The document provides an introduction to Unix concepts including:
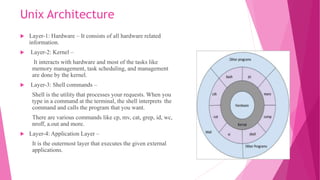
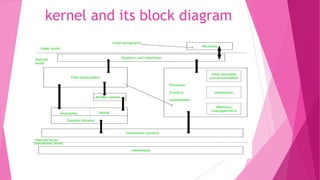
1. It describes the architecture of Unix as having 4 layers - hardware, kernel, shell commands, and application layer. The kernel interacts with hardware and manages tasks like memory and process scheduling.
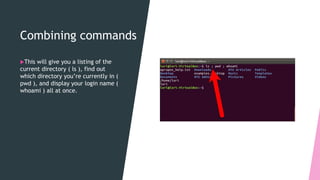
2. It lists some basic Unix commands like ls, echo, printf, who, date, passwd, cal and explains how to combine commands using operators like && and ||.
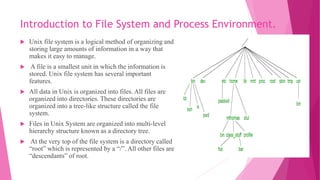
3. It explains Unix files and directories are organized in a hierarchical tree structure with the root directory at the top. There are different types of files like ordinary, special, pipes and symbolic links.







![Unix Command Line Structure
A command is a program that tells the Unix system to do something. It has the
form:
command [options] [arguments]
where an argument indicates on what the command is to perform its action,
usually a file or series of files. An option modifies the command, changing the
way it performs.
Commands are case sensitive. command and Command are not the same.
Options are generally preceded by a hyphen (-), and for most commands, more
than one option can be strung together, in the form:
command -[option][option][option]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2ndchapter-220201105221/85/Chapter-2-Introduction-to-Unix-Concepts-11-320.jpg)


![echo Command
echo command in linux is used to display line of text/string that
are passed as an argument . This is a built-in command that is
mostly used in shell scripts and batch files to output status text to
the screen or a file.
Syntax :
echo [option] [string]
Displaying a text/string :
Syntax :
echo [string]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2ndchapter-220201105221/85/Chapter-2-Introduction-to-Unix-Concepts-14-320.jpg)
![Printf command
“printf” command in Linux is used to display the
given string, number or any other format
specifier on the terminal window. It works the
same way as “printf” works in programming
languages like C.
Syntax:
$printf [-v var] format [arguments]
printf can have format specifiers, escape
sequences or ordinary characters.
Format Specifiers: The most commonly used
printf specifiers are %s, %b, %d, %x and %f.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2ndchapter-220201105221/85/Chapter-2-Introduction-to-Unix-Concepts-15-320.jpg)

![who command
who command is used to find out the following
information :
1. Time of last system boot
2. Current run level of the system
3. List of logged in users and more.
Description : The who command is used to get
information about currently logged in user on to system.
Syntax : $who [options] [filename]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2ndchapter-220201105221/85/Chapter-2-Introduction-to-Unix-Concepts-17-320.jpg)

![Date command
date command is used to display the system
date and time. date command is also used to
set date and time of the system. By default the
date command displays the date in the time
zone on which unix/linux operating system is
configured.You must be the super-user (root) to
change the date and time.
Syntax:
date [OPTION]... [+FORMAT]
Command:
$date
Output:
Tue Oct 10 22:55:01 PDT 2017](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2ndchapter-220201105221/85/Chapter-2-Introduction-to-Unix-Concepts-19-320.jpg)
![Passwd command
passwd command in Linux is used
to change the user account
passwords. The root user
reserves the privilege to change
the password for any user on the
system, while a normal user can
only change the account
password for his or her own
account.
Syntax:
passwd [options] [username]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2ndchapter-220201105221/85/Chapter-2-Introduction-to-Unix-Concepts-20-320.jpg)
![cal command
If a user wants a quick view of calendar
in Linux terminal, cal is the command
for you. By default, cal command shows
current month calendar as output.
cal command is a calendar command in
Linux which is used to see the calendar
of a specific month or a whole year.
Syntax:
cal [ [ month ] year]
Rectangular bracket means it is optional,
so if used without option, it will display
a calendar of current month and year.
cal : Shows current month calendar on
the terminal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2ndchapter-220201105221/85/Chapter-2-Introduction-to-Unix-Concepts-21-320.jpg)

![Option Three: The
Logical OR Operator (||)
Sometimes you might want to execute a second
command only if the first command does not
succeed. To do this, we use the logical OR
operator, or two vertical bars ( || ). For example,
we want to check to see if the MyFolder
directory exists ( [ -d ~/MyFolder ] ) and create
it if it doesn’t ( mkdir ~/MyFolder ). So, we
type the following command at the prompt and
press Enter.
[ -d ~/MyFolder ] || mkdir ~/MyFolder
Be sure there is a space after the first bracket
and before the second bracket or the first
command that checks if the directory exists will
not work.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2ndchapter-220201105221/85/Chapter-2-Introduction-to-Unix-Concepts-24-320.jpg)
