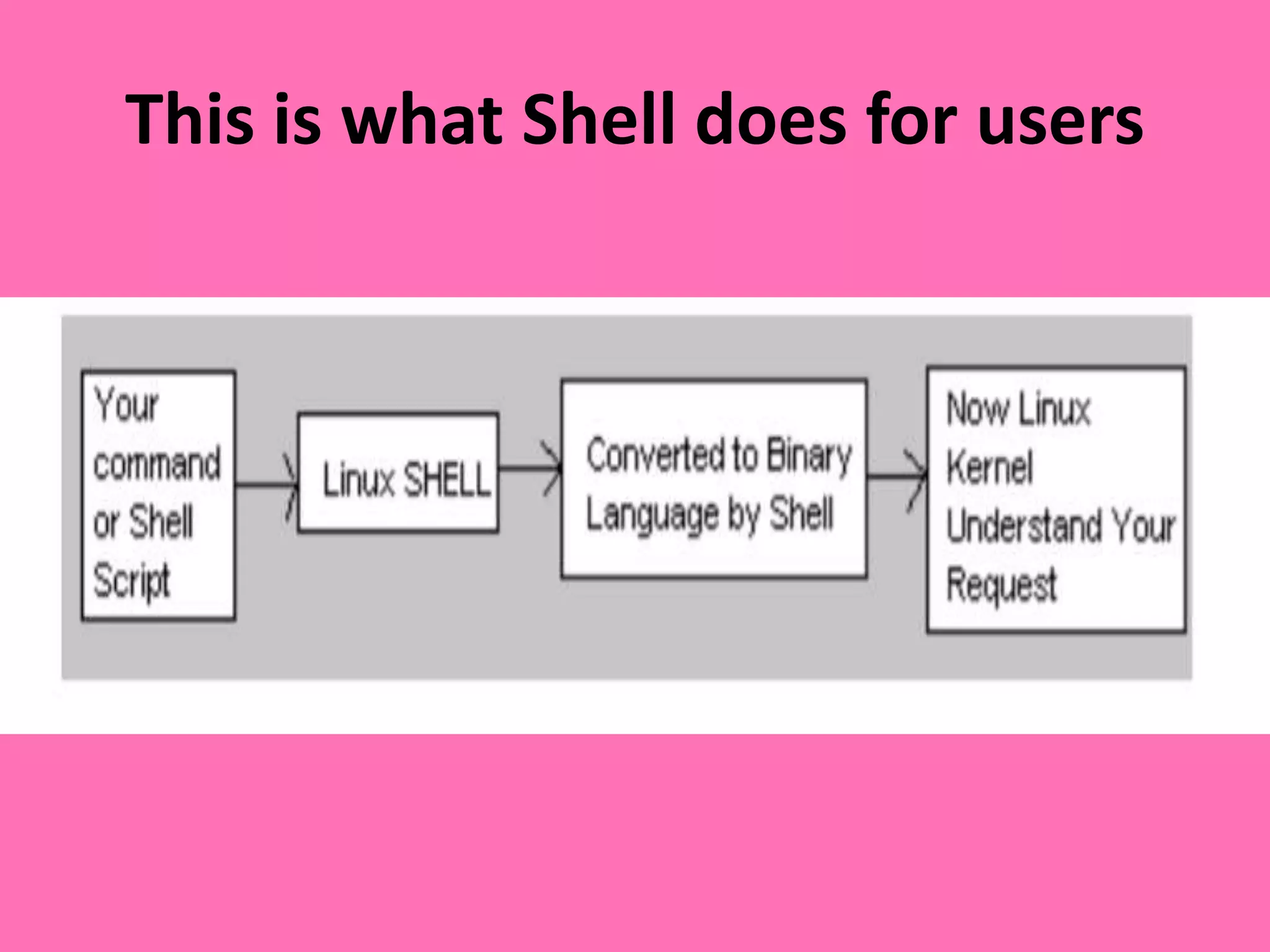
The UNIX system consists of two main components: utilities/commands and the kernel. Utilities are programs that can be executed, like the date and who commands. Commands refer to programs and any arguments used to change their behavior. The kernel is the core of the operating system that manages resources and performs tasks like I/O, process, device, file, and memory management. It loads utilities into memory for execution and remains resident even when utilities are not running.