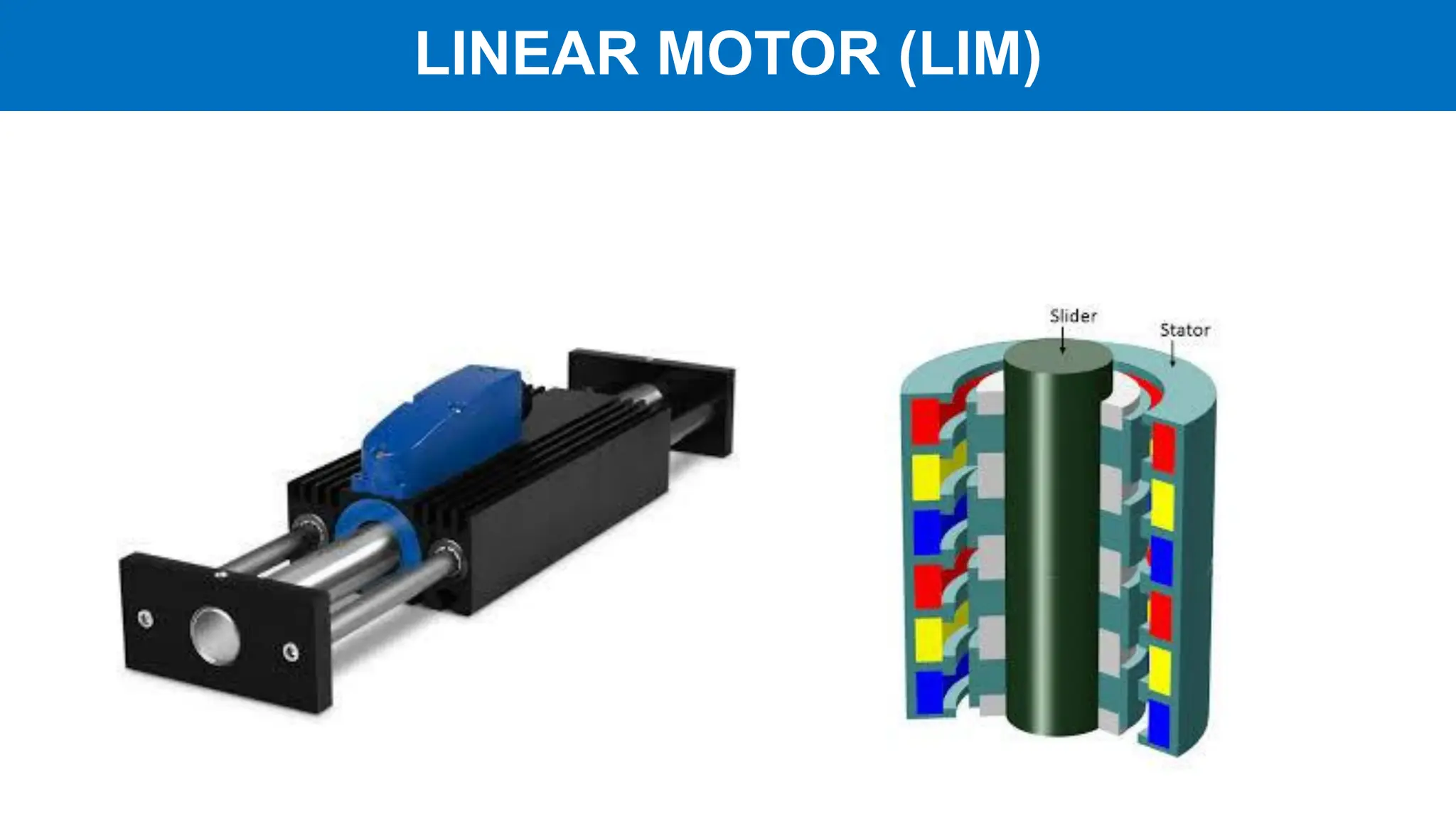
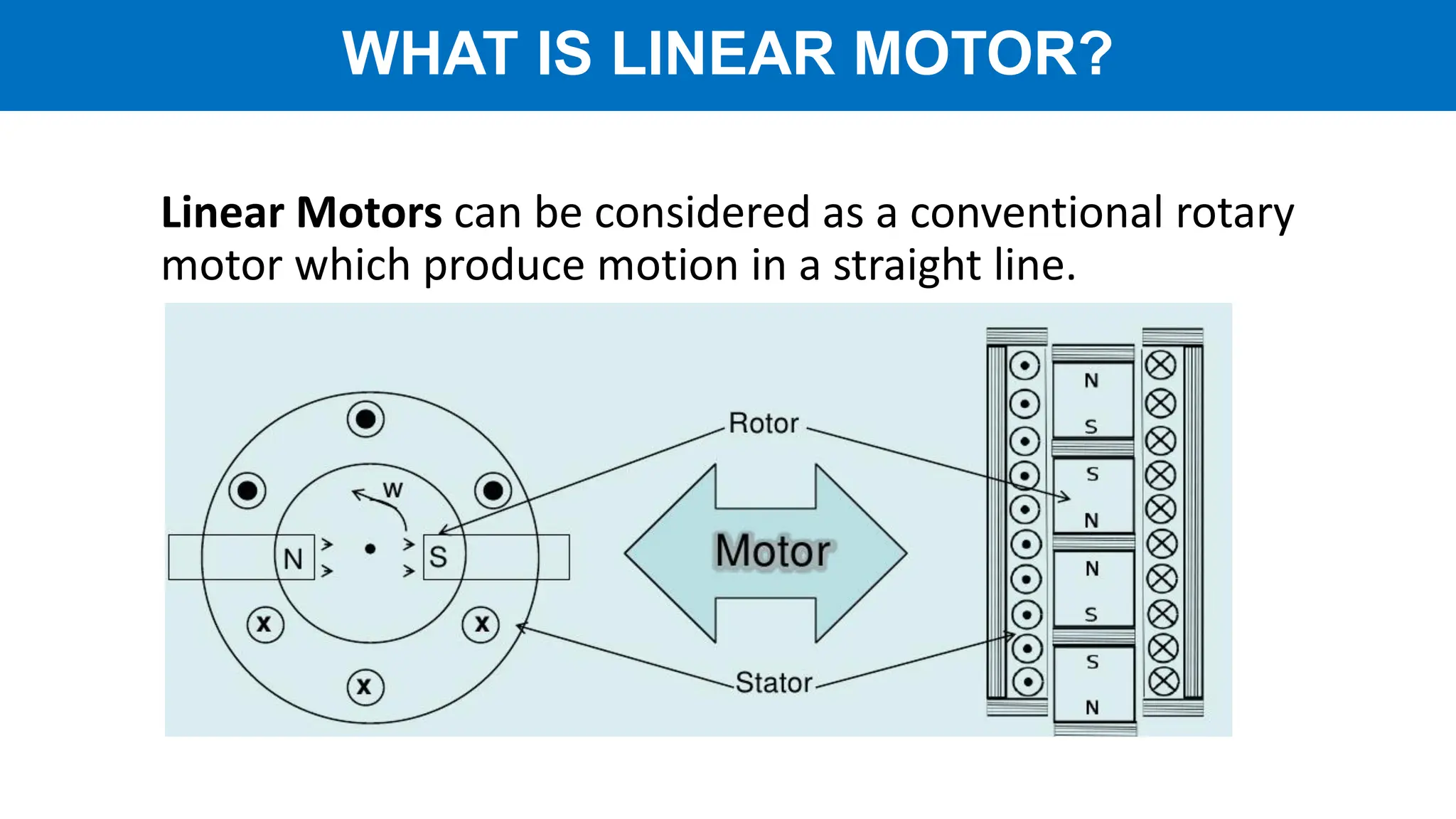
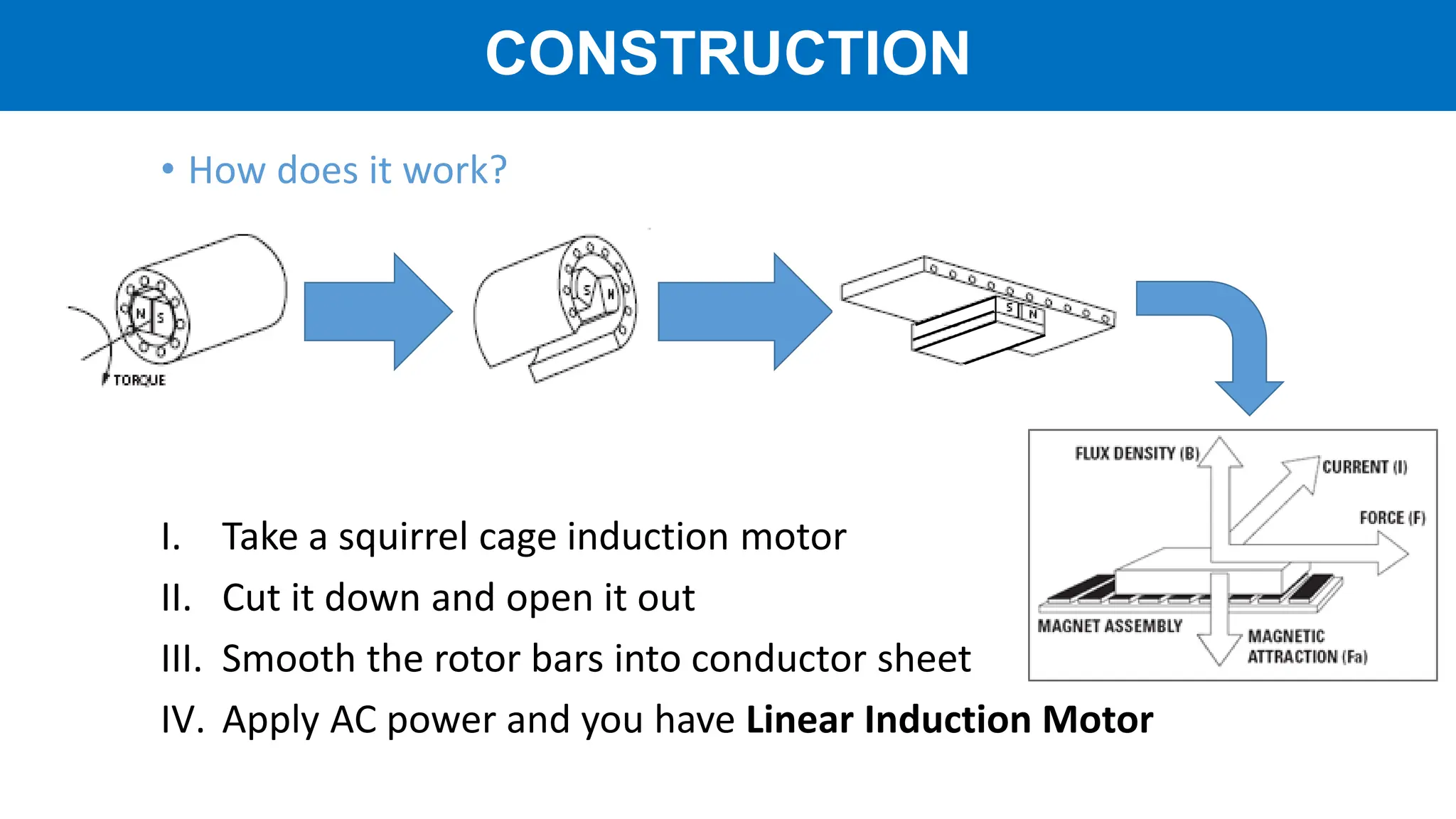
