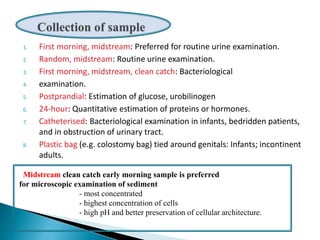
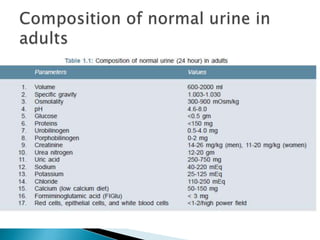
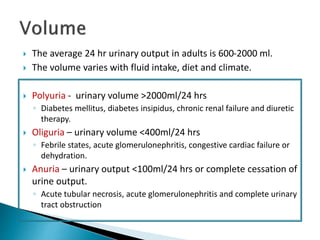
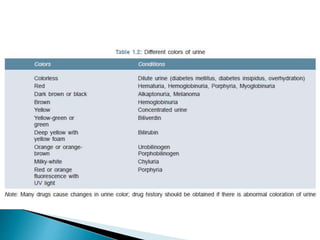
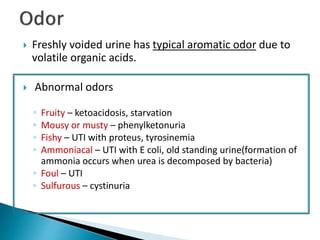
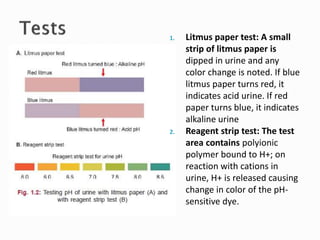
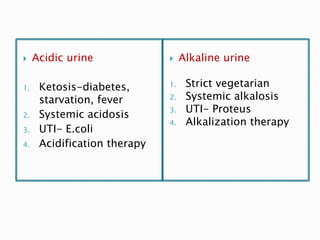
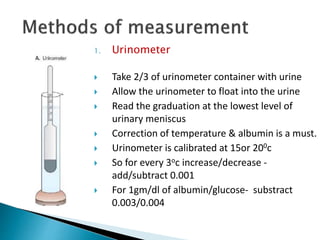
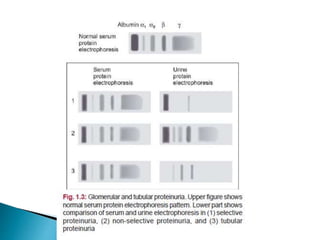
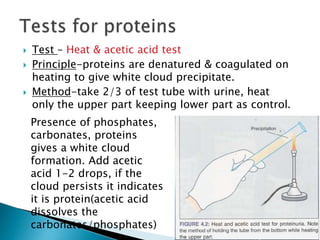
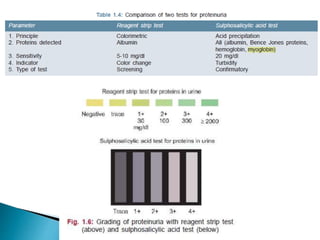
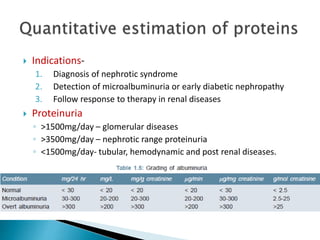
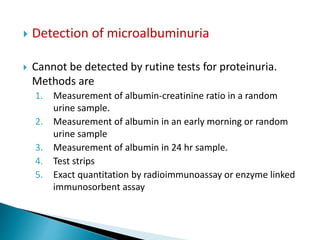
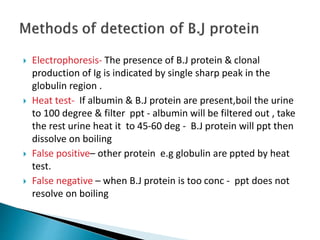
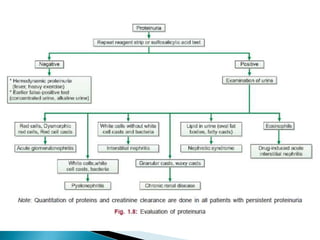
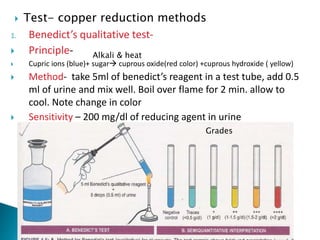
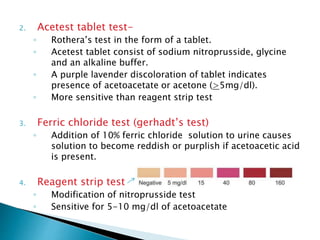
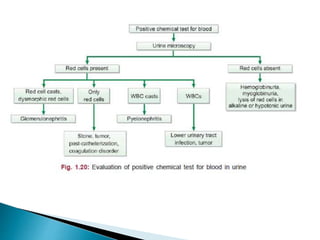
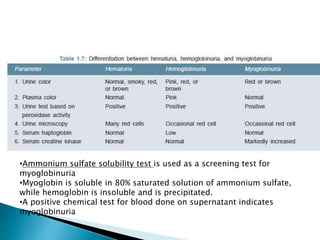
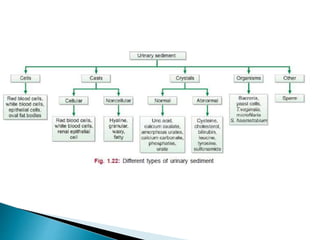
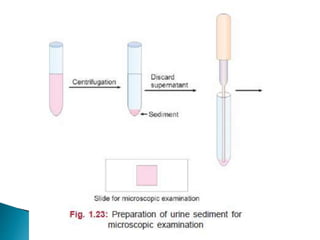
