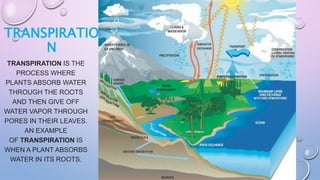
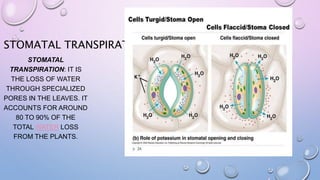
Transpiration is the process by which plants absorb water through their roots and release water vapor through pores in their leaves. It serves two main functions: cooling the plant and pumping water and minerals to the leaves for photosynthesis. The majority (80-90%) of water loss from plants occurs through stomatal transpiration, which takes place through specialized pores called stomata located mostly on the undersides of leaves. Transpiration is important as it creates suction that draws water up from the roots and cools the plant through evaporative cooling.