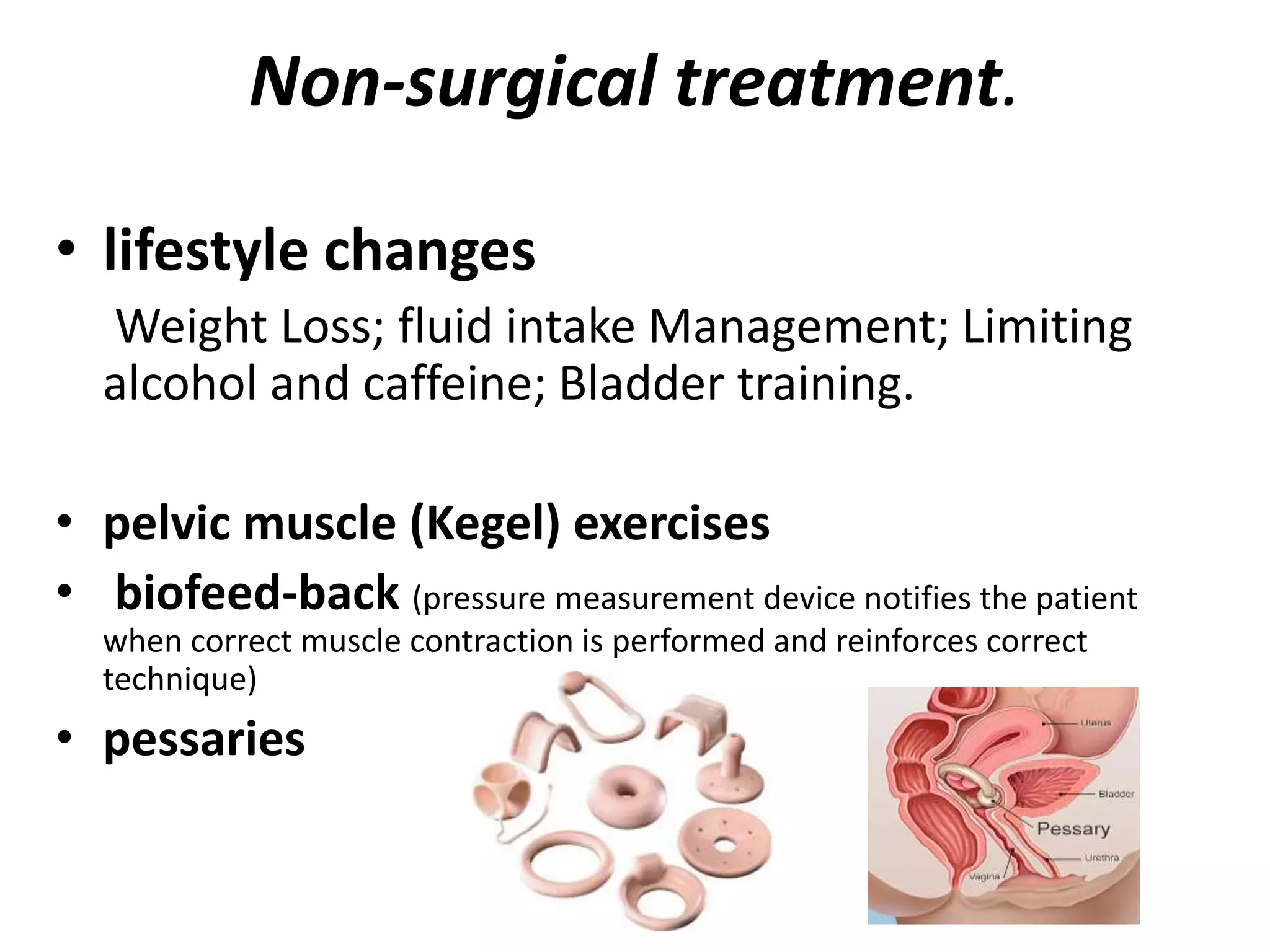
Urinary incontinence is the involuntary leakage of urine, varying in severity and affecting a significant percentage of older women. Its causes include urinary tract infections, diuretics, pelvic floor disorders, constipation, and neurological issues, and can manifest as stress, urge, or overflow incontinence. Diagnosis involves thorough history-taking, physical examinations, and various tests, with treatment options ranging from lifestyle changes and pelvic exercises to surgical interventions.