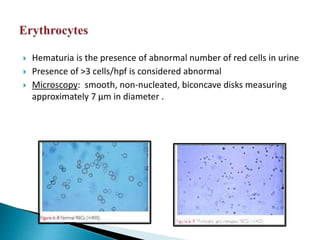
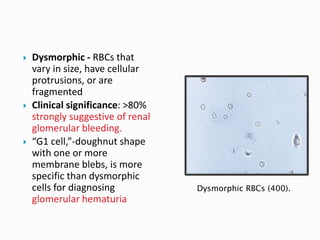
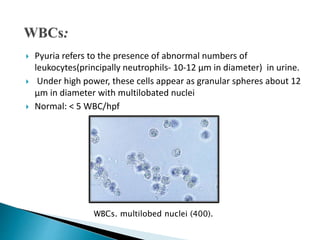
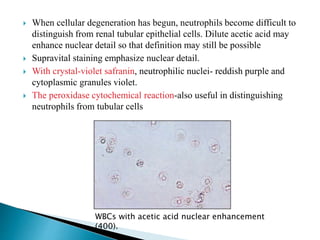
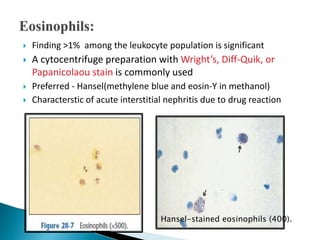
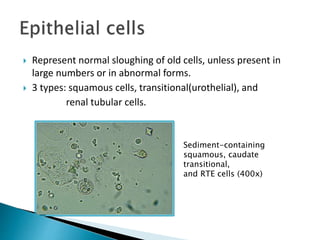
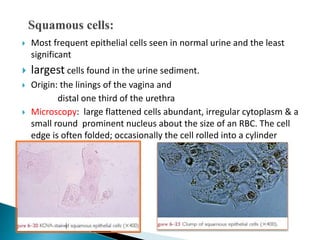
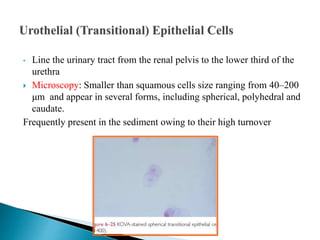
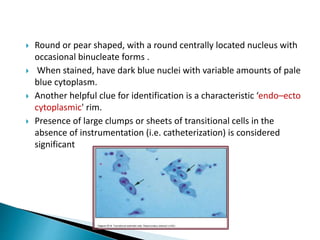
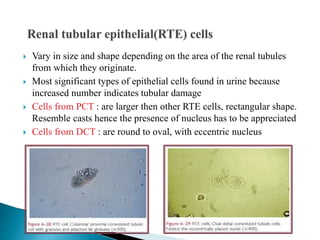
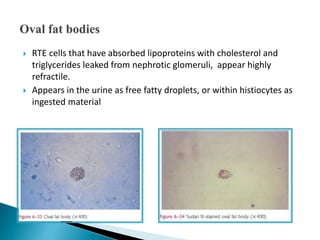
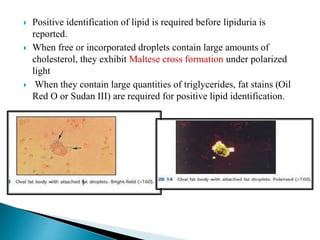
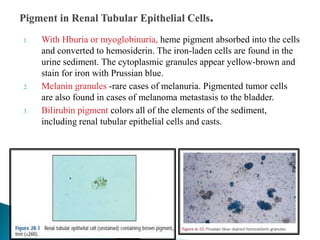
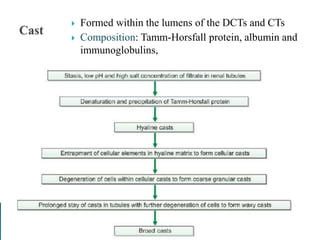
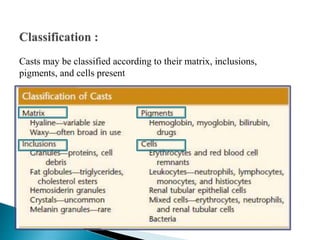
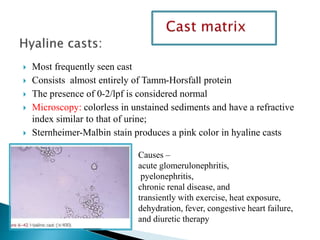
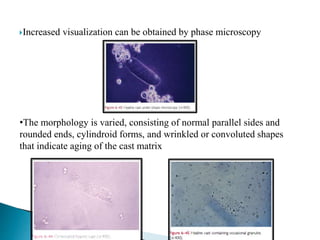
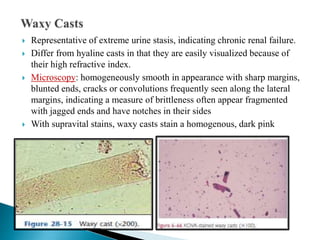
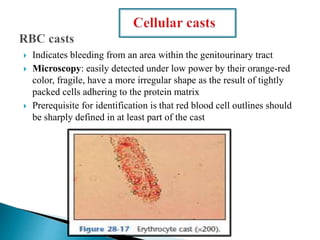
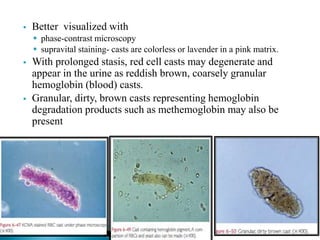
