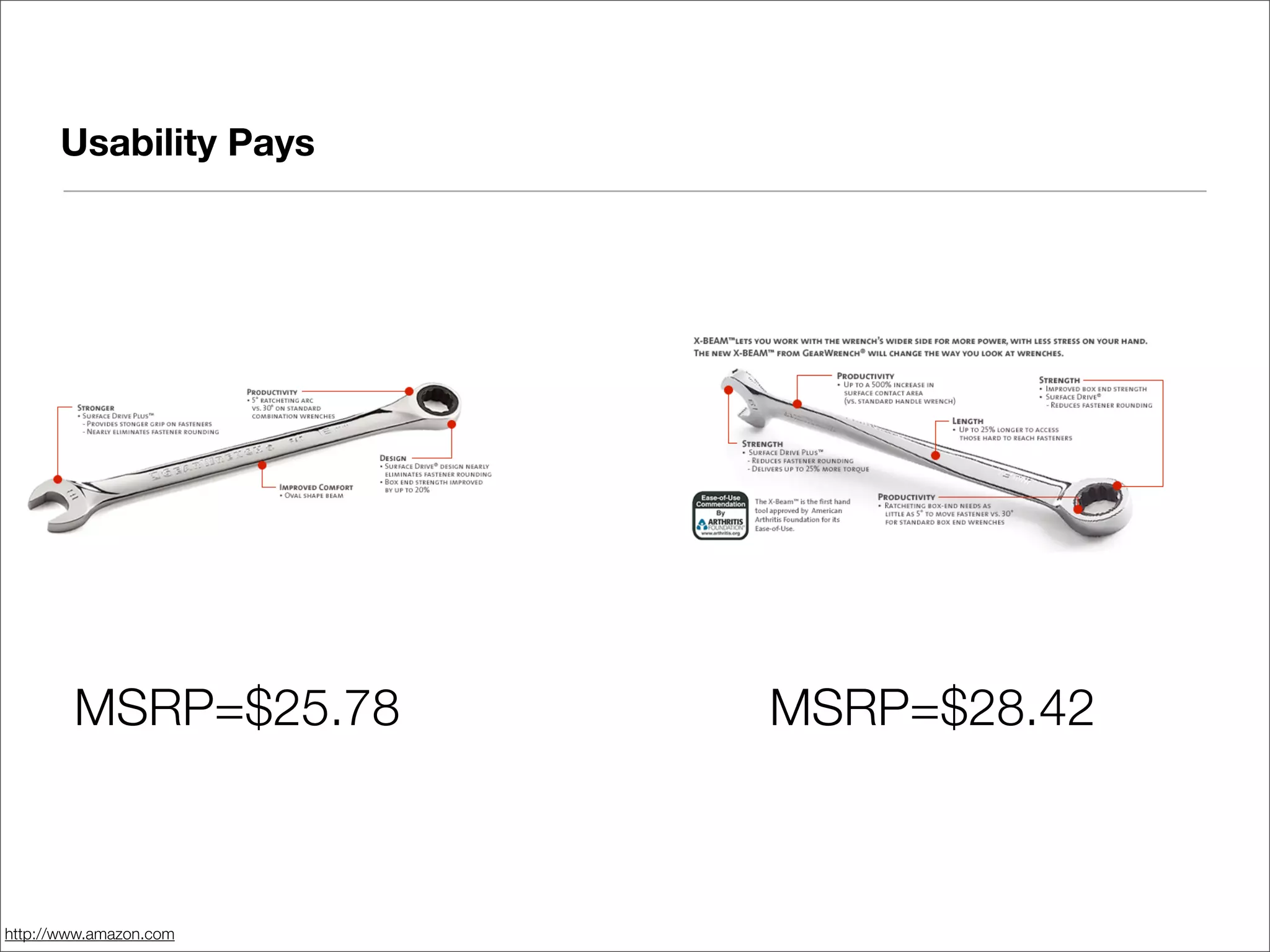
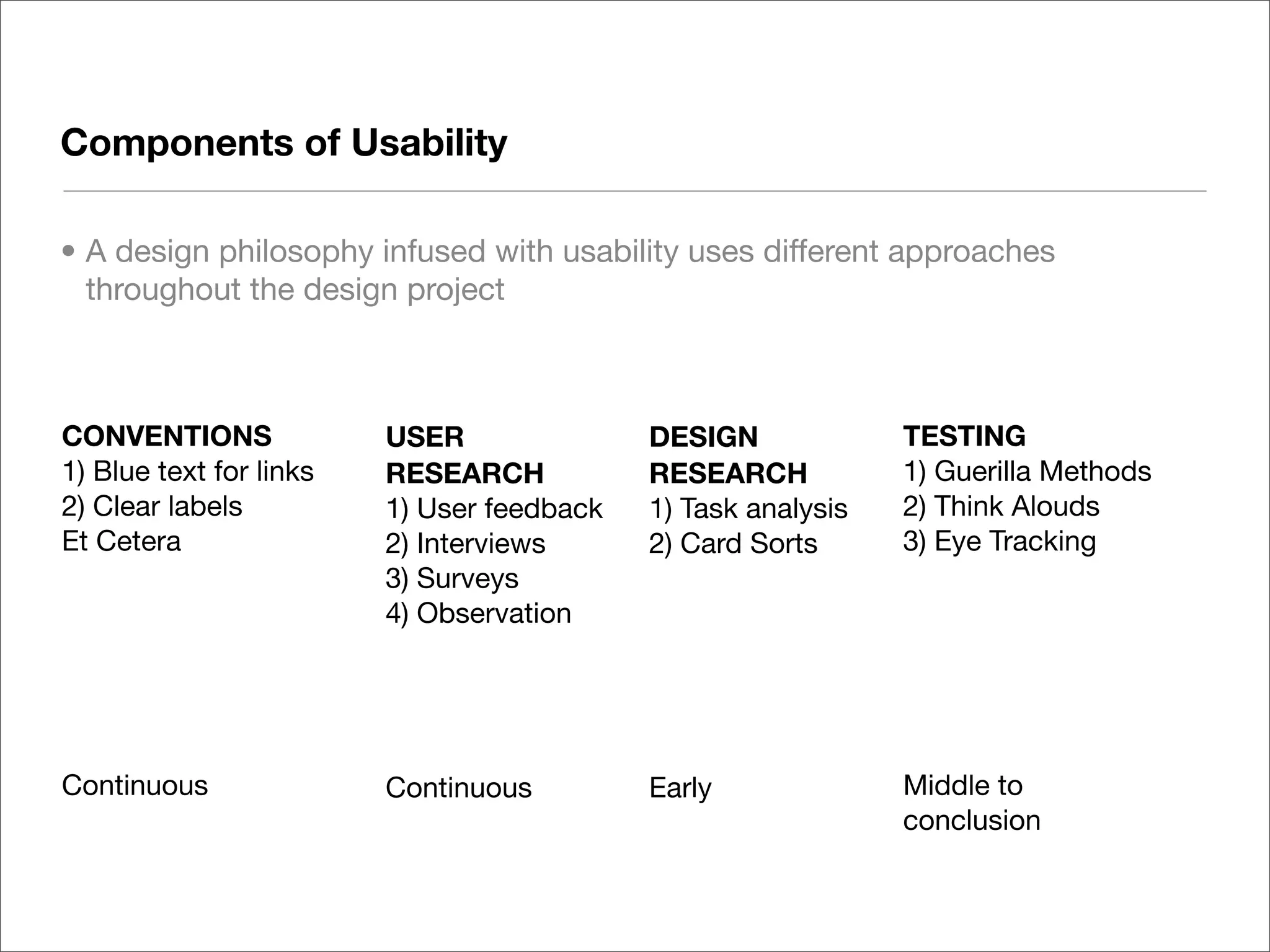
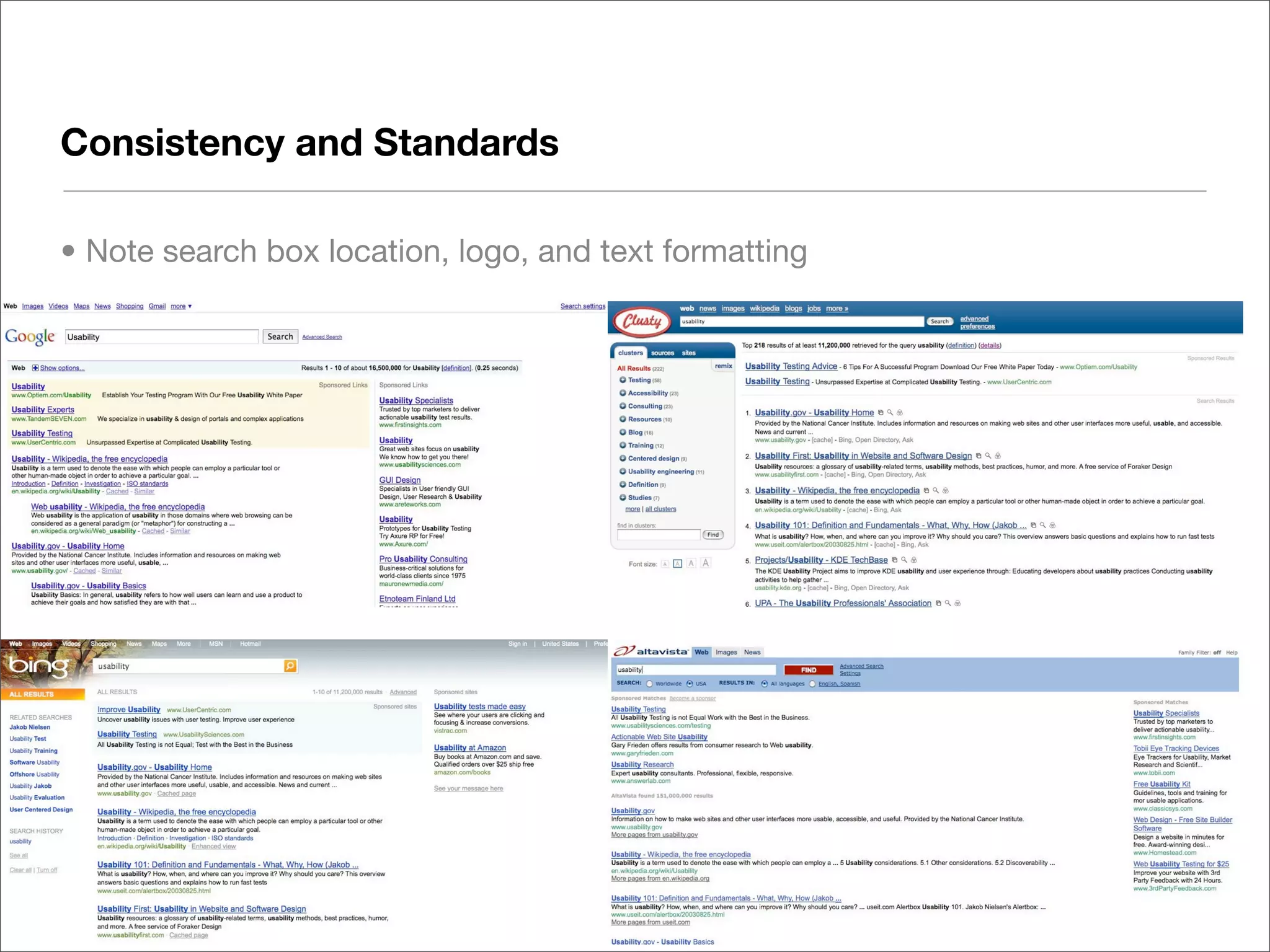
