Embed presentation
Downloaded 26 times



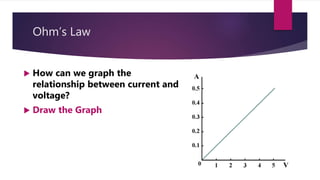

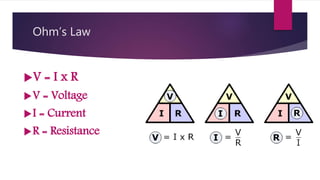
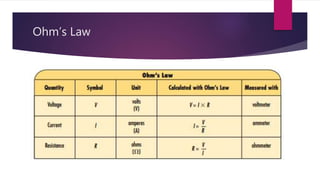




Ohm's Law states that the current through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied, provided the resistance remains constant. Georg Simon Ohm discovered this relationship in the 1800s and developed a mathematical formula relating voltage (V), current (I), and resistance (R) such that V=I×R. Various devices can measure these electrical properties, and changing the temperature of a resistor alters its resistance and causes Ohm's Law to break down.










