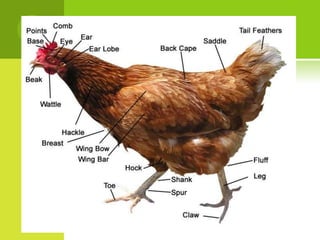
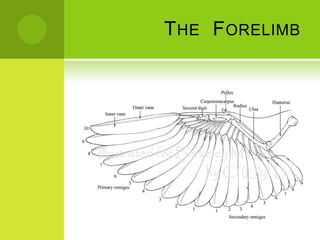
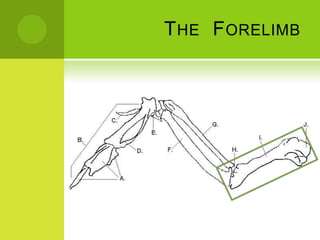
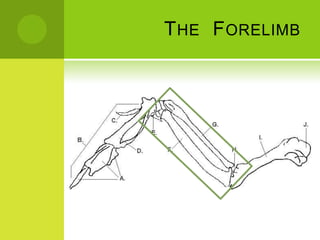
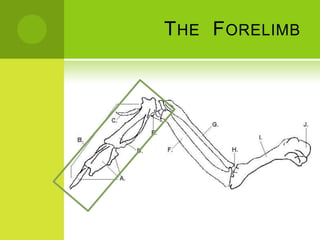
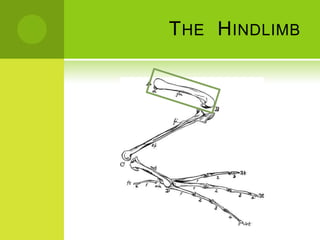
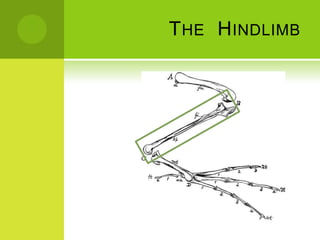
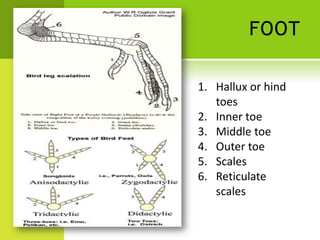
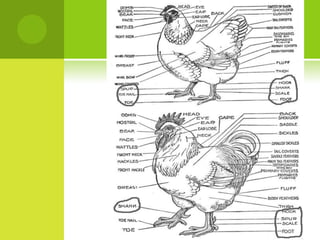
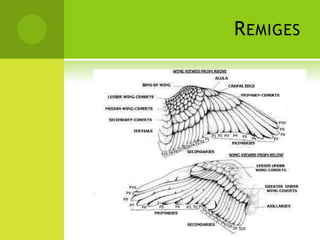
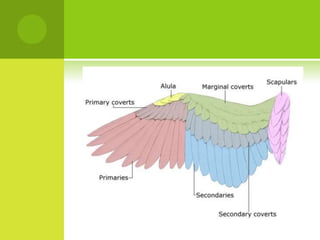
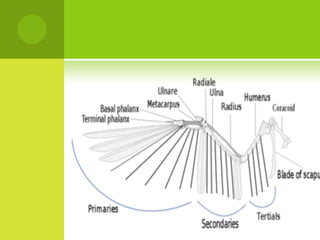
This document summarizes the external anatomy of chickens. It describes key features such as their eyes and eyelids, beaks, combs, wattles, forelimbs used for flight, hindlimbs used for walking, feet, feathers, and skin patterns where feathers do and do not grow. The chicken is classified as kingdom Animalia, phylum Chordata, class Aves, order Galliformes, family Phasianidae, subfamily Phasianinae, genus Gallus, and species Gallus gallus domesticus.