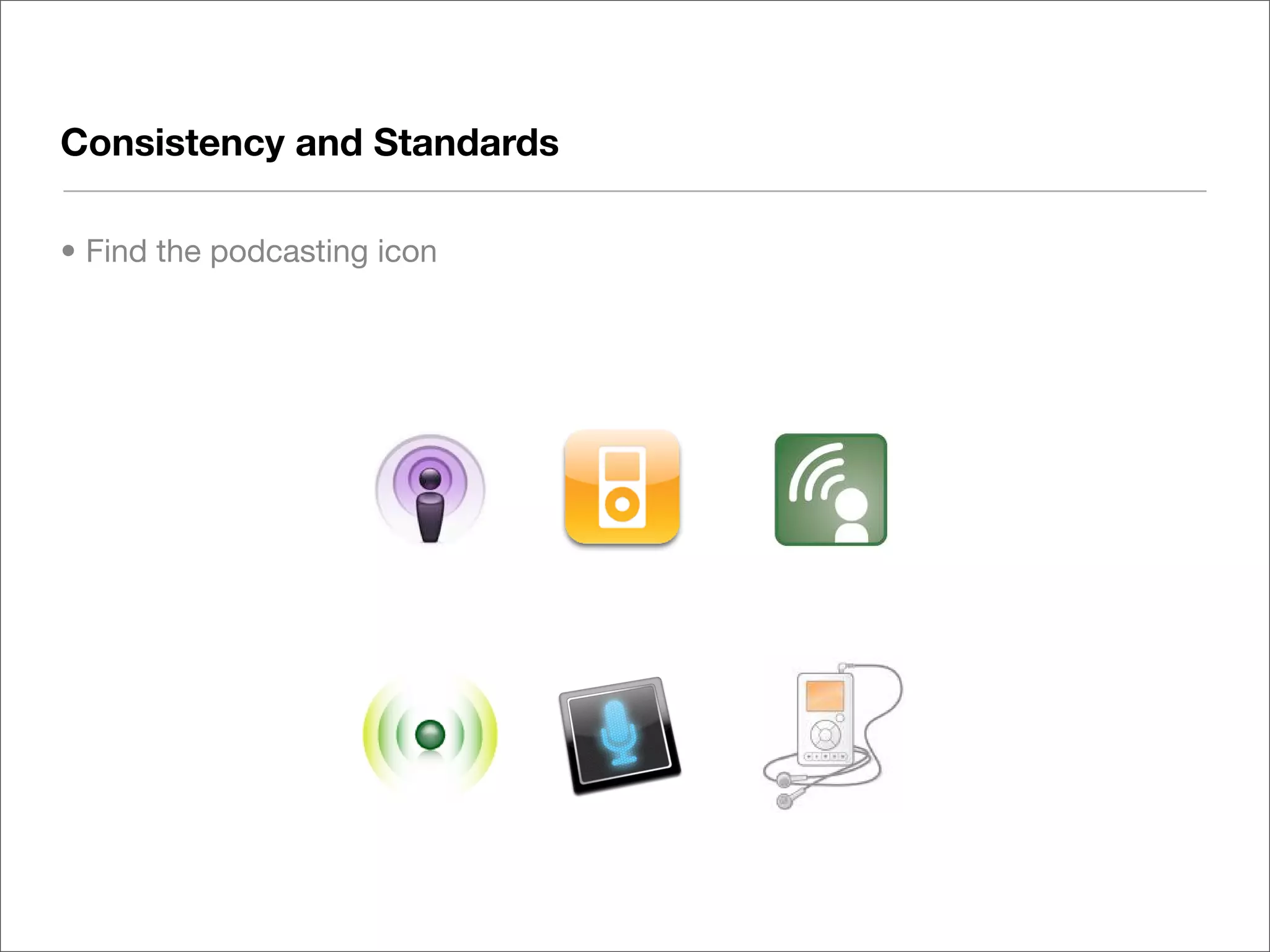
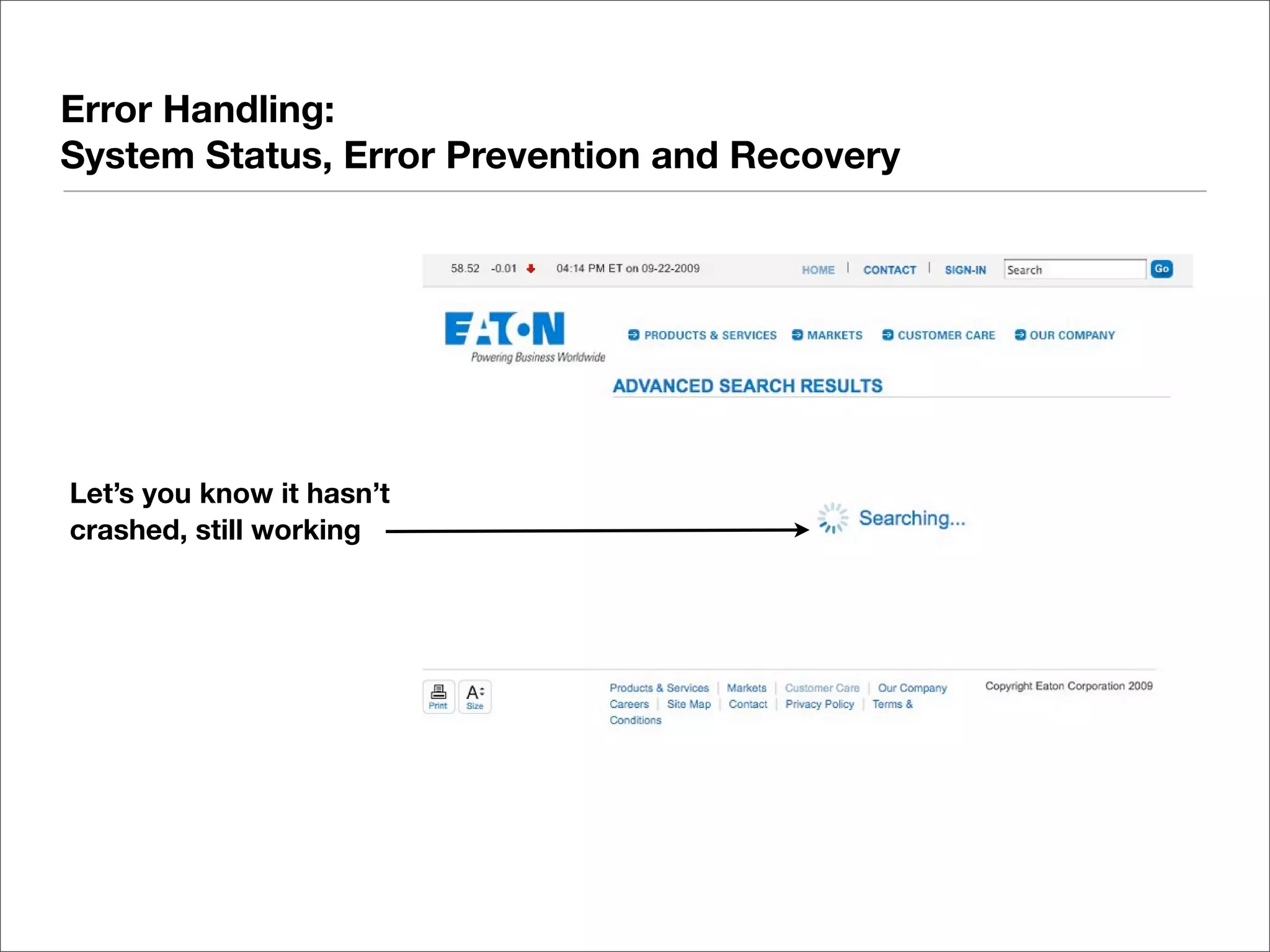
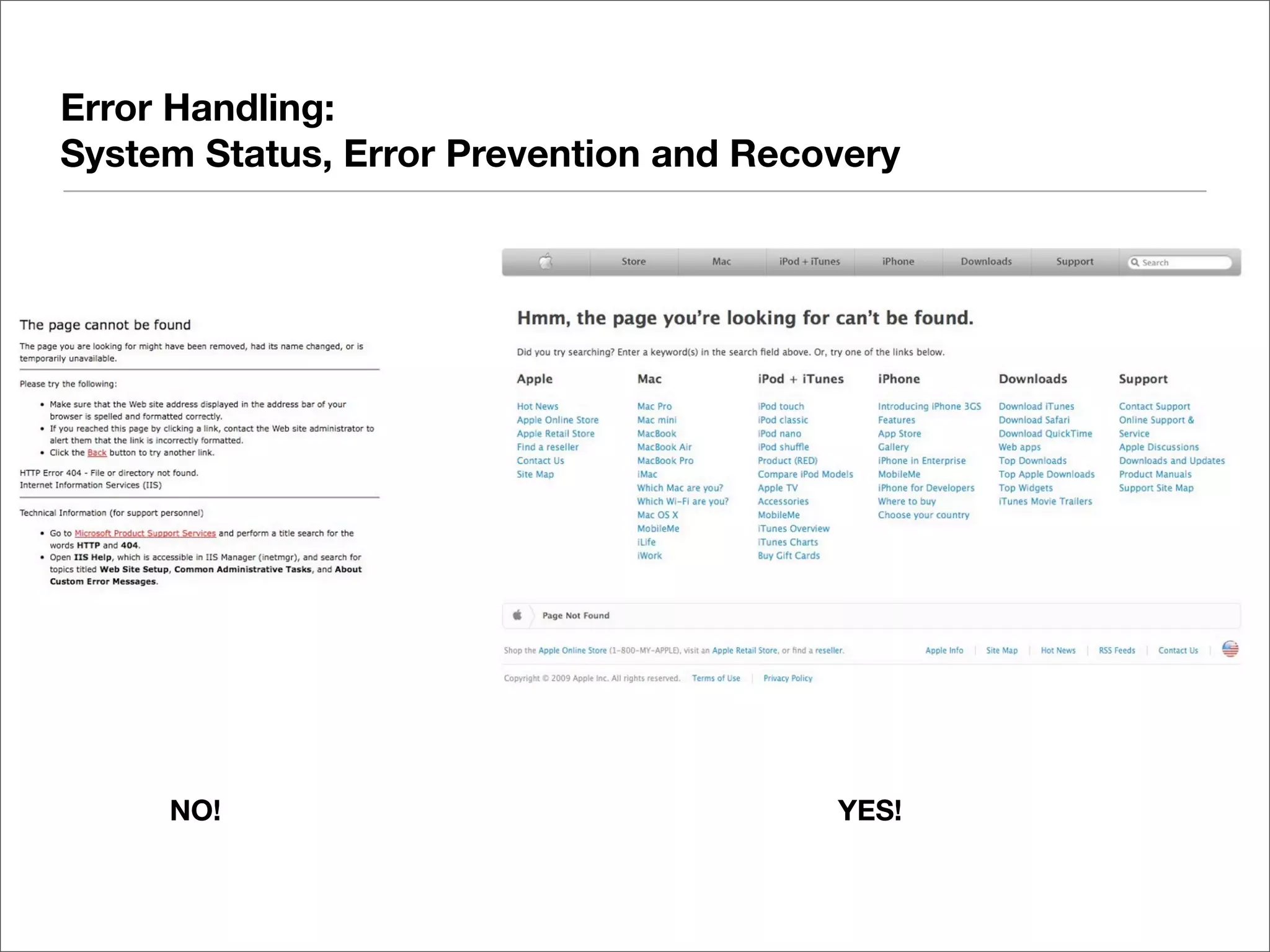
