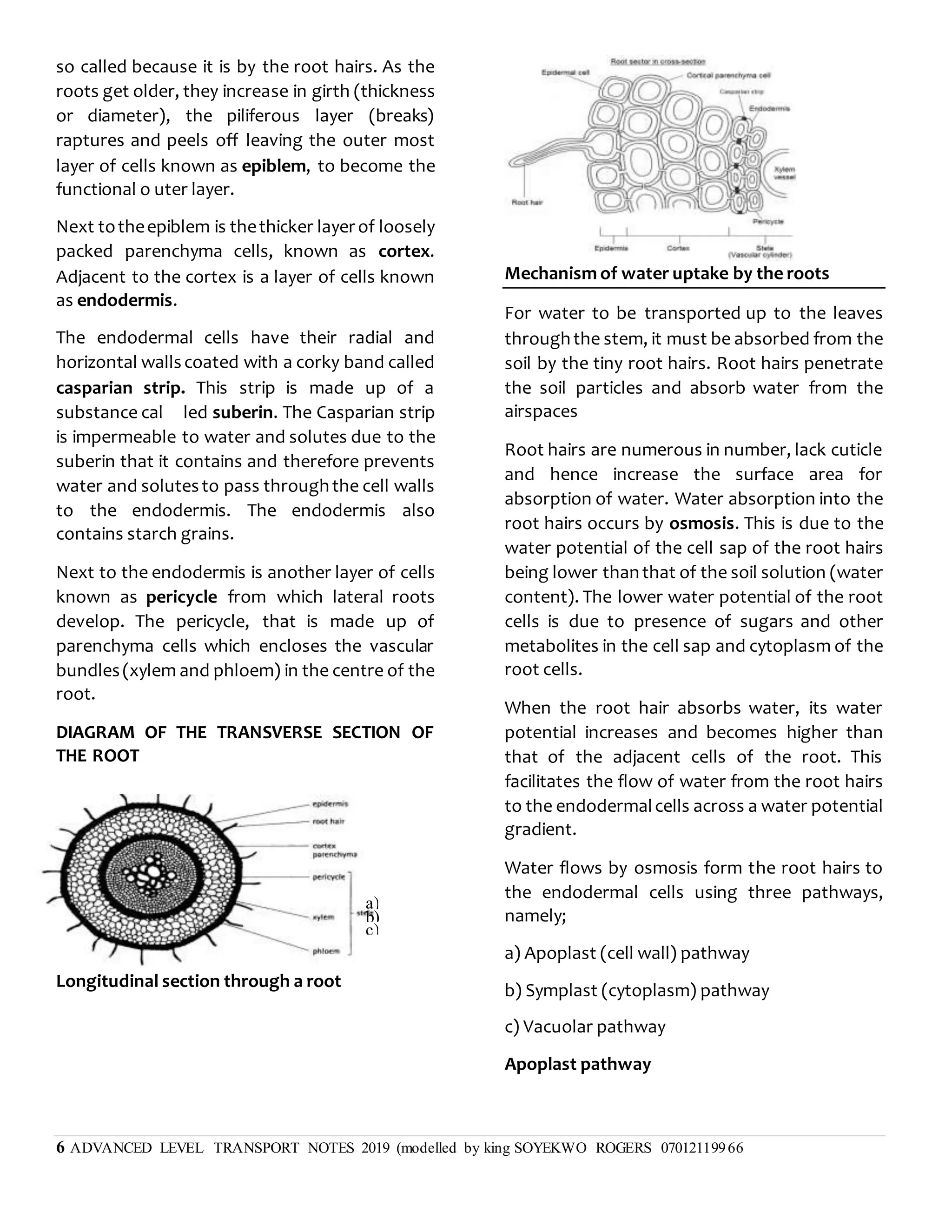
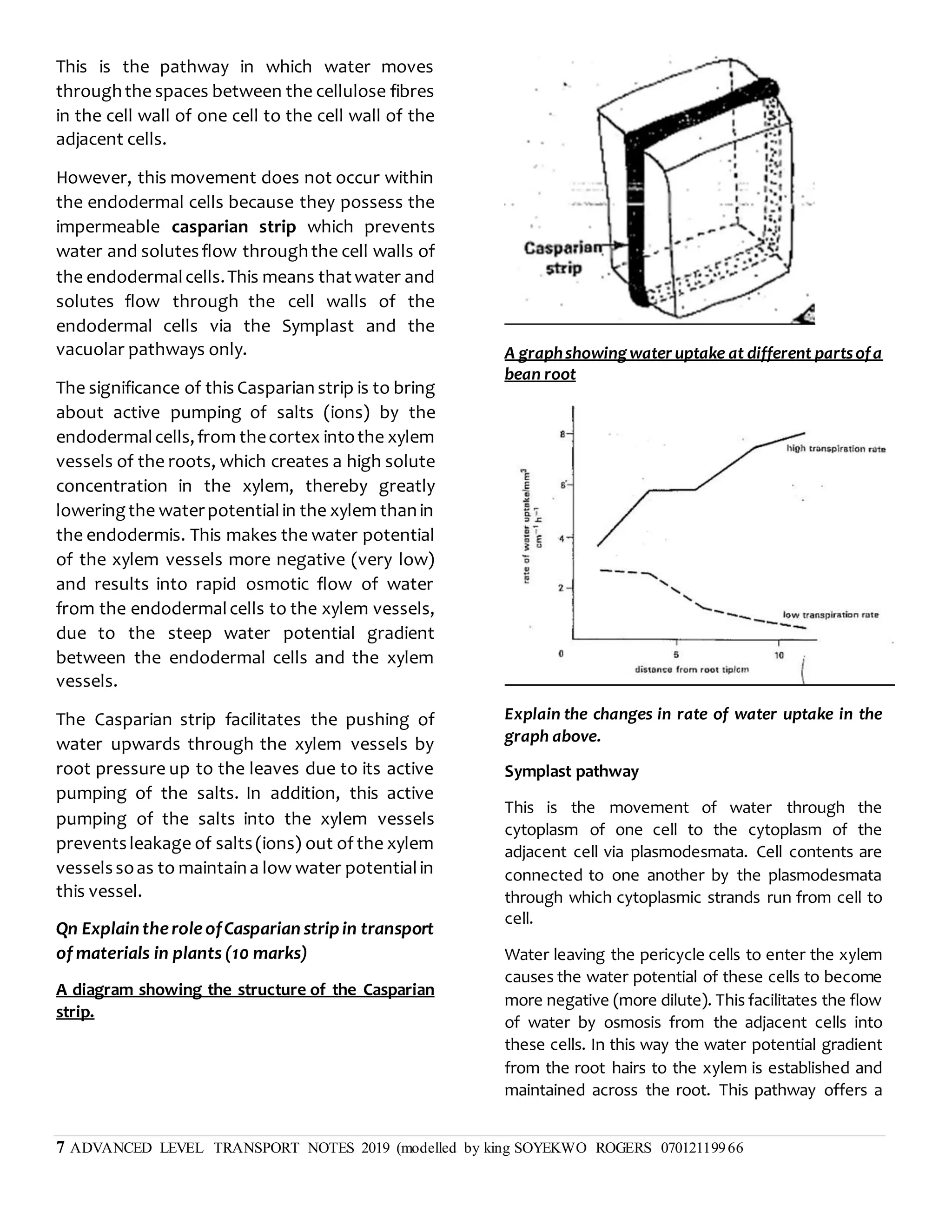
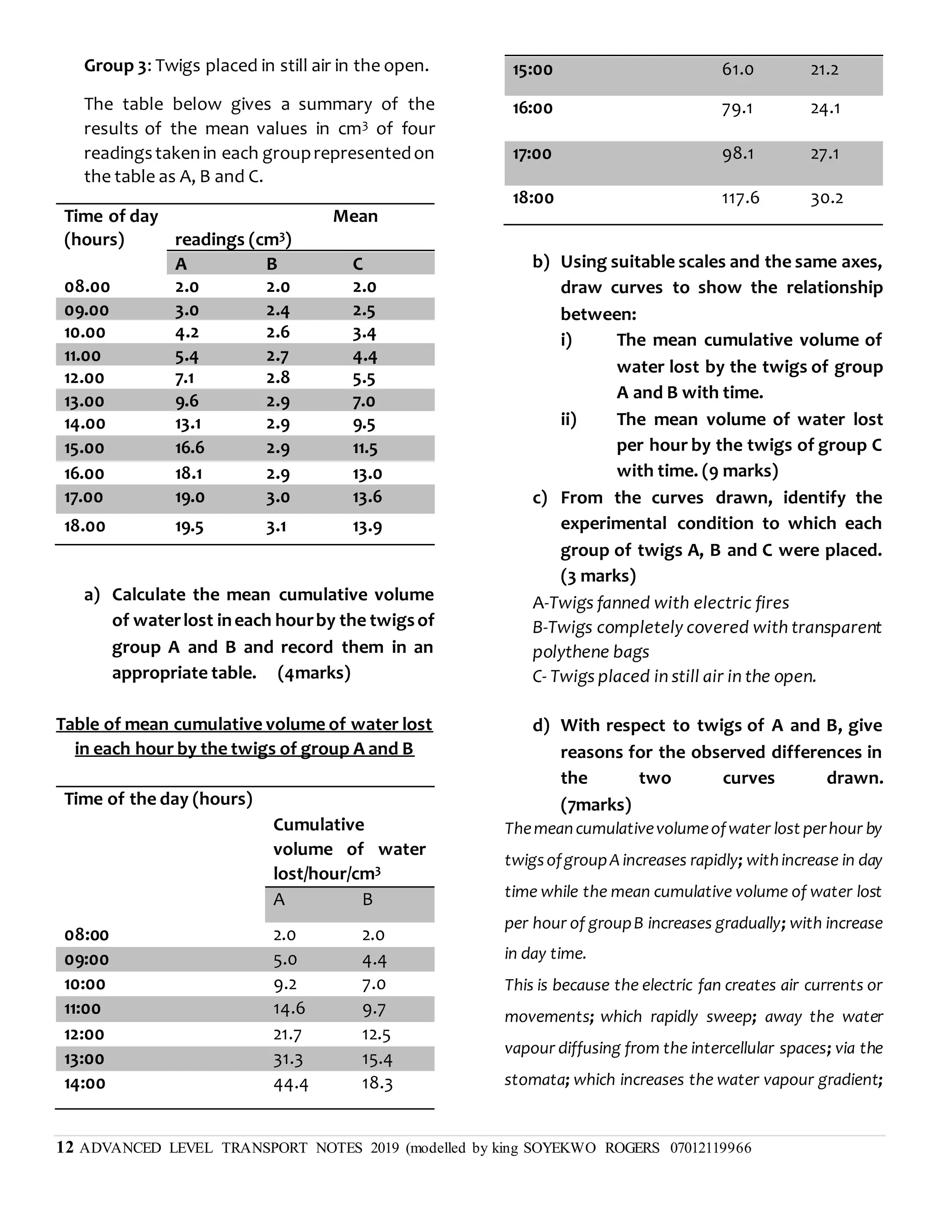
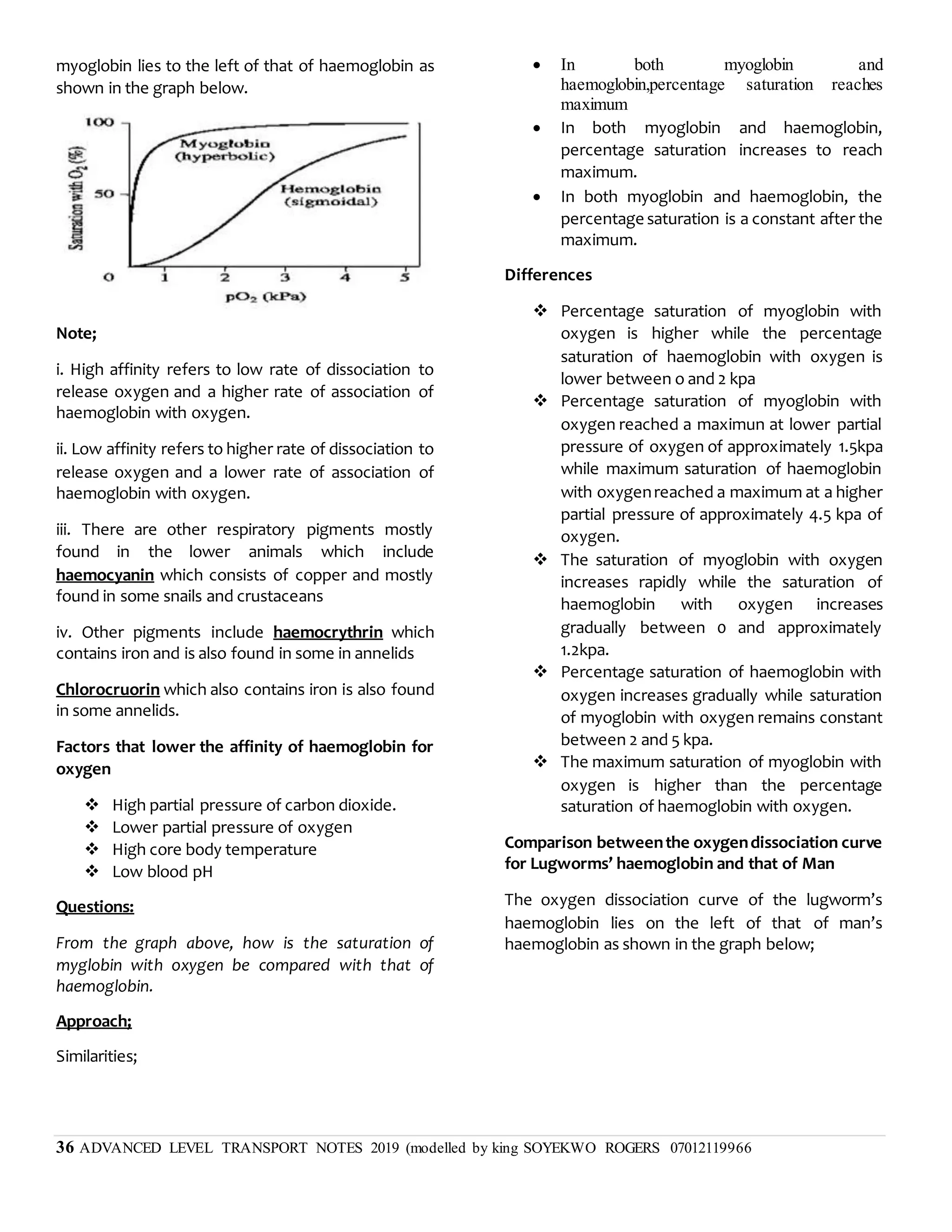
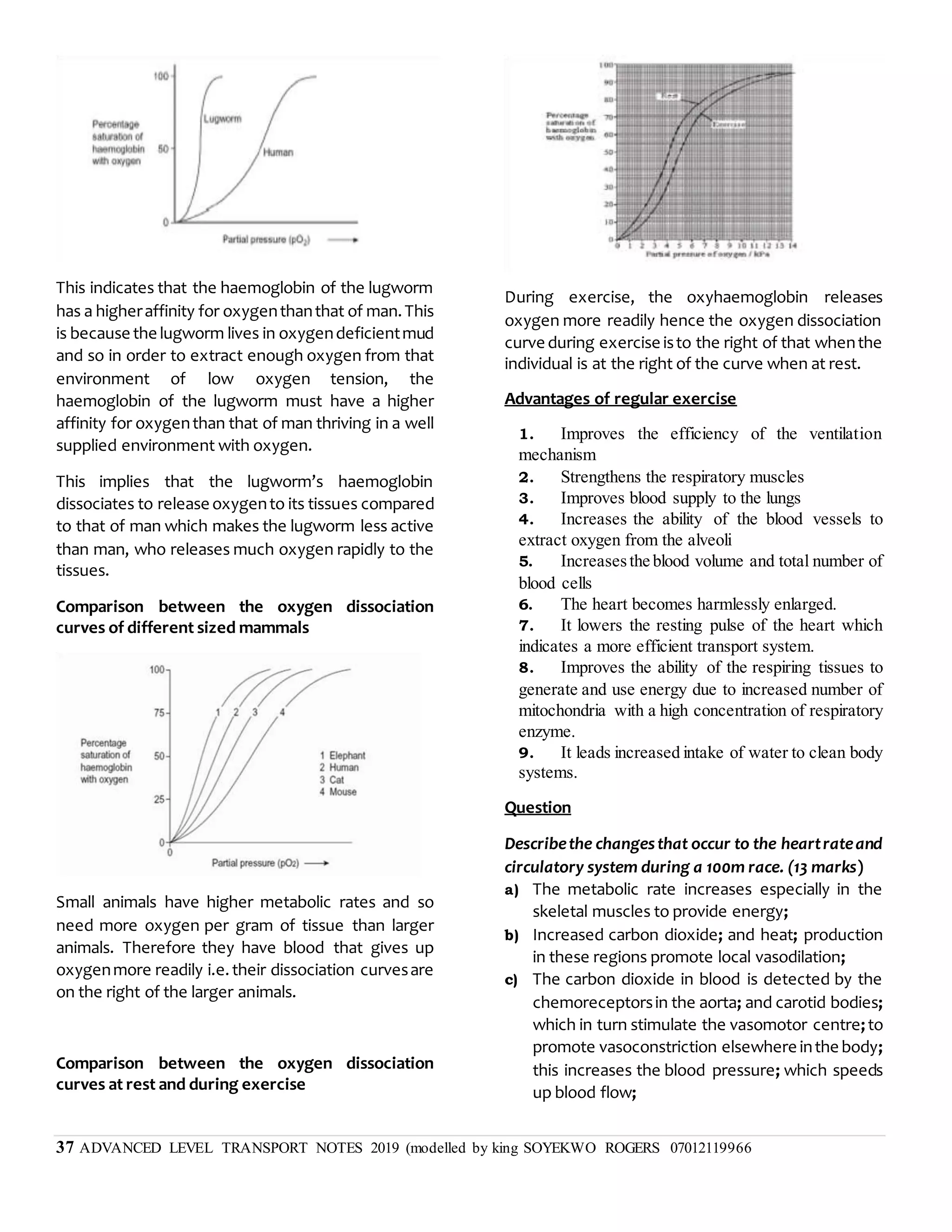
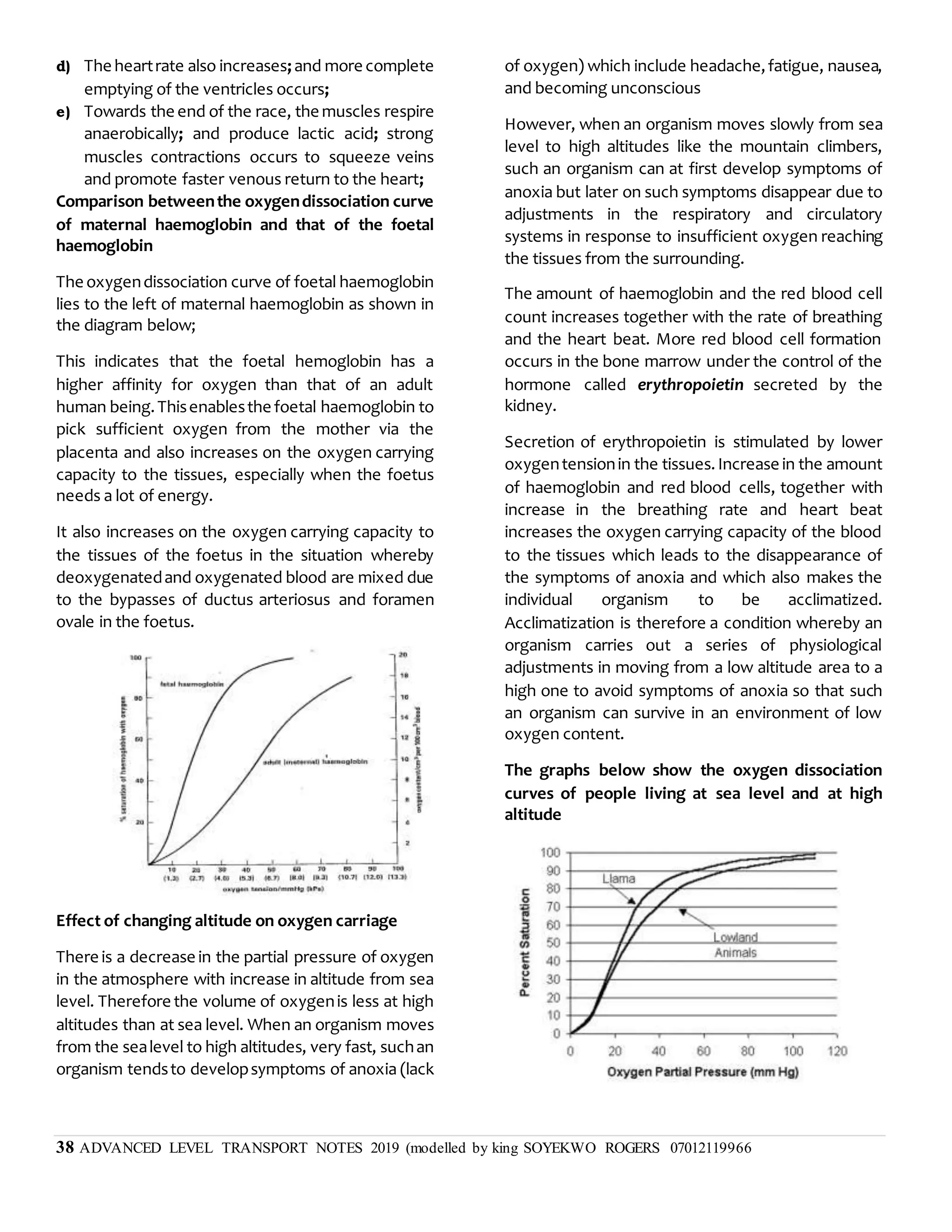
This document discusses transpiration in plants and the factors that affect it. It provides details on the three types of transpiration - stomatal, cuticular, and lenticular. Stomatal transpiration accounts for 90% of water loss through pores in the leaves. The rate of transpiration can be measured using a potometer or by measuring mass loss. Environmental factors like humidity and