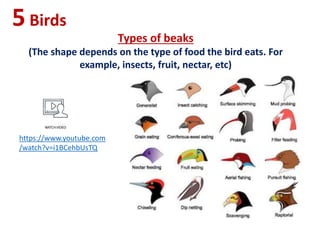
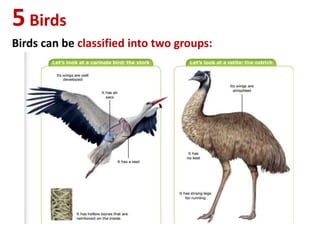
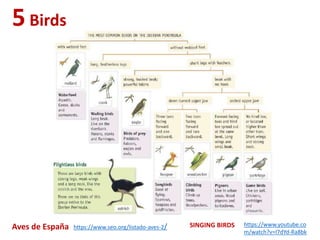
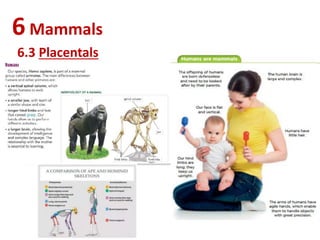
The document summarizes key characteristics of vertebrate groups including birds and mammals. It describes birds as having feathers, wings, beaks and laying eggs. Their bodies are adapted for flight through lightweight skeletons and muscles. Mammals are described as hairy, warm-blooded, having different types of teeth and giving live birth or laying eggs. They are divided into monotremes, marsupials and placentals depending on their reproductive strategies.