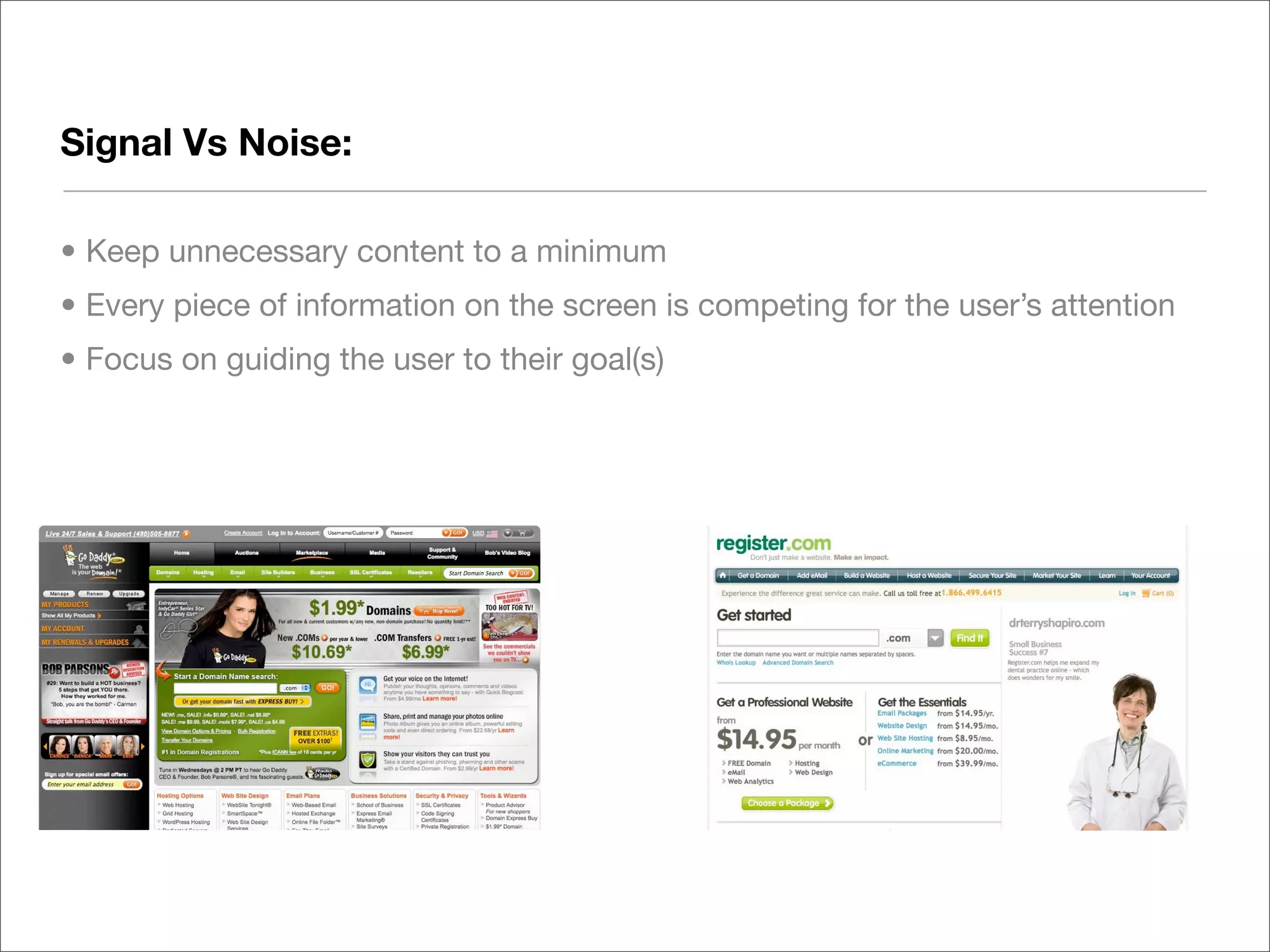
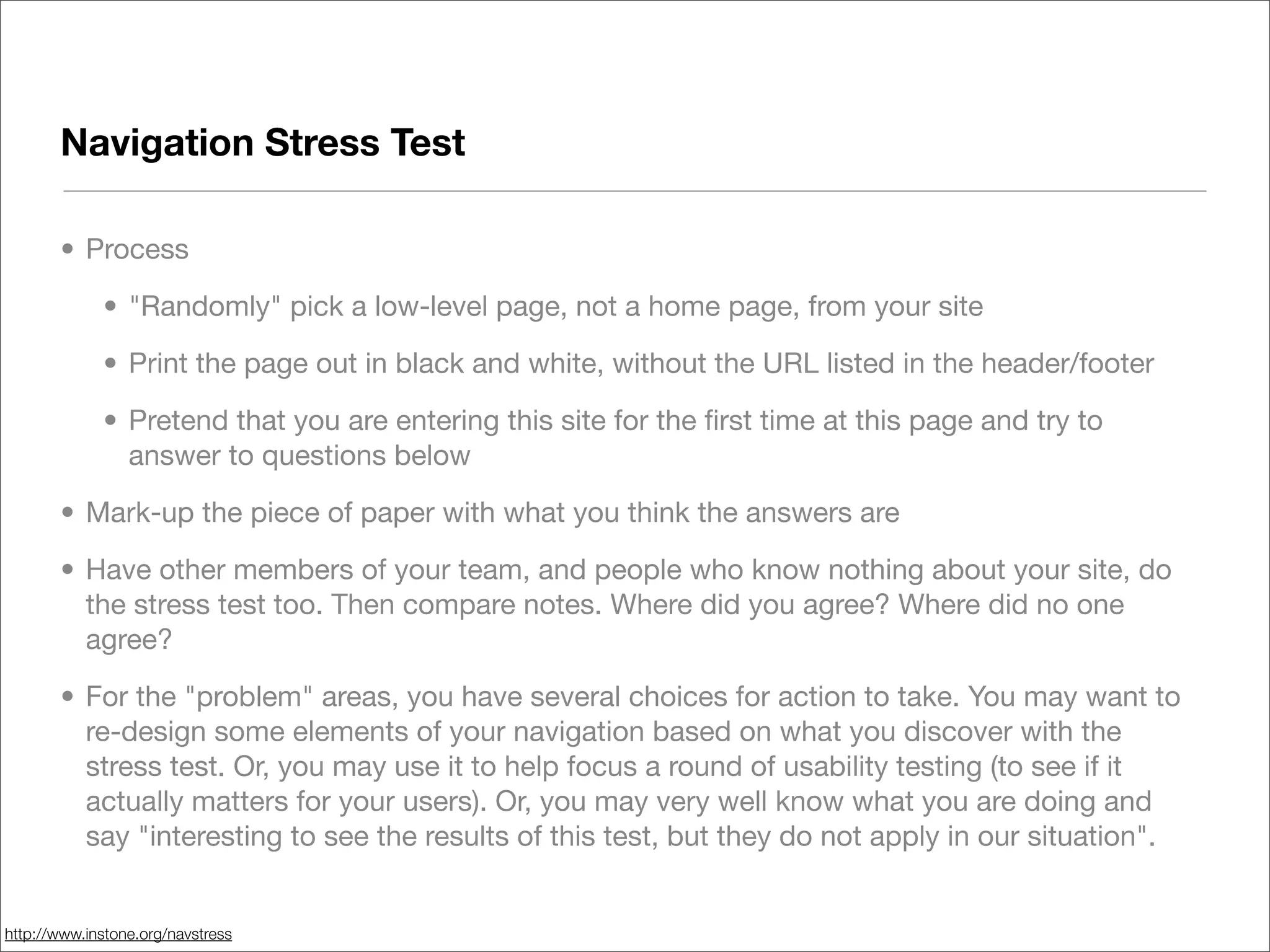
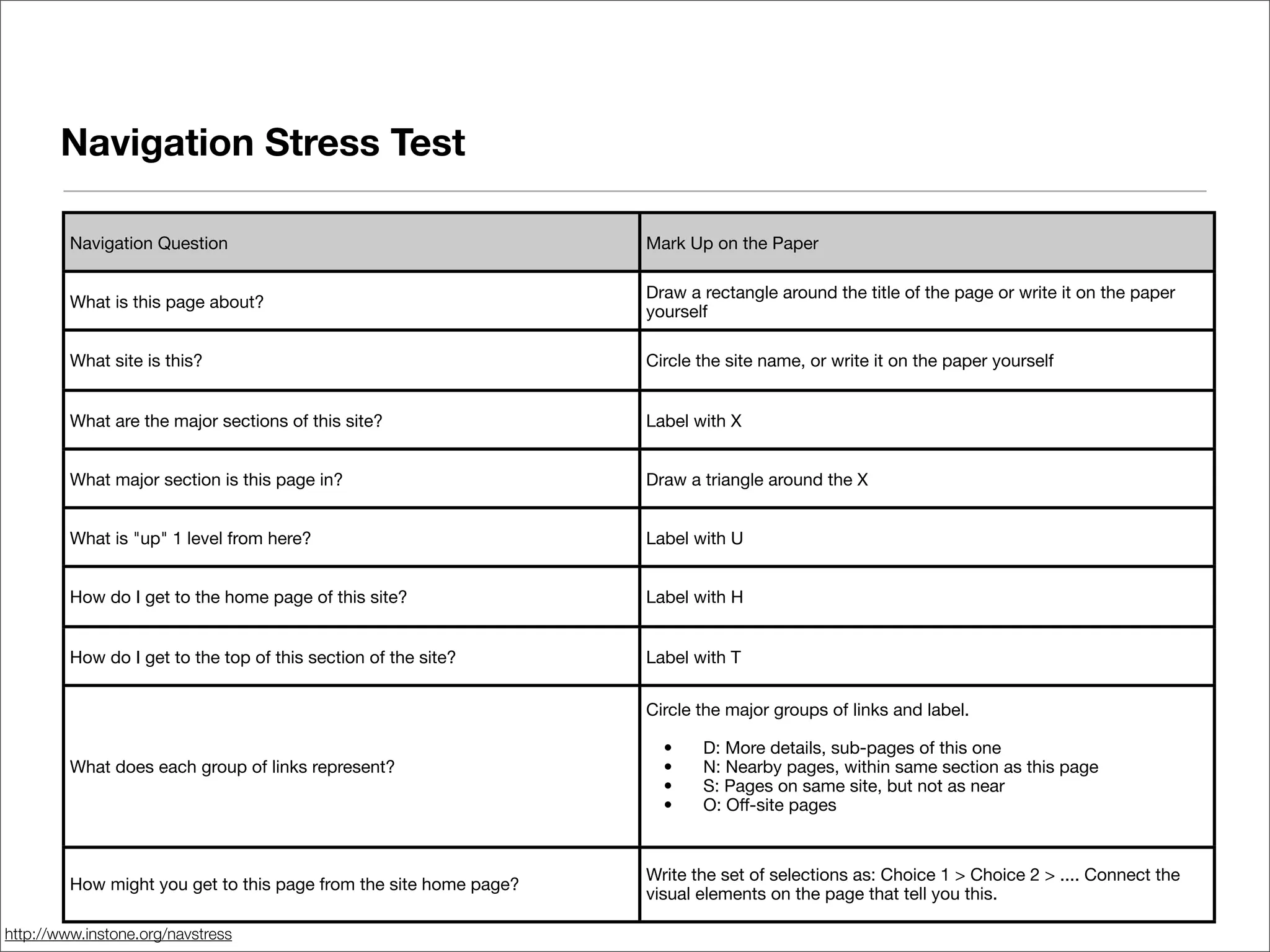
