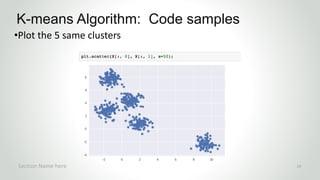
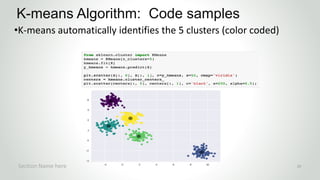
This document outlines a machine learning course focused on unsupervised learning and clustering techniques, led by Peter Chen, a chief data scientist with extensive experience. It covers various clustering algorithms such as k-means, Gaussian mixture models, and hierarchical clustering, along with practical Python examples and applications in different industries. The course is designed for individuals with a basic understanding of Python and mathematics, aiming to provide a conceptual understanding of clustering and its methodologies.