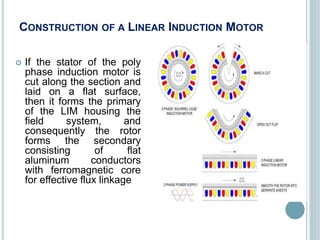
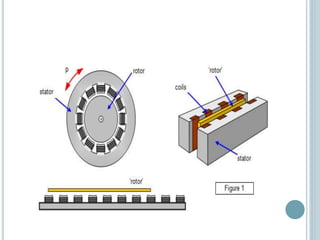
This document discusses linear induction motors. It explains that linear induction motors produce straight line motion rather than rotational motion like traditional motors by having a flat, unwrapped stator that the rotor moves past. It describes how a linear induction motor is constructed by cutting the stator of a polyphase induction motor and laying it flat. It also explains how linear induction motors work by inducing a traveling magnetic flux in the primary from a three-phase power supply that interacts with the secondary to produce a linear force. Some applications mentioned include automatic sliding doors in trains and mechanical handling equipment.