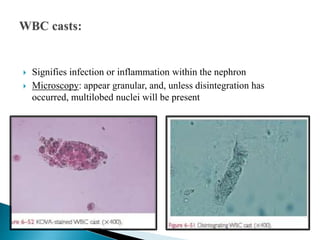
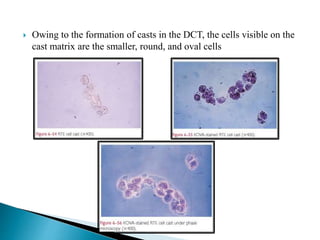
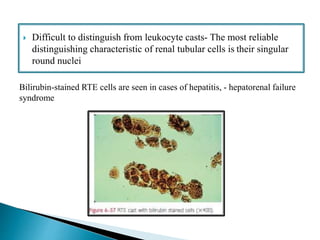
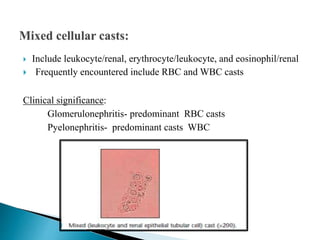
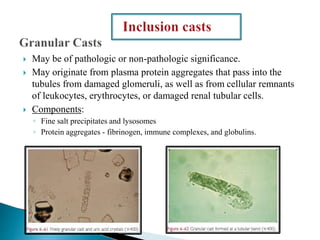
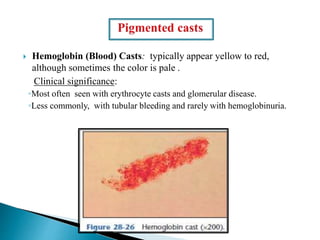
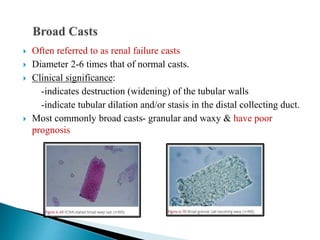
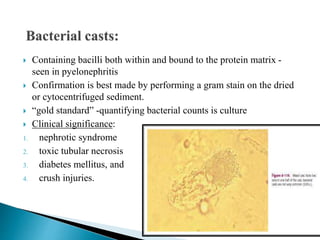
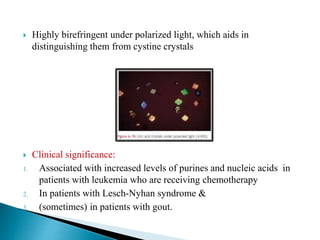
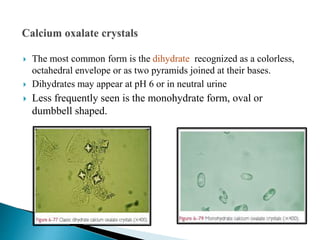
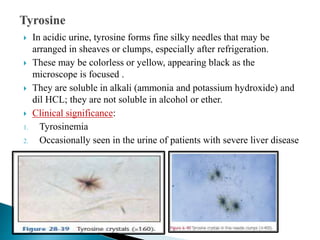
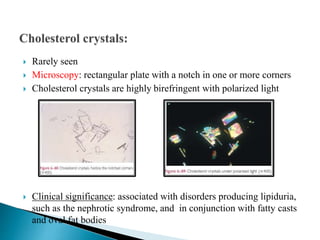
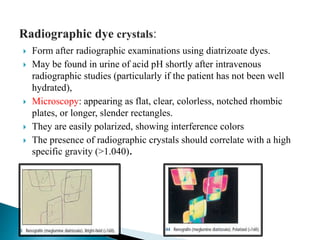
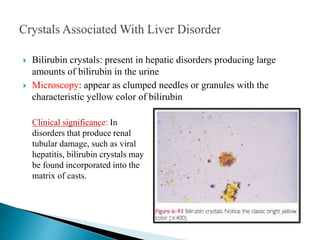
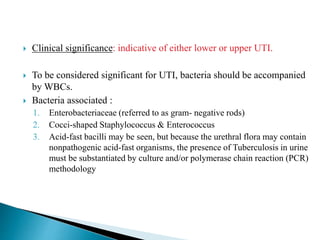
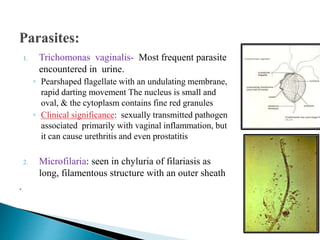
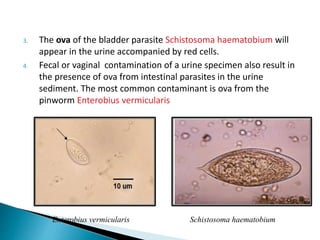
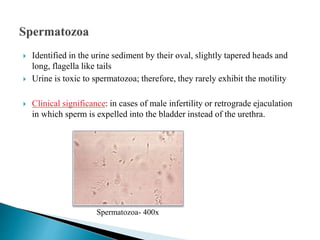
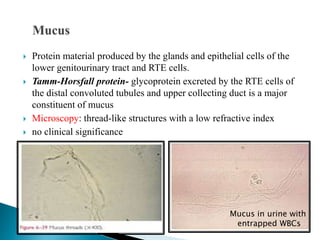
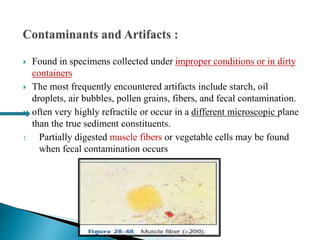
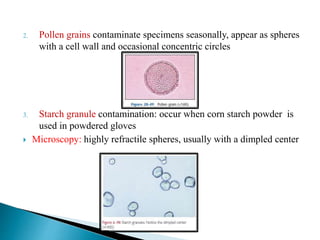
