Embed presentation
Downloaded 83 times


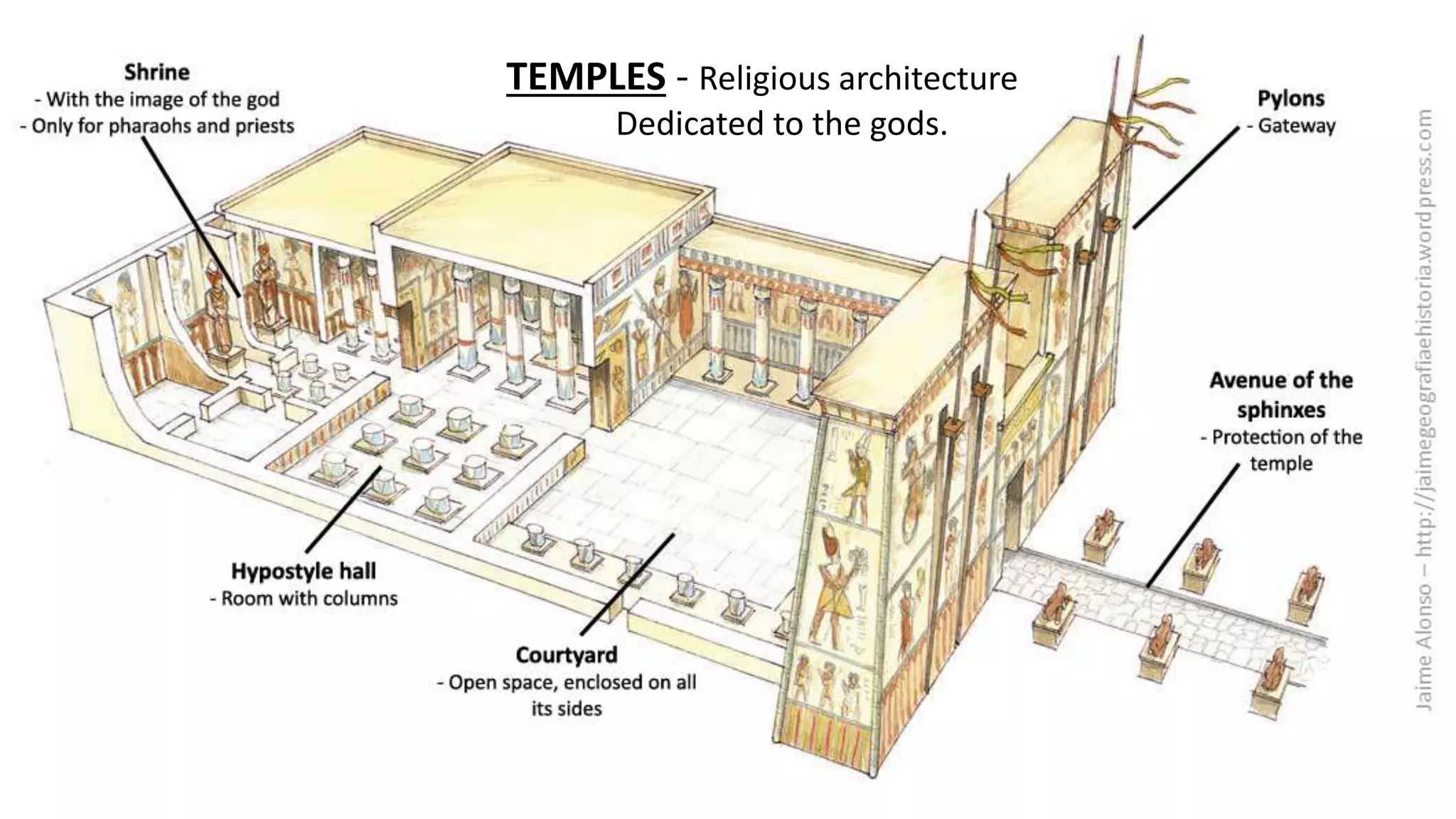






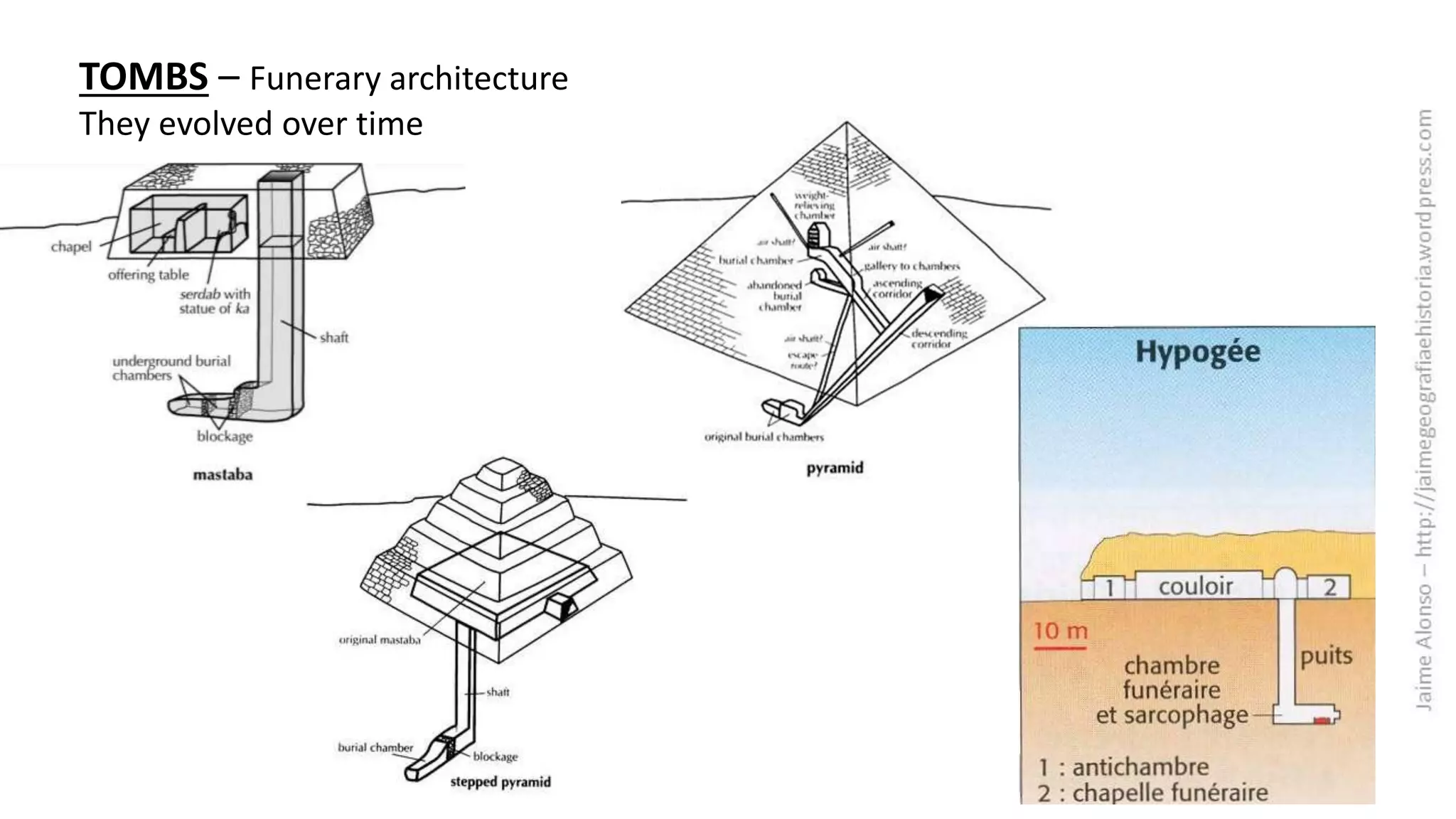
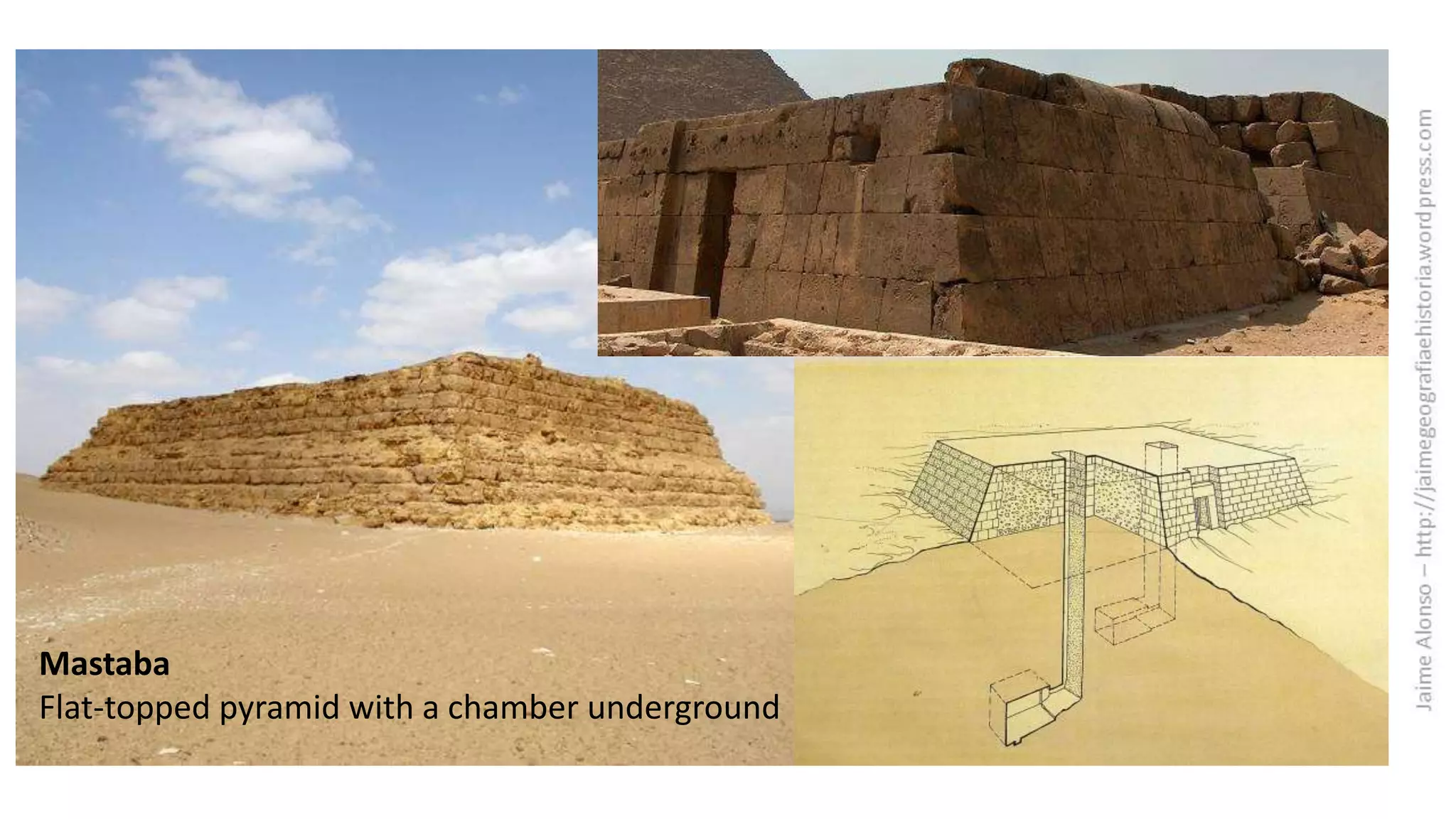