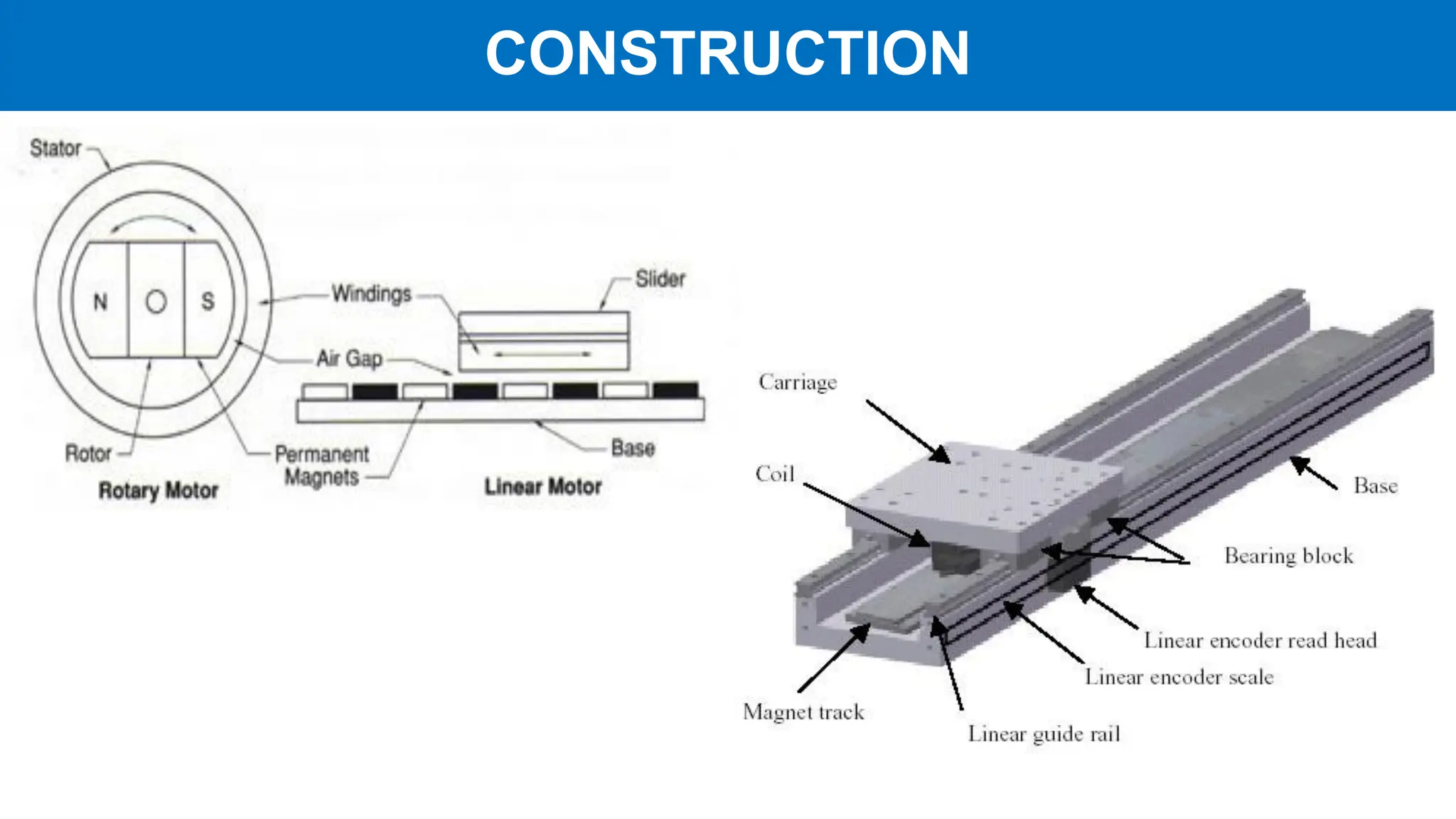
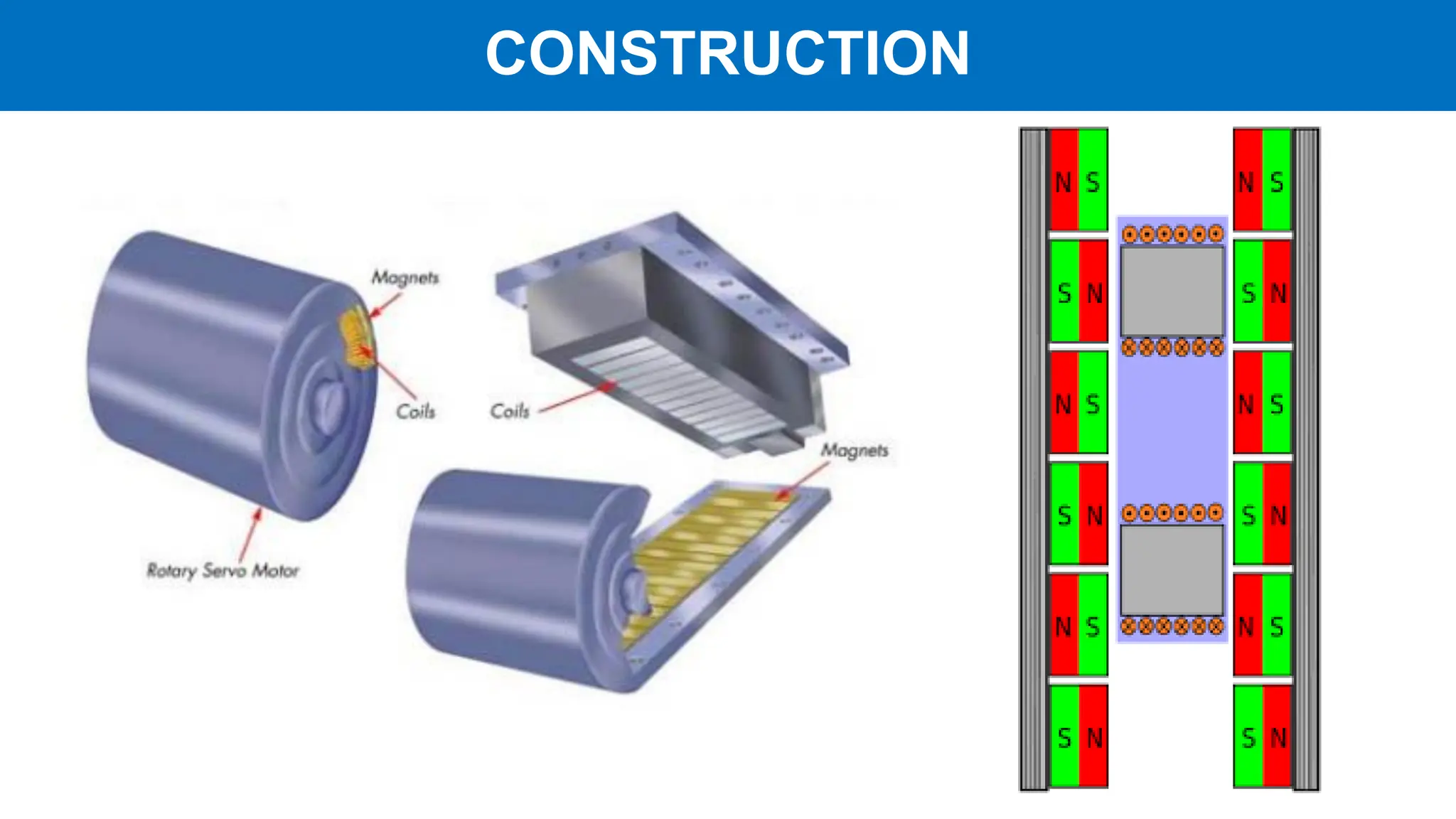
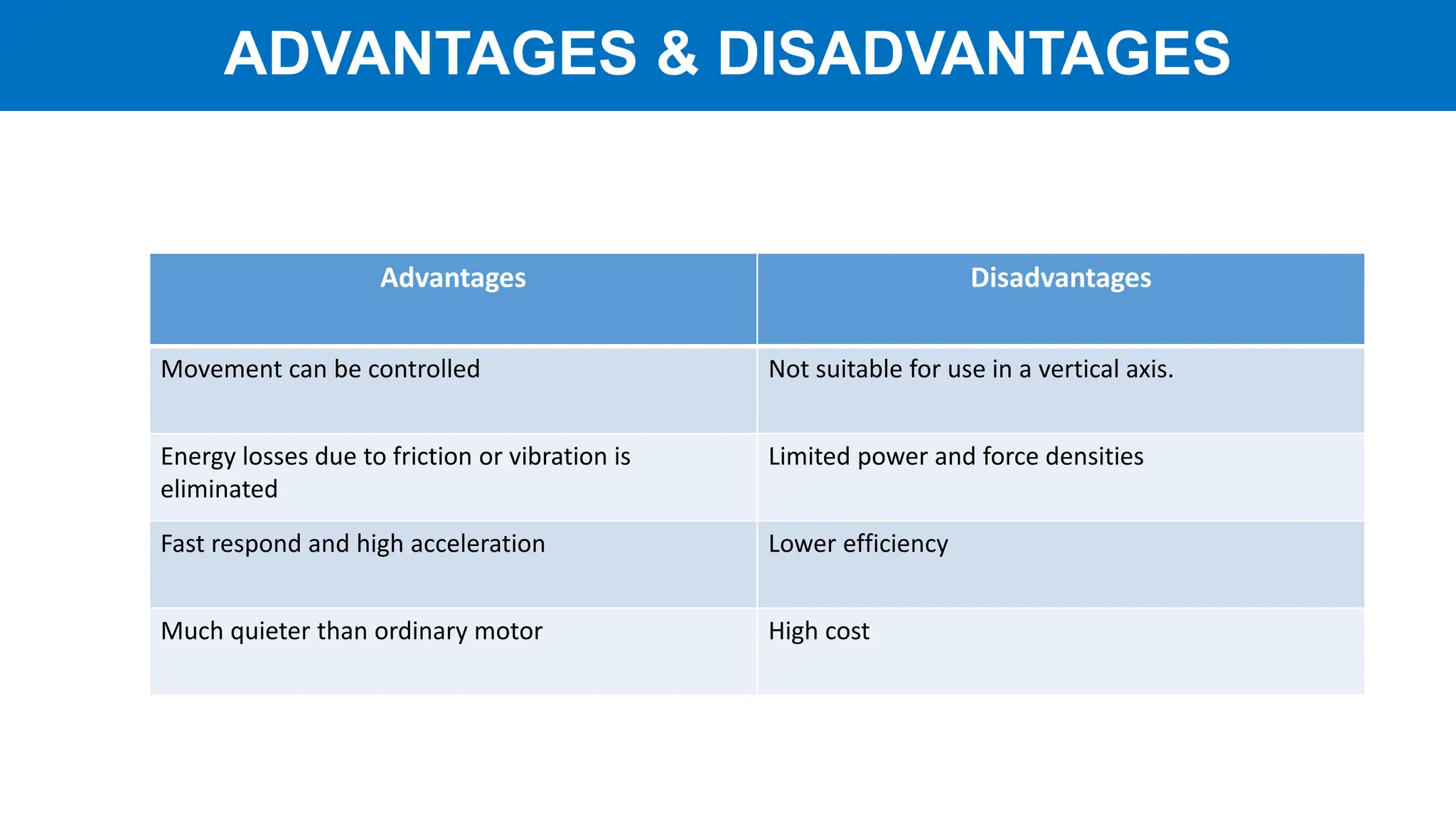
