1. Animation involves rapidly displaying sequential images to create the illusion of motion. It can be done by hand drawing or using software to animate graphics.
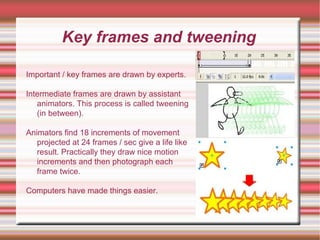
2. There are two main types of animators - lead artists who draw key frames showing major changes, and assistants who draw intermediate frames between key frames through a process called tweening.
3. Techniques of animation include onion skinning to see frames flow together, motion cycling for repetitive motions, and masking to make objects move behind protected areas of the frame. Color cycling and morphing are also techniques.