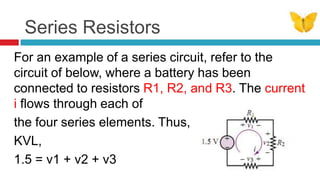
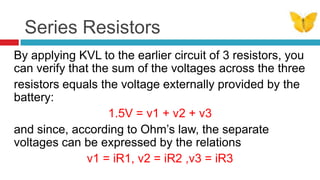
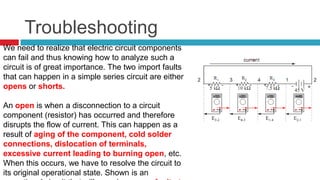
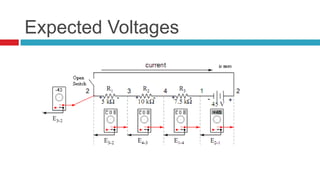
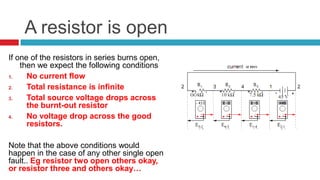
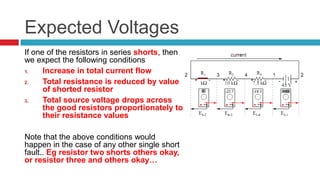
1. The document discusses series circuits and how voltage is divided among resistors in series. It explains that the total resistance of resistors in series is equal to the sum of the individual resistances.
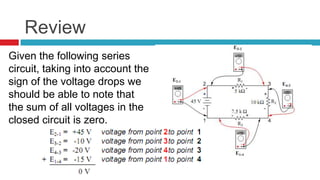
2. A key concept covered is the voltage divider rule - the voltage across each resistor in a series circuit is directly proportional to the ratio of its resistance to the total resistance.
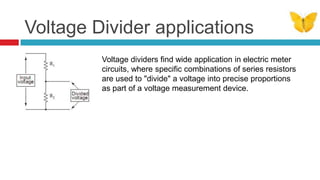
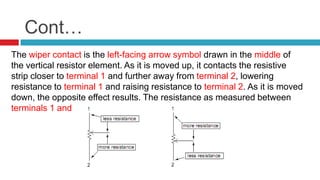
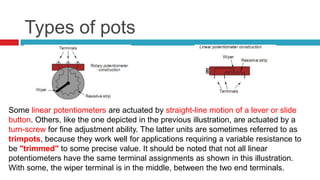
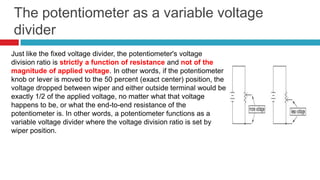
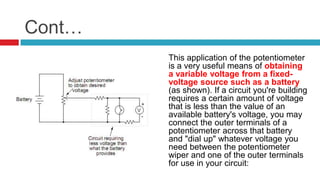
3. Applications of voltage dividers include using potentiometers (variable resistors) to obtain a variable output voltage from a fixed voltage source.