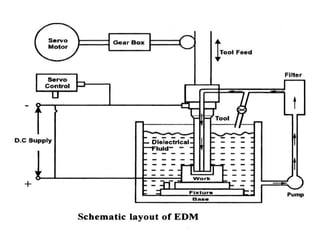
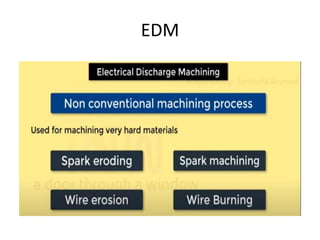
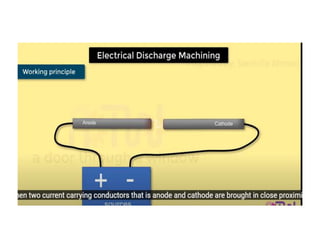
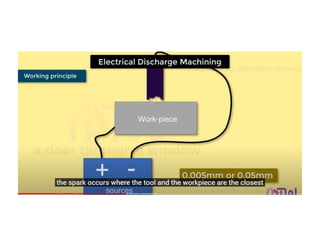
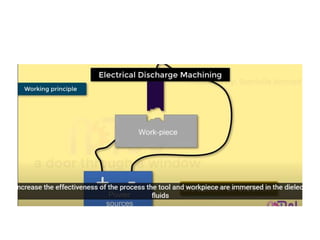
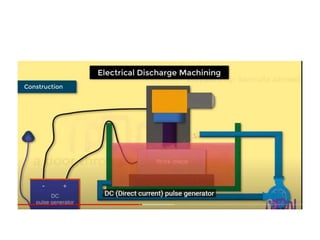
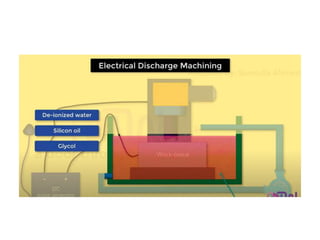
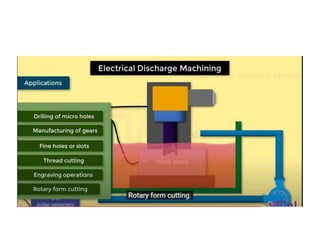
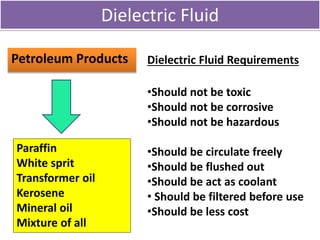
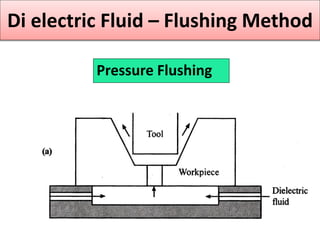
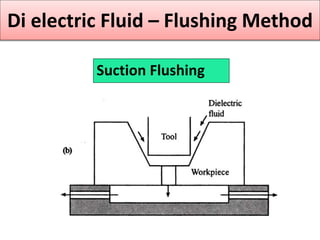
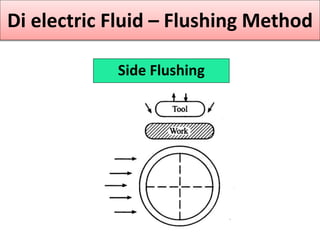
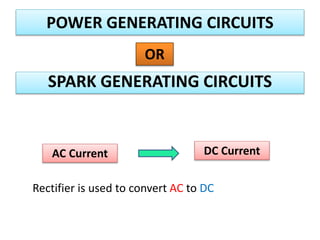
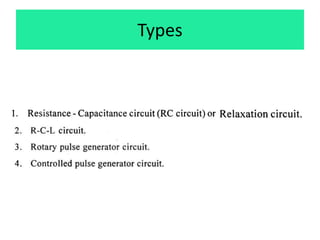
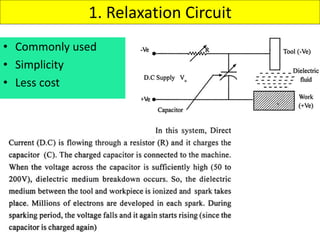
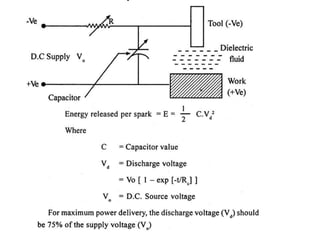
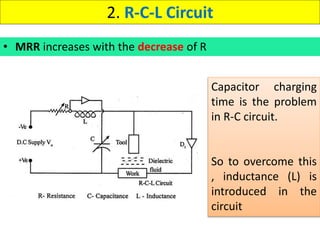
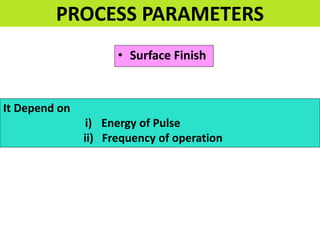
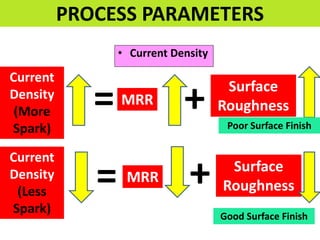