temperature affect the rate, with higher temperatures and lower humidity increasing transpiration. Transpiration allows water and mineral uptake and provides mechanical support and cooling for plants. Excessive transpiration can lead to wilting and death.













































![54 ADVANCED LEVEL TRANSPORT NOTES 2019 (modelled by king SOYEKWO ROGERS 07012119966
pressure above ventricular pressure; forcing
bloodflow from the leftatrium throughtheopen
bicuspid value; into the relaxed left ventricular;
From 0.14 seconds to 0.38 seconds represents
ventricular systole; There is more powerful
contraction of left ventricular cardiac muscle
than the atrial cardiac muscle; which decreases
ventricular volume while increasing ventricular
pressureabove atrialpressure;forcing closureof
bicuspid valve to prevent backflow of blood into
the left atrium; Ventricular pressure increases
furtherexceeding aortic pressureat0.16seconds
to force open semilunar/aortic valves; hence
allowing left ventricular blood flow into aorta;
From 0.38 seconds to 0.6 seconds represents
diastole; The left ventricular cardiac muscle
relaxes to increase ventricular volume and
decrease ventricular pressure below aortic
pressure; forcing closure of semilunar / aortic
valve to prevent backflow of blood; At 0.4
seconds ventricular pressure decreases further
below atrial pressure to force opening of
bicuspid valve; and flow of oxygenated blood
from the left atrium into the left ventricle;
1. (d) (i) Pattern of electrical activity
P wave corresponds to the wave of electrical
excitation spreading over the atria during atrial
systole/contraction;
QRS wave corresponds to the wave of electrical
excitation spreading over the ventricles during
ventricular systole/contraction;
T wave corresponds to the wave of electrical
excitation spreading over the ventricles during
ventricular diastole/relaxation;