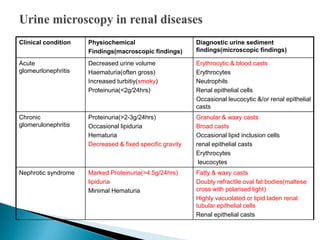
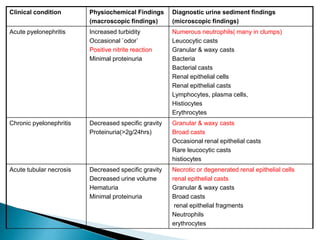
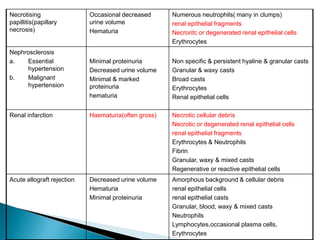
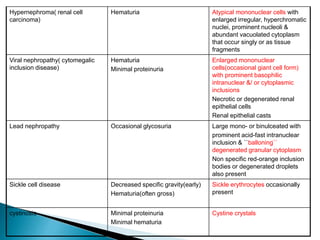
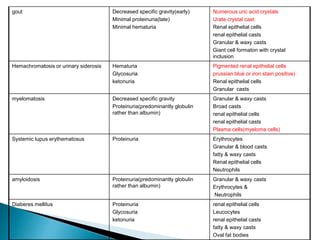
This document provides information on evaluating proteinuria in urine. It discusses the different types of proteinuria including glomerular, tubular, overflow and hemodynamic proteinuria. Glomerular proteinuria is caused by damage to the glomerular basement membrane and can be selective or non-selective. Tubular proteinuria occurs when low molecular weight proteins are excreted due to tubular damage. Tests for detecting and quantifying protein in urine include heat and acetic acid test, reagent strip, sulphosalicylic acid test, and 24-hour urine collection. The document provides normal ranges and indications for proteinuria testing.