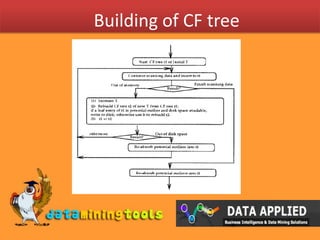
This document provides an introduction to clustering techniques and the BIRCH algorithm. It defines clustering as dividing data instances into natural groups rather than predicting classes. The BIRCH algorithm incrementally clusters multi-dimensional data to produce high quality clusters using minimal resources. It can handle large datasets by performing clustering in one data scan and allows for outliers. The algorithm builds a CF tree using clustering features to summarize cluster information during the incremental clustering process.







![CF TreesA CF tree is a height balanced tree with two parameters: branching factor B and threshold T Each non-leaf node contains at most B entries of the form [CF_i,child_i], where $child_i $ is a pointer to its ith child node and $CF_i$ is the subcluster represented by this childA leaf node contains at most L entries each of the form $[CF_i]$ . It also has to two pointers prev and next which are used to chain all leaf nodes togetherThe tree size is a function of T. The larger the T is, the smaller the tree](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataappliedclustering-100306091941-phpapp02/85/Data-Applied-Clustering-8-320.jpg)