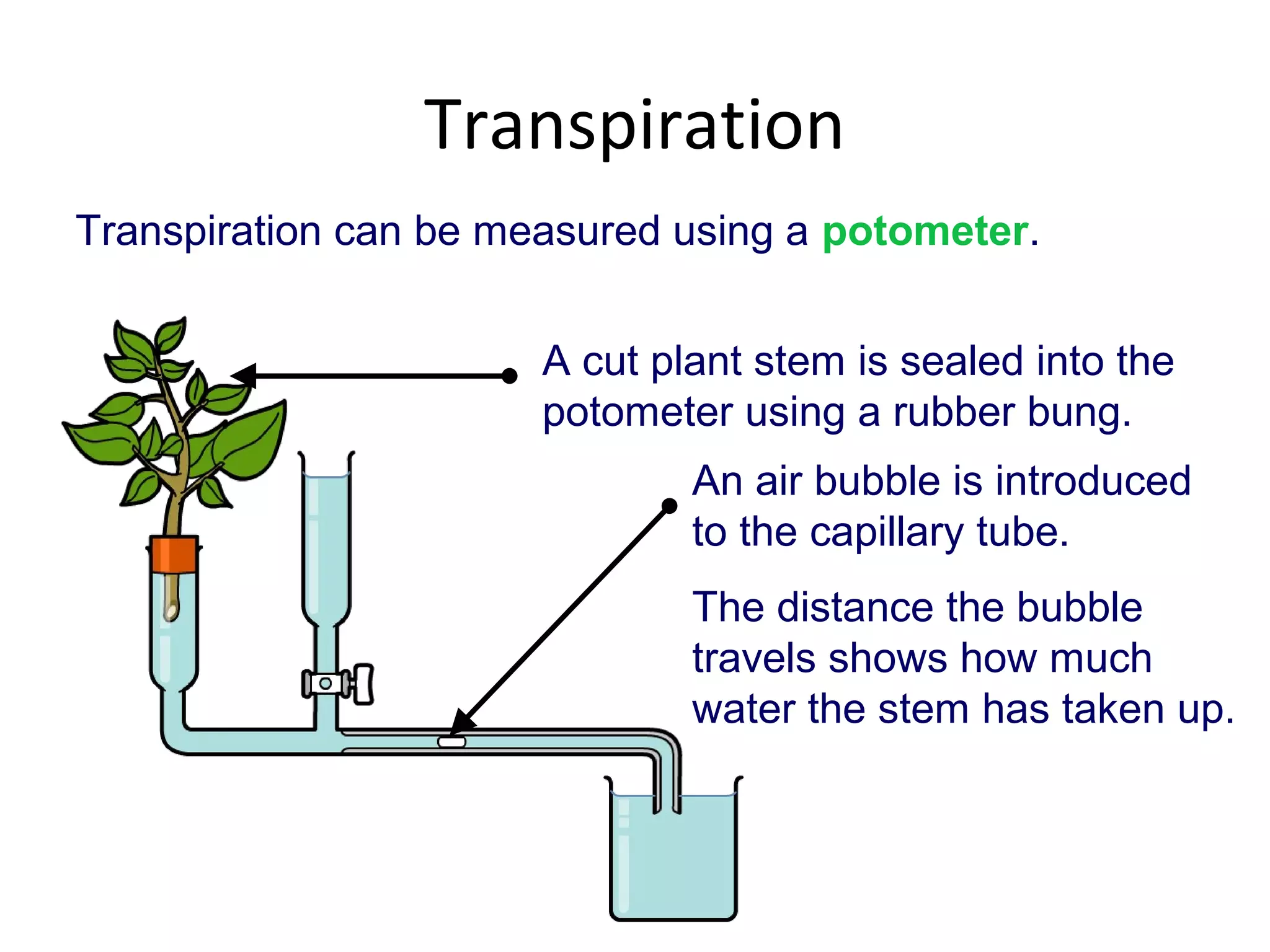
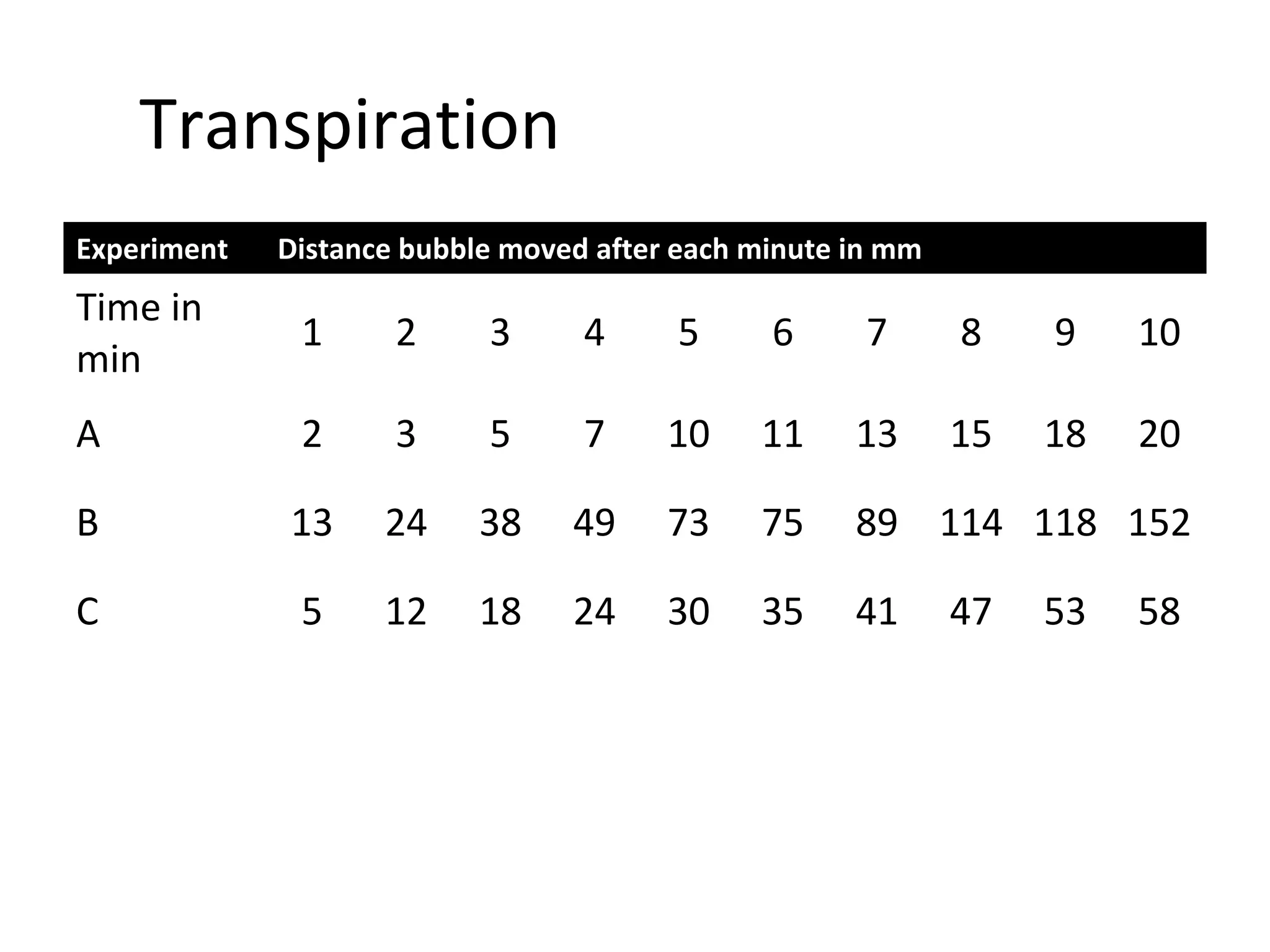
Transpiration is the process by which water moves through a plant from the roots through the xylem to the leaves, where it evaporates from the underside of the leaf and escapes as water vapor through openings called stomata. An experiment is described that uses a potometer to measure the rate of transpiration by recording the distance a bubble moves in a capillary tube as water is carried up through a cut plant stem. The document discusses factors that influence the rate of transpiration such as humidity, light intensity, temperature, air movement, and mechanisms plants use to control water loss like closing stomata.