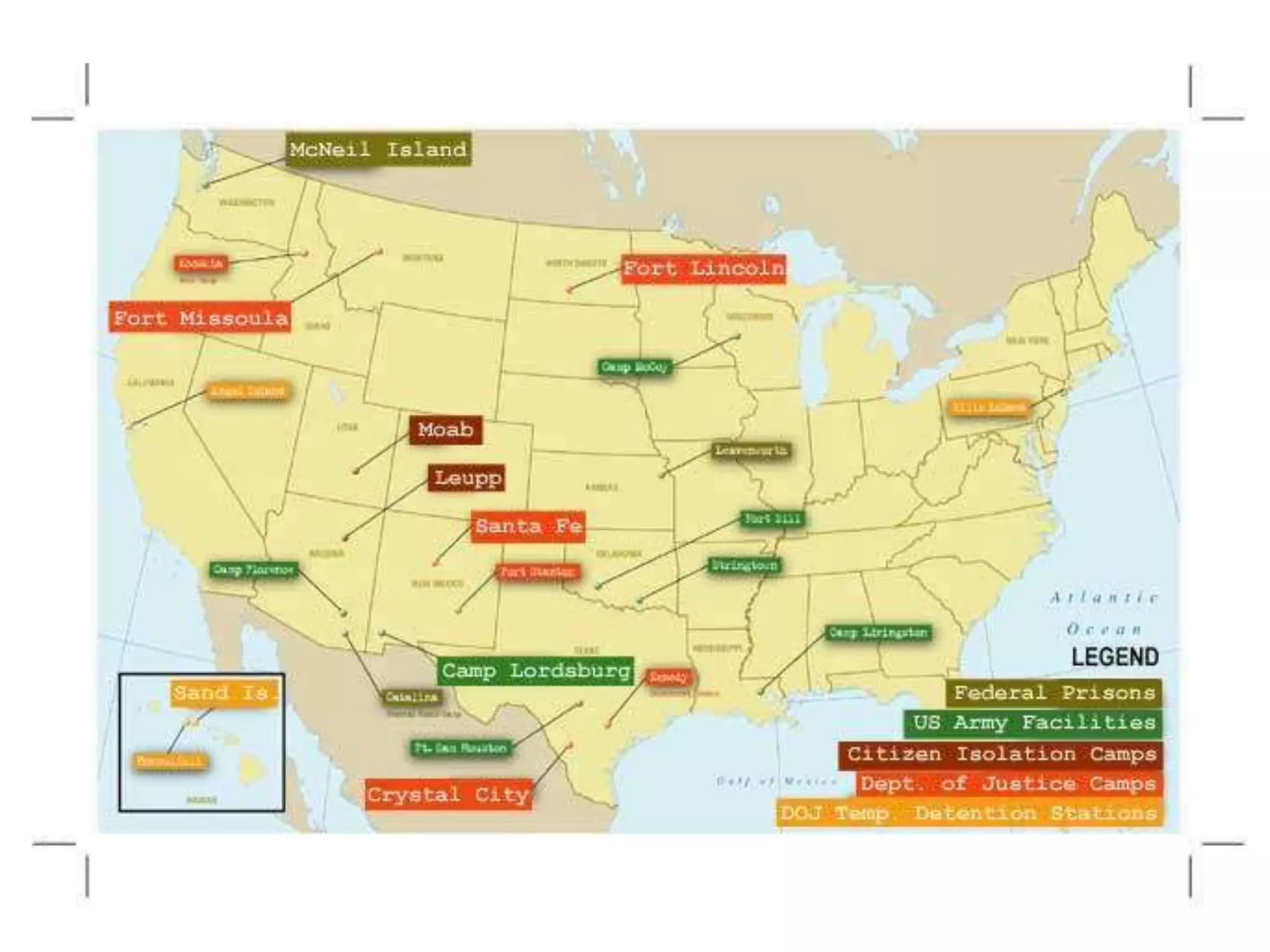
The US mobilized for WWII on an unprecedented scale, transforming the economy and society. The government took on expanded roles, controlling wages, prices and production to support the war effort. Unemployment dropped from 14% to 2% as millions of Americans, including many women and minorities, went to work in newly-expanded industries producing vast quantities of military equipment. Over 40 million men were drafted, though the military remained segregated and discrimination persisted at home, including the internment of Japanese Americans. Despite shortages, most Americans embraced sacrifices to support the war through rationing, scrap drives, and buying war bonds.