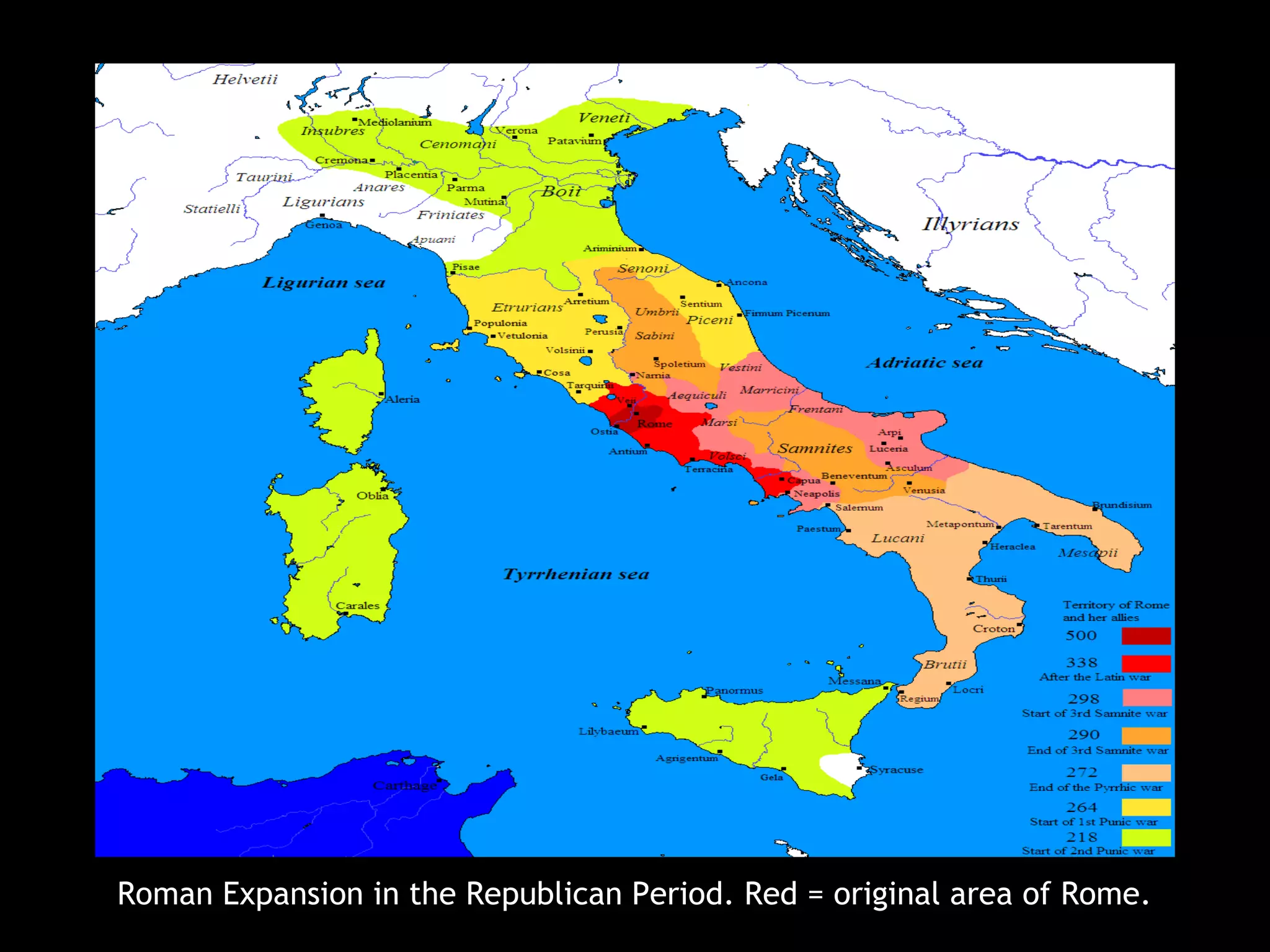
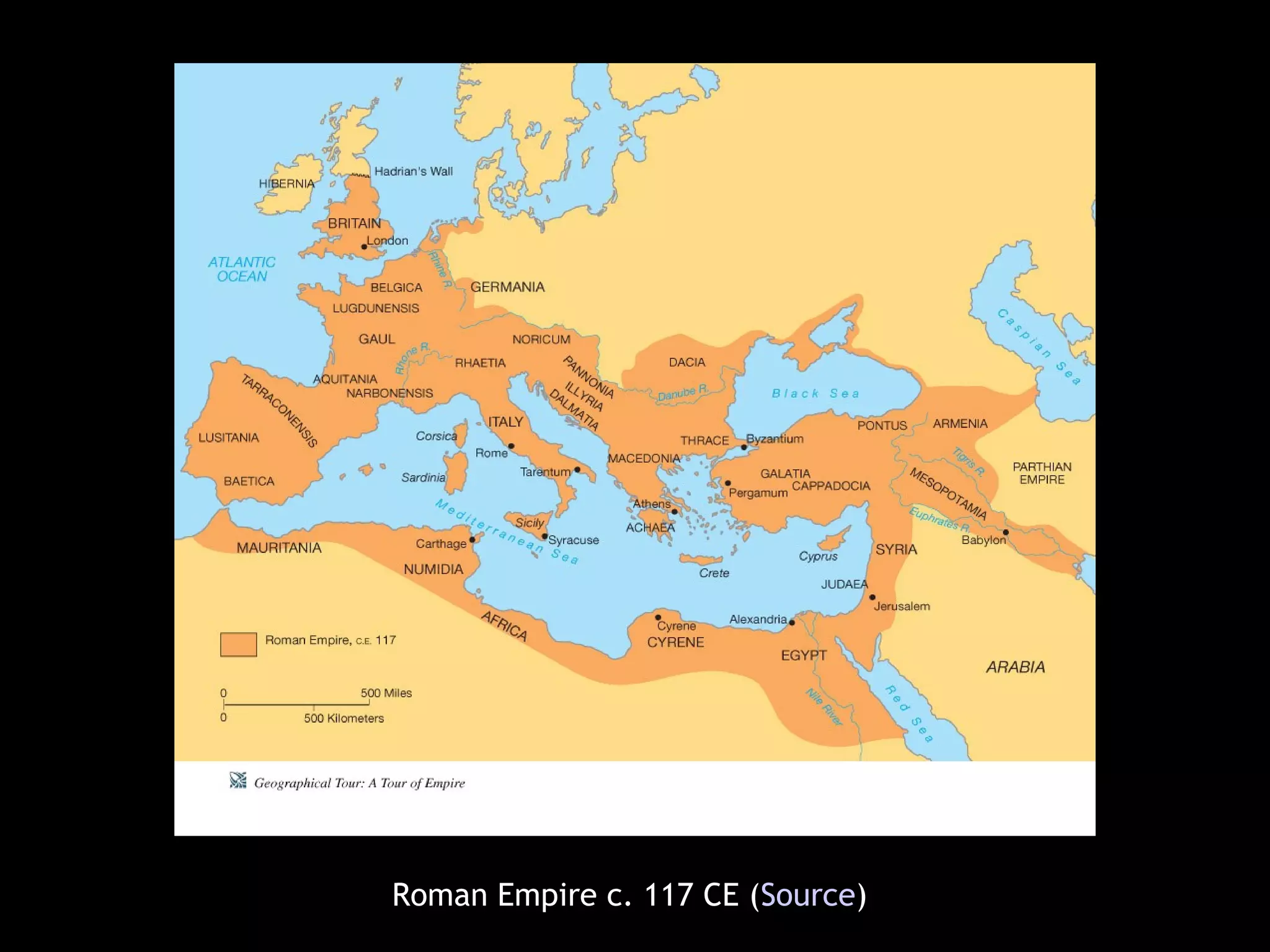
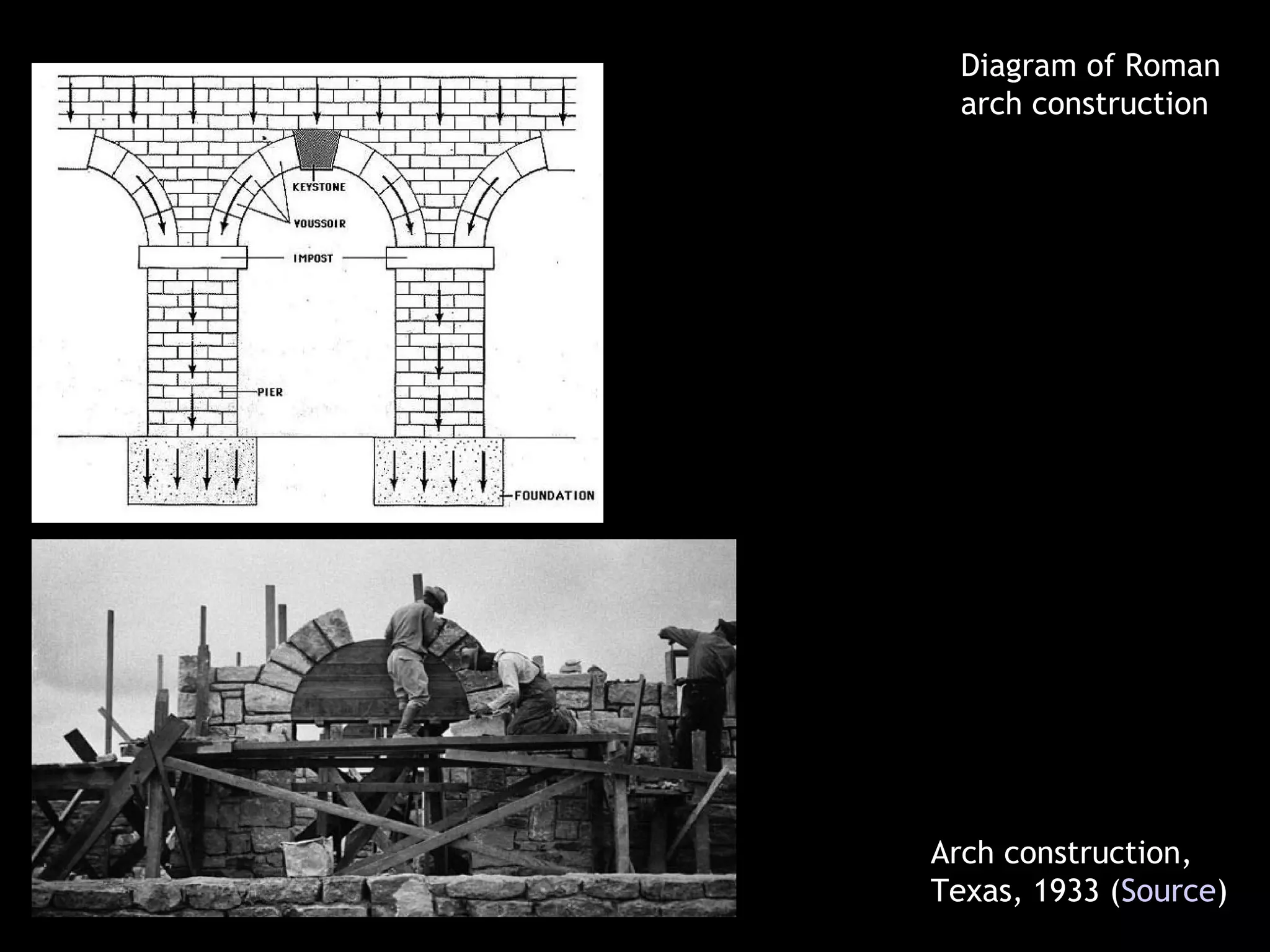
The document highlights key artworks and architectural achievements from ancient Roman and Etruscan periods, featuring significant pieces such as the painted terracotta Apollo and the Augustus of Primaporta. It outlines the timeline of Roman expansion and cultural milestones, including the founding of Rome and the transition to the Imperial period. Additionally, it describes artistic techniques and important structures like the Pantheon and the Arch of Titus.