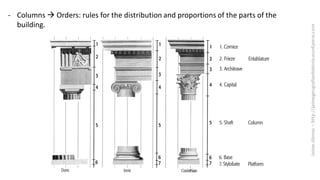
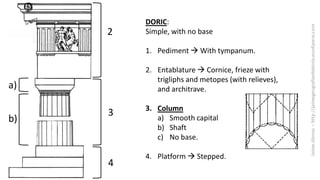
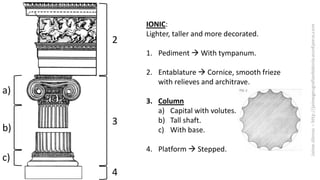
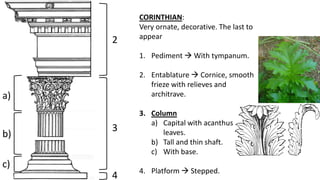
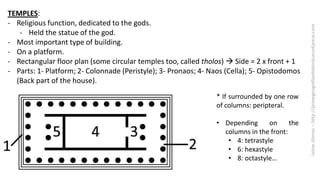
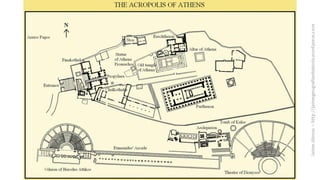
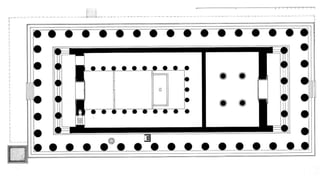
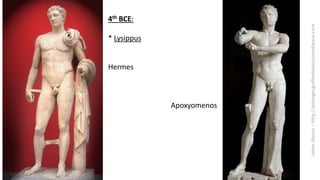
The document summarizes some of the main characteristics of Greek art in different areas. It discusses the emphasis on proportion, balance, and referencing the human form in architecture, sculpture, and other art forms. Some key points are that Greek architecture featured the orders of columns (Doric, Ionic, Corinthian), temples were the most important buildings and had specific parts, and sculpture evolved from the archaic to classical periods focusing increasingly on naturalism and idealized representations of the human body and myths.