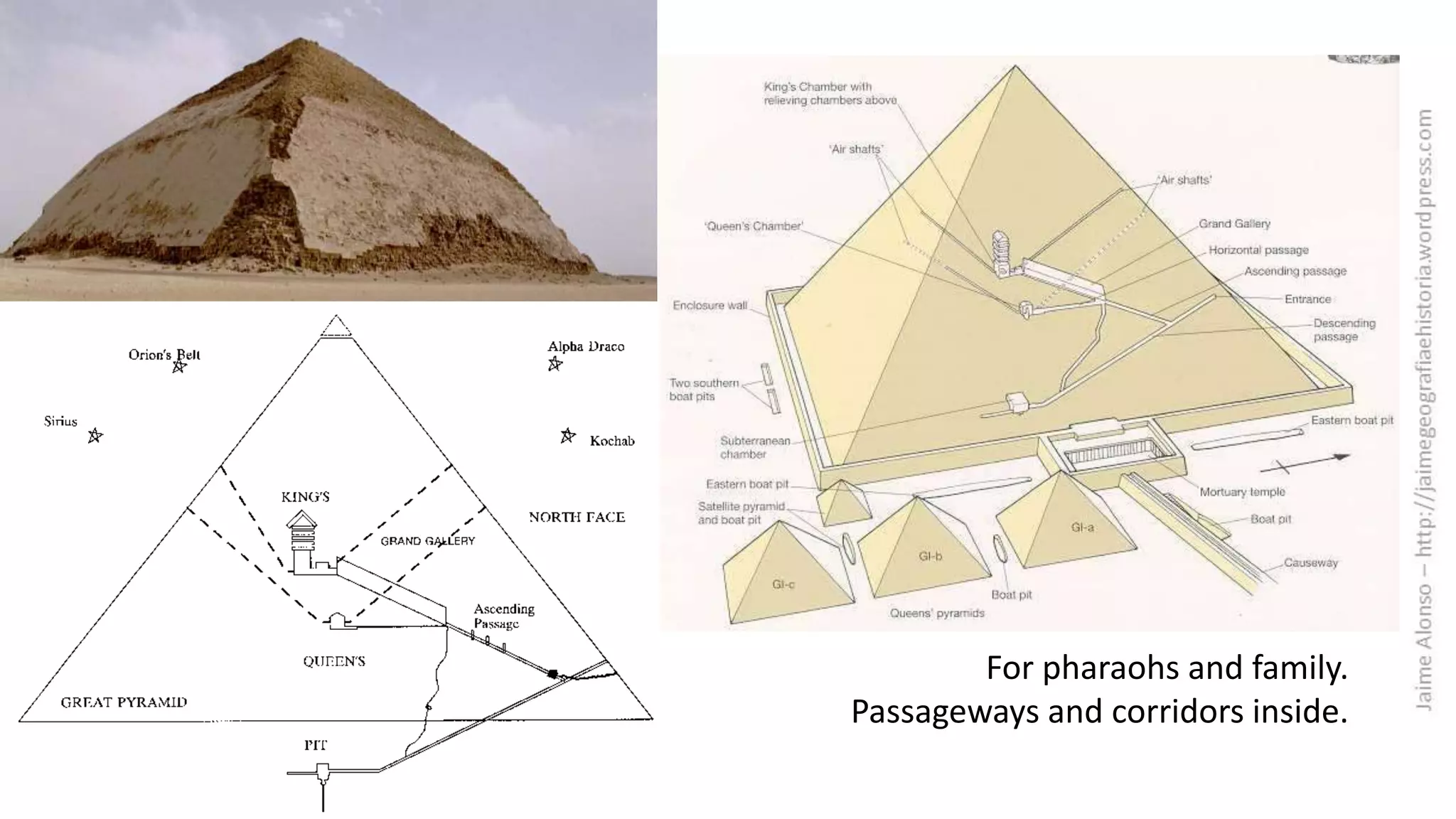

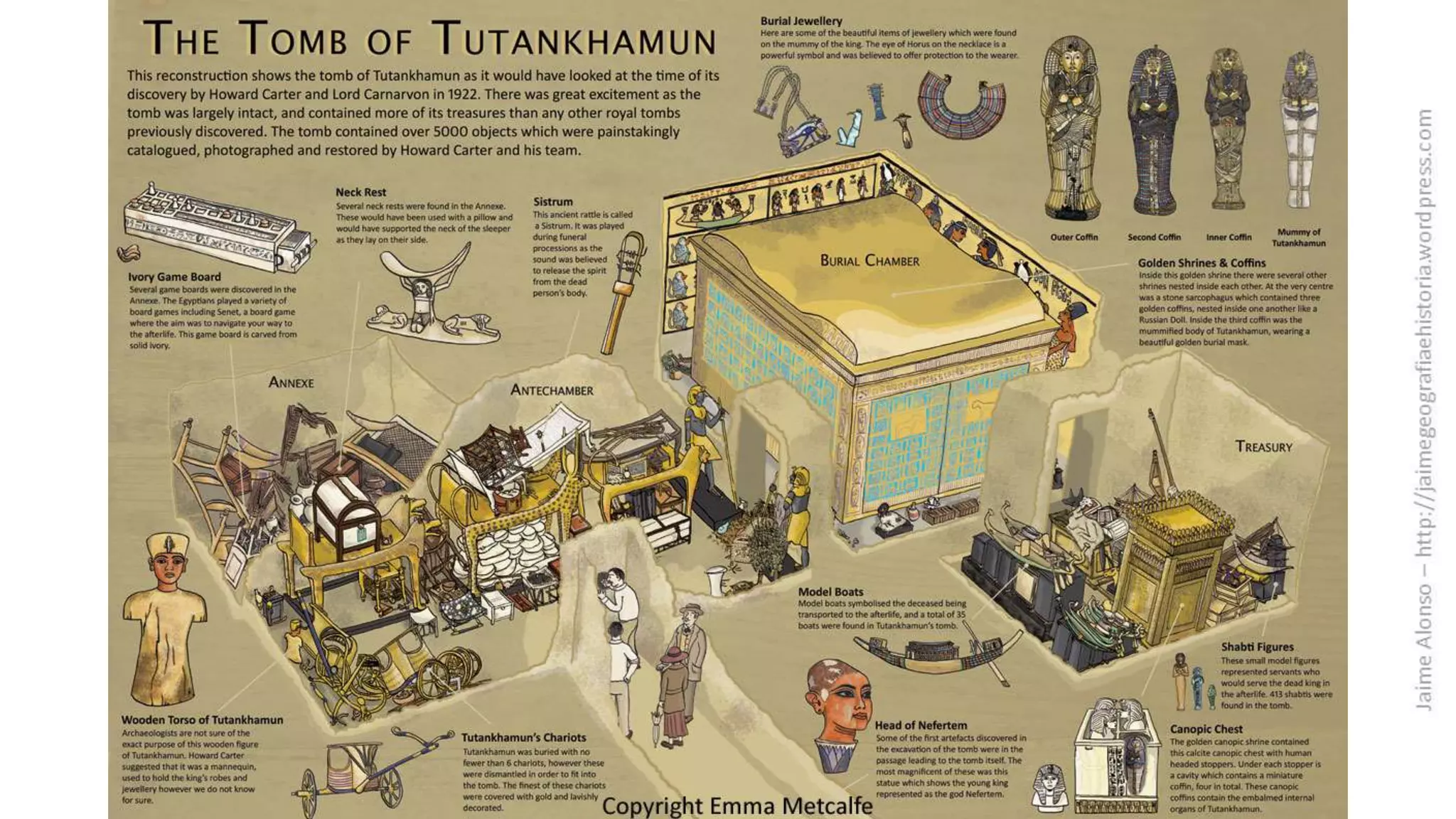





Egyptian architecture was made of stone and consisted of columns and flat roofs. The main types were tombs and temples. Temples were dedicated to gods such as those at Luxor and Karnak, while tombs evolved over time from mastabas to pyramids like those at Giza. Sculptures depicted pharaohs, gods and nobles in a rigid, frontal style with attached arms and expressionless faces. Paintings decorated temples and tombs with religious and hierarchical scenes in an idealized, frontal perspective.



















