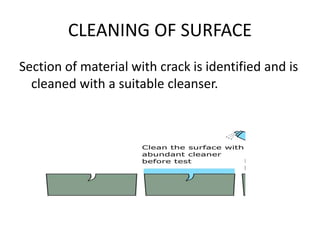
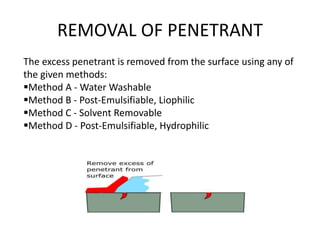
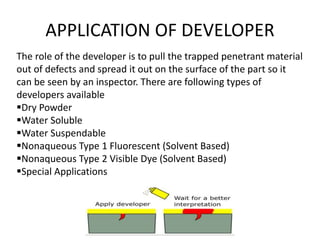
This presentation summarizes non-destructive testing (NDT) and focuses on liquid penetrant inspection. It defines NDT as techniques used to evaluate materials without causing damage. It outlines various NDT methods like visual inspection, magnetic particle inspection, and ultrasonic inspection. For liquid penetrant inspection, it describes the process of cleaning surfaces, applying penetrant, removing excess penetrant, applying developer, and limitations like needing surface access and very tight defects being difficult to find. The presentation was intended to inform Dr. P.K. Gupta and Prof. Arpit Rastogi on this topic.