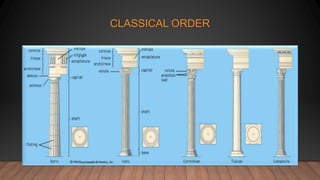
There are five classical orders of architecture - Doric, Ionic, Corinthian, Tuscan, and Composite. Each order has a distinct column design and entablature above. The Greek orders are Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian. Doric has a simple capital without decoration. Ionic has volutes on the capital. Corinthian has acanthus leaves and small volutes. The Romans adapted these and added Tuscan, with smooth columns, and Composite, combining elements of Ionic and Corinthian.