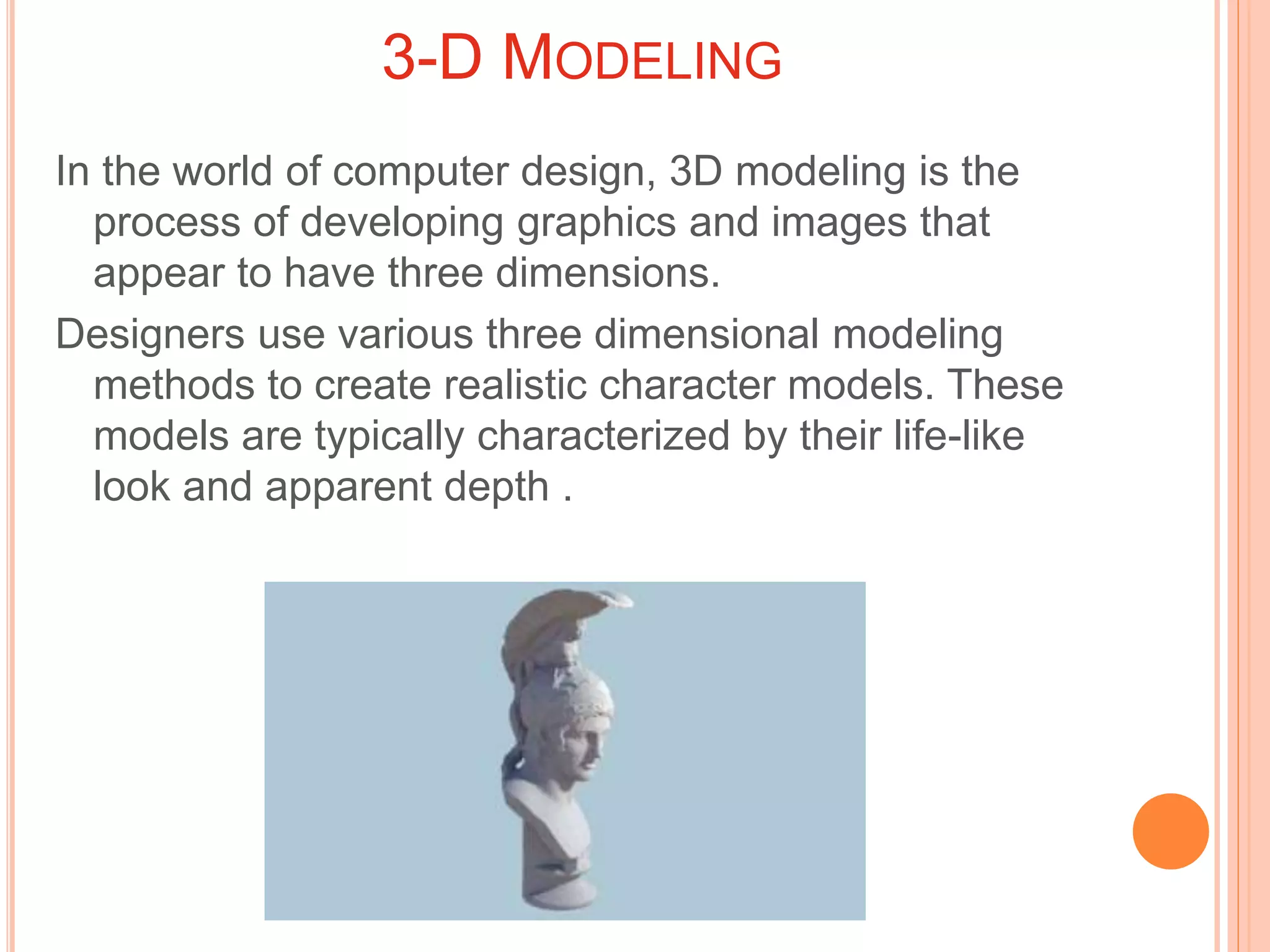
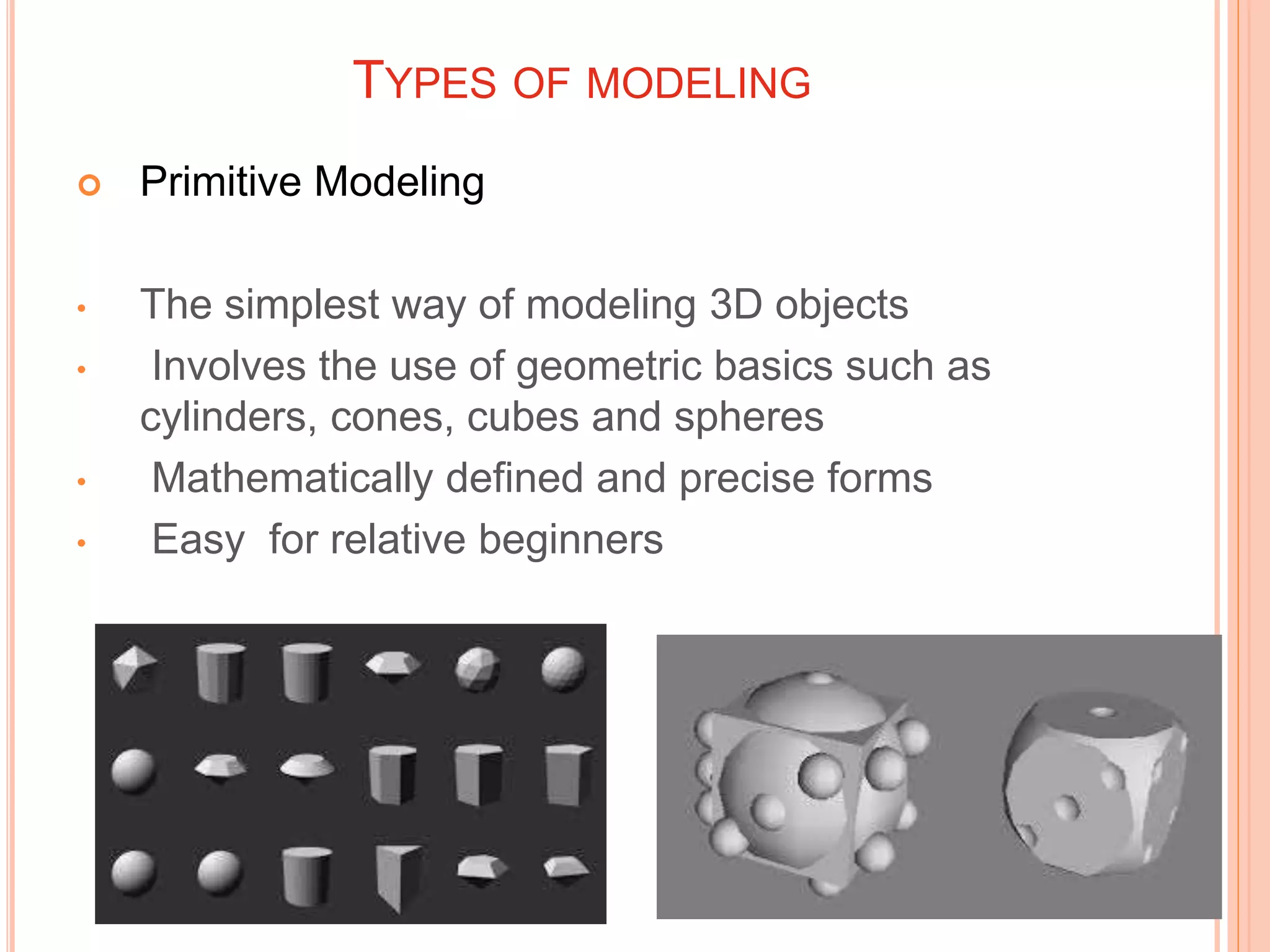
This document provides an overview of 3D modeling and computer animation. It discusses various 3D modeling methods like primitive, polygonal, and NURBS modeling which are used to create realistic 3D characters. It also describes different types of animation like 2D computer-assisted animation and 3D computer generated animation. Early animation techniques like keyframe animation, cel animation, and rotoscoping are compared to modern CGI methods like keyframing, motion capture, and simulation. Finally, applications of 3D modeling and animation are outlined in various fields like entertainment, medicine, architecture, engineering, forensics, and gaming.



![ NURBS Modeling
• Non-uniform rational B-spline modeling(NURBS)
• One of the best ways to create truly curved smooth
surfaces.
• NURBS modeling actually does “bend” the space.
• Commonly used in computer-aided design (CAD),
manufacturing (CAM), and engineering (CAE)
• The control points determine the shape of the
curve.[6] Typically, each point of the curve is
computed by taking a weighted sum of a number of
control points.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3dmodanim-180420182317/75/3D-Modelling-and-Animation-6-2048.jpg)