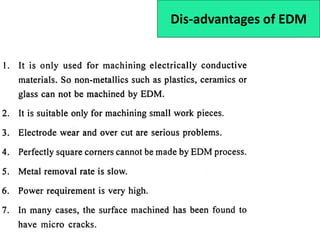
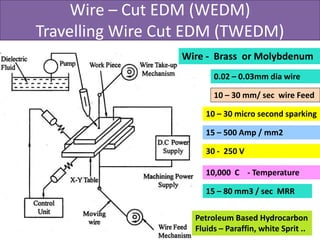
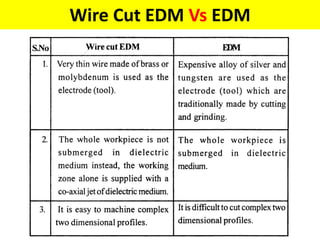
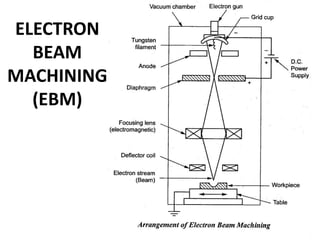
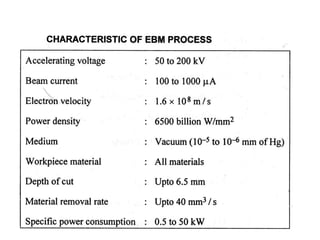
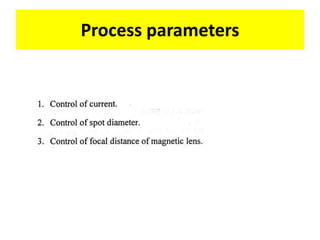
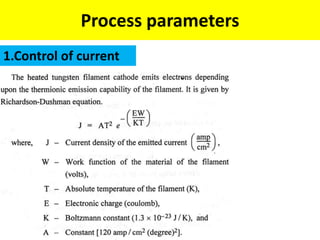
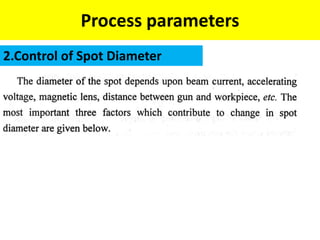
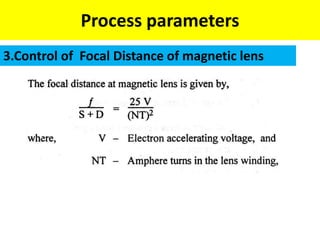
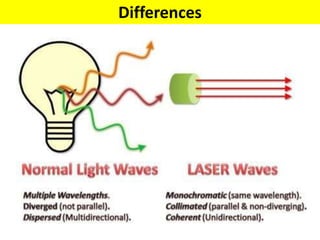
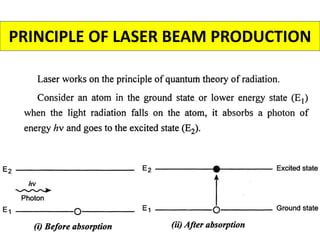
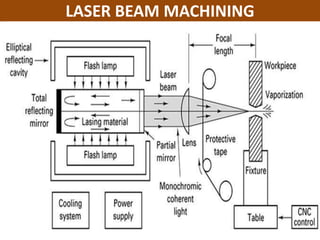
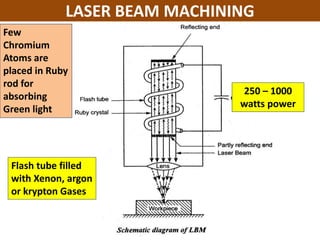
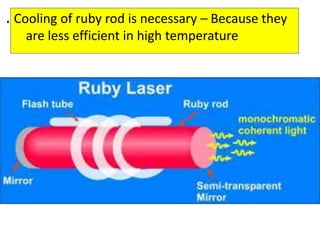
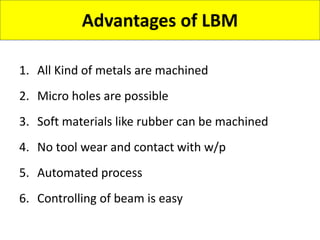
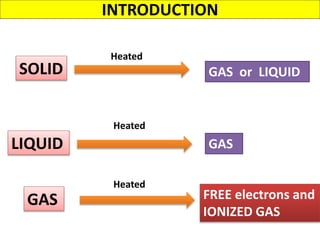
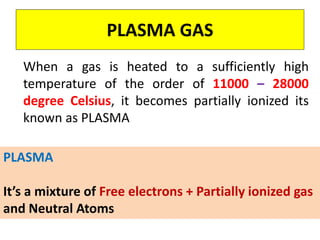
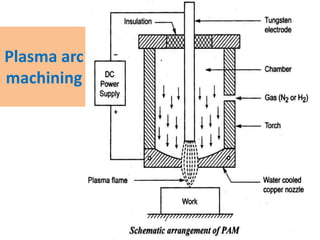
