1. The document discusses different types of keys used in mechanical engineering including taper keys, parallel keys, gib head keys, woodruff keys, and their standard dimensional proportions.
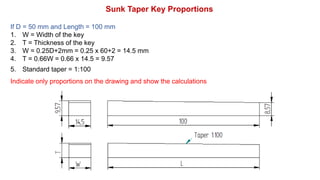
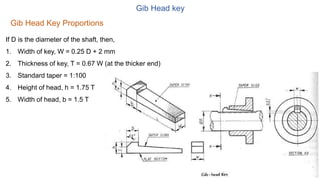
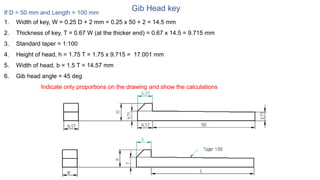
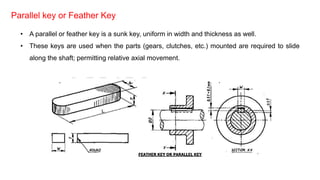
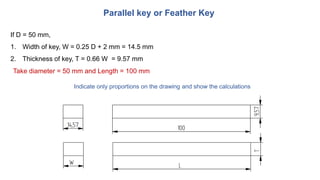
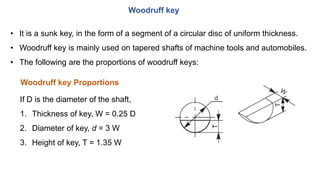
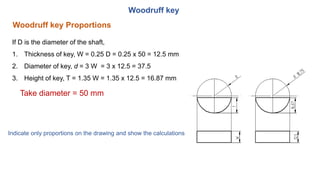
2. Standard proportions are provided for taper keys, gib head keys, parallel keys, and woodruff keys based on the diameter of the shaft. Examples of calculating the dimensions for each key type are shown.
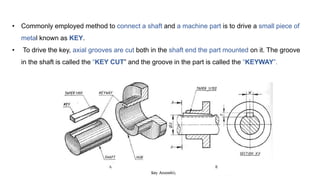
3. Keys are used to connect rotating machine elements to shafts to transmit torque and prevent relative motion between the shaft and hub. Keyways are slots cut in the shaft and hub to accommodate keys.