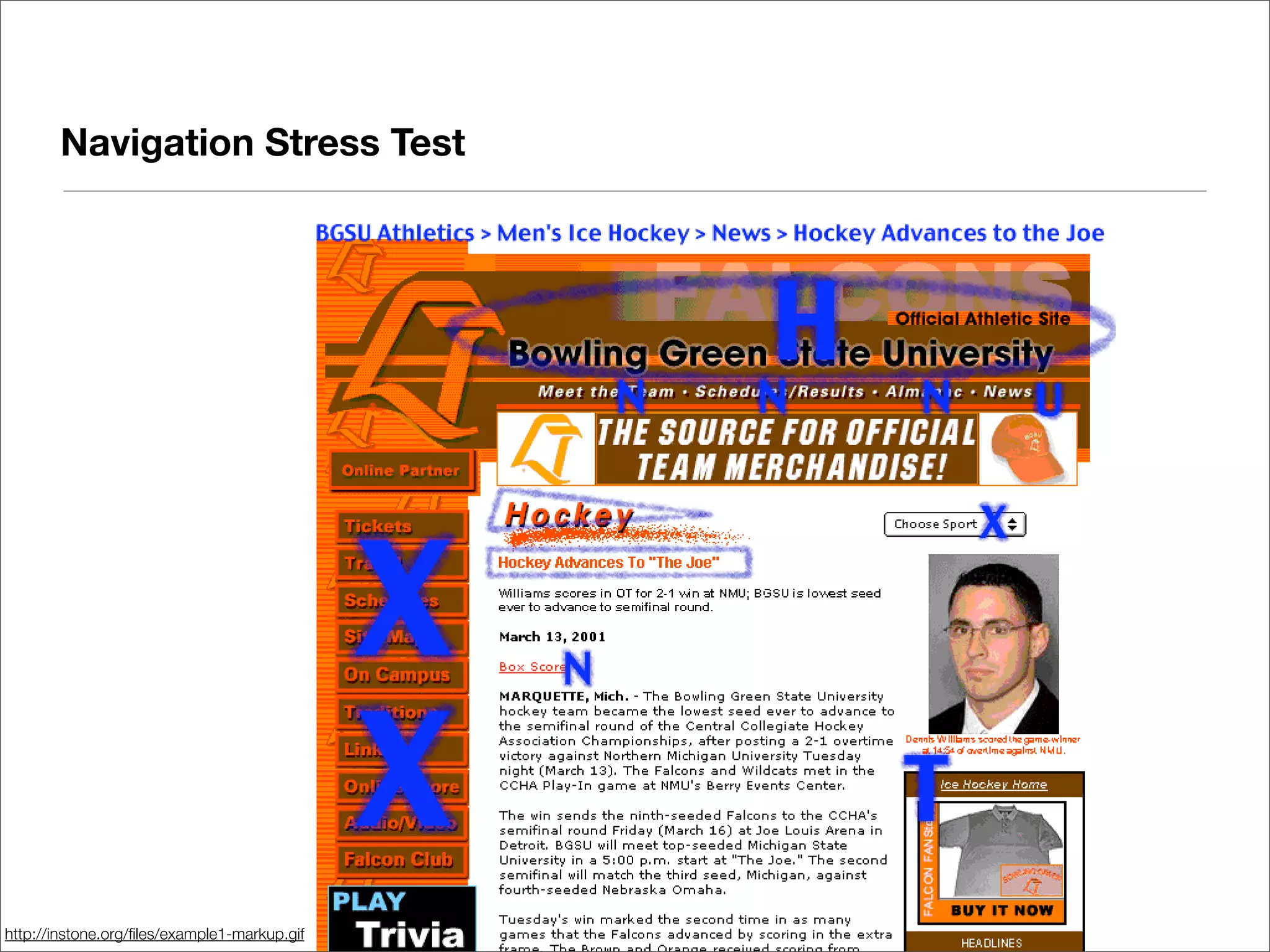
This document discusses web usability for designers. It begins with an introduction to usability, providing examples of usability guidelines and techniques for do-it-yourself usability testing. Some of the key guidelines discussed include consistency and standards, error handling, recognition over recall, and limiting unnecessary content. The document also provides a navigation stress test technique for testing usability without user recruitment. Resources for learning more about usability include research firms, books, and organizations.