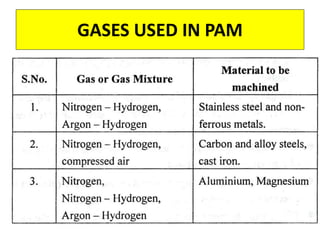
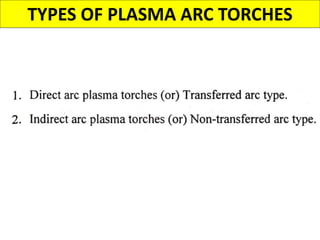
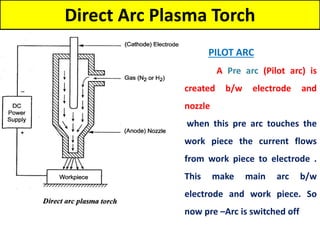
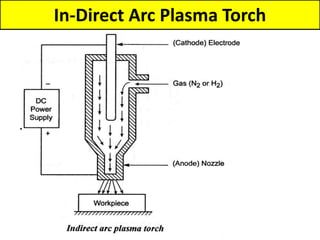
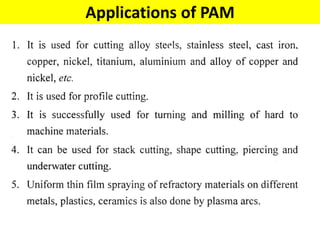
This document discusses various unconventional machining processes involving thermal and electrical energy. It focuses on electric discharge machining (EDM) and wire cut EDM, describing their working principles, process parameters, equipment and applications. Key topics covered include the use of dielectric fluids, power circuits and electrode materials in EDM. Thermal energy based processes of laser beam machining, electron beam machining and plasma arc machining are also introduced, outlining their principles, beam control techniques and typical applications in industry.