(ii) Pattern of Sounds on the phonocardiogram
1 is the first heart sound produced by the sudden
closure of the atrioventricular valves; [described
as the ‘lub’]
2 is the second heart sound produced by the
sudden closure of the semilunar valves of the
aorta and pulmonary artery; [described as the
‘dub’]
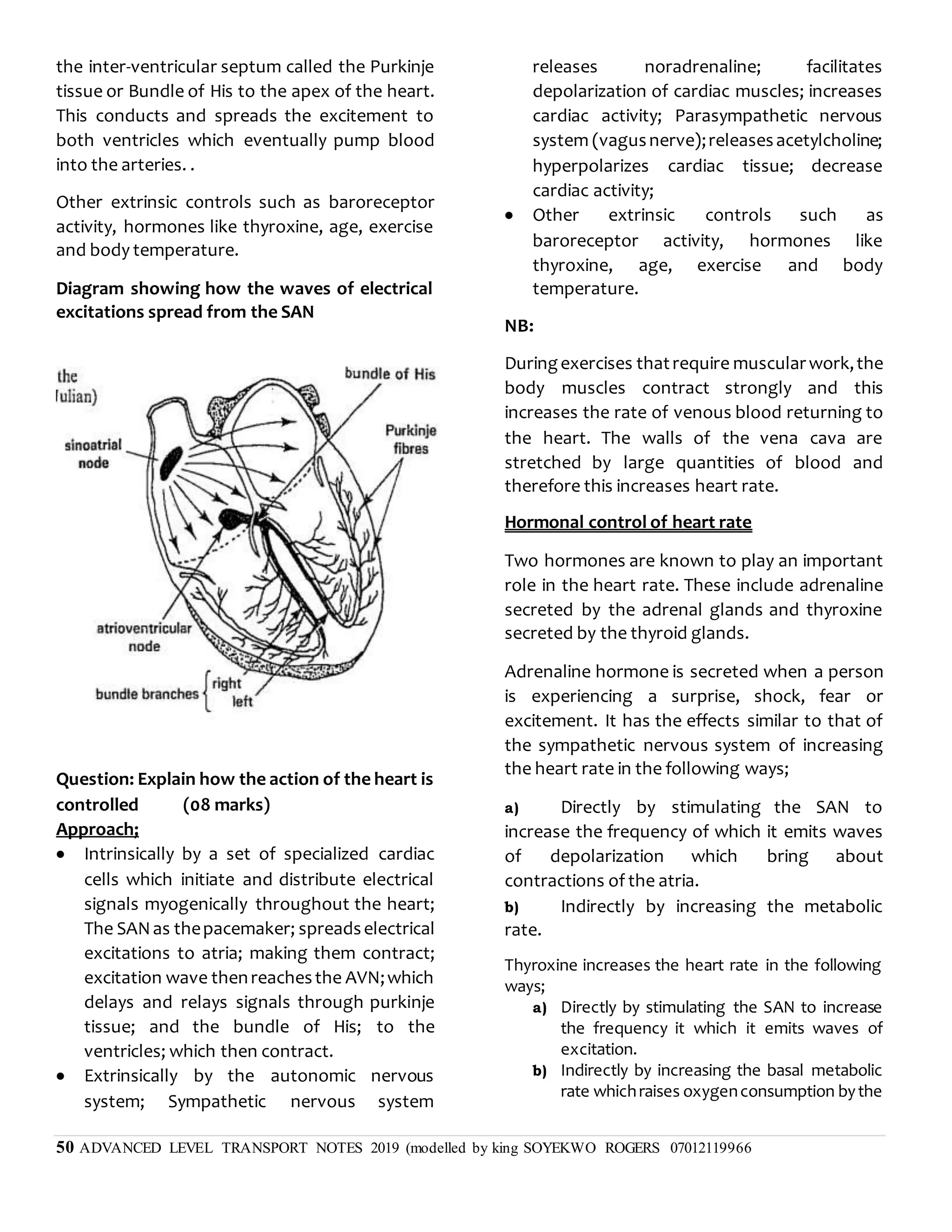
(e) Explain how the internal heart structure is
related to its functioning
- Cardiac muscle fibres interconnected to form a
network of fibre to ensure rapid and uniform
spread of excitation throughout the walls of the
heart;
- Heart divided into 4 chambers to enable
differential generation of pressure;
- Ventricles have thicker walls than auricles to
generatehigher pressuretodrive bloodover long
distance into more elaborate circulation/to the
lungs and to all body tissues;
- Walls of left ventricles are thicker than those of
right ventricles to generate more pressure to
pump
blood to longer distance in the systemic
circulation/rest of the body;
- Longitudinal septum which separates the heart
into two halves to prevent mixing of oxygenated
and deoxygenated blood;
- Valves to prevent back flow of blood;
- Valves have strands of connecting tissue
(chordas tendinae) to prevent them from being
pushed
inside out when ventricles contract;
- Sino Atrial Node (S.A.N) acts a pacemaker
regulatingrate of beating and excitation of heart;
- Heart located in the thoracic cavity where it is
protected from any external mechanical damage;
- Atrio Ventricular node (A.V.N) which delays
depolarization wave from Sino Atrial Node to
ensure thatauricles empty completely before the
ventricles contract;
- Purkinje tissues to relay waves from A.V.N to
ventricular myocardium;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uptakeandtransportinplantsupdated2020-210803155049/75/Uptake-and-transport-in-plants-updated-2020-54-2048.jpg)















