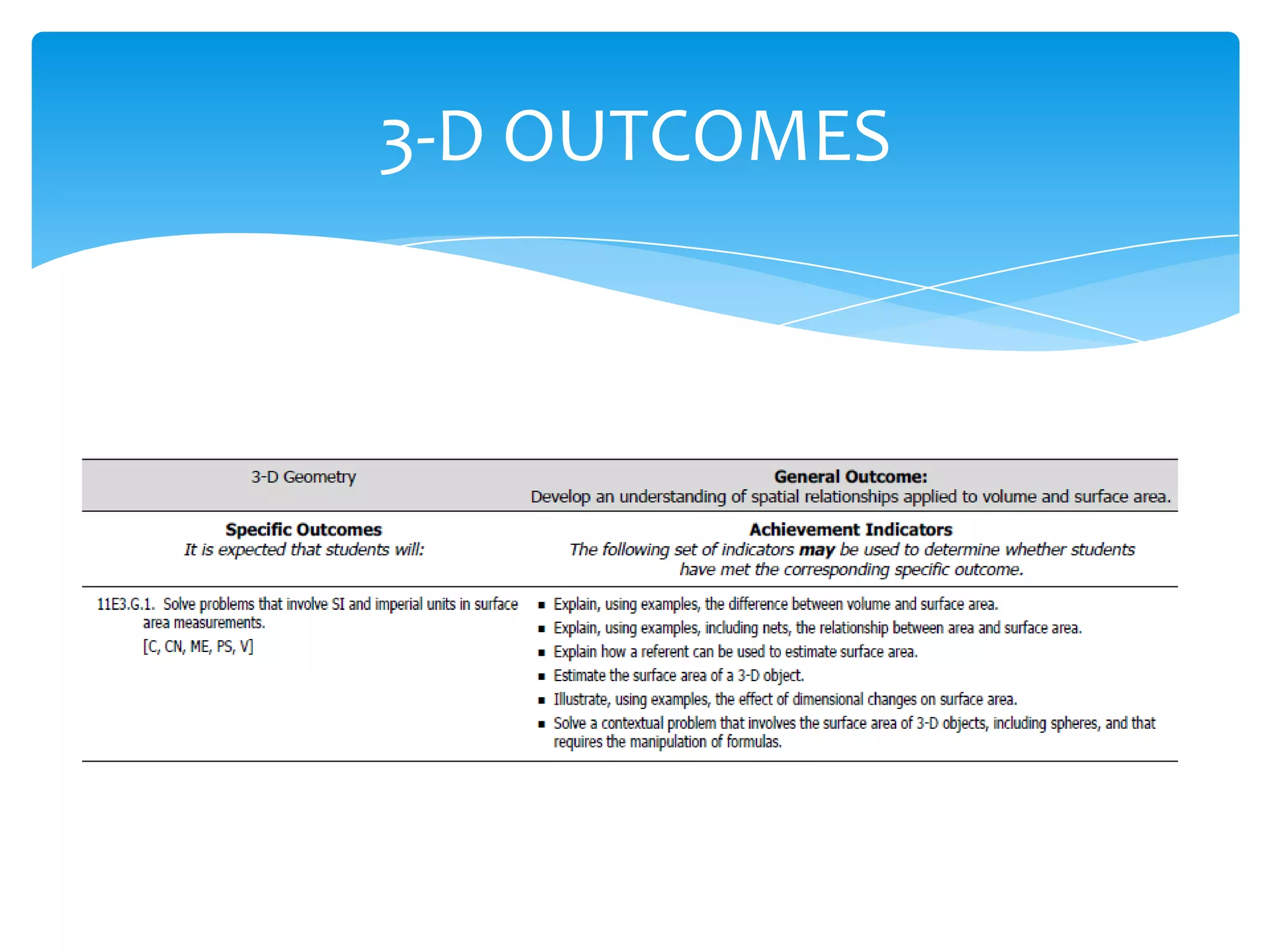