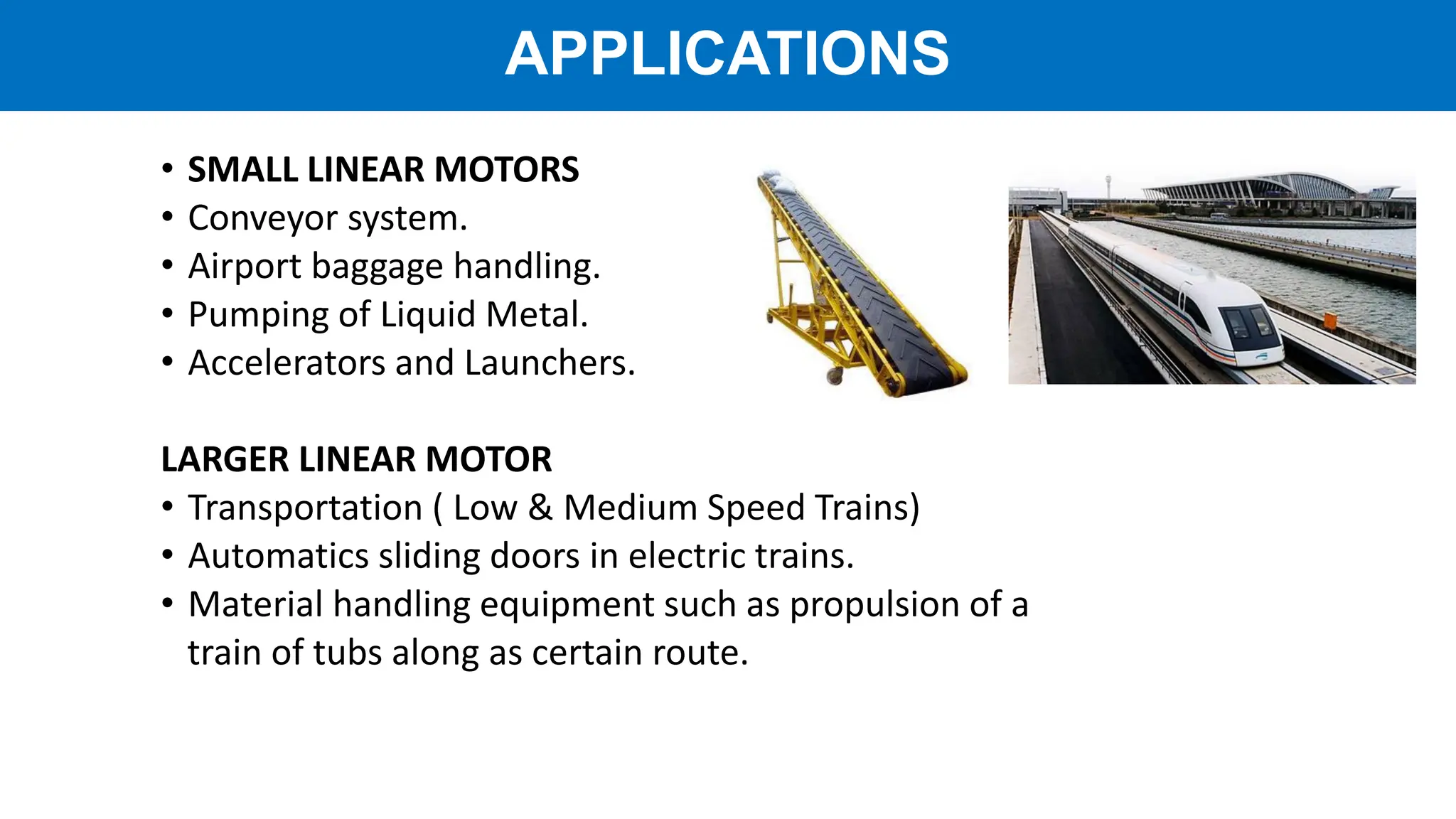
Linear motors (LIM) operate by transforming conventional rotary motors into devices that produce linear motion through electromagnetic processes. They feature stators that generate changing magnetic poles, while their rotors utilize superconducting magnets, leading to advantages like reduced energy loss and high acceleration but also challenges like high costs and limited power density. Applications include transportation systems and material handling, though their complexity and cost make them less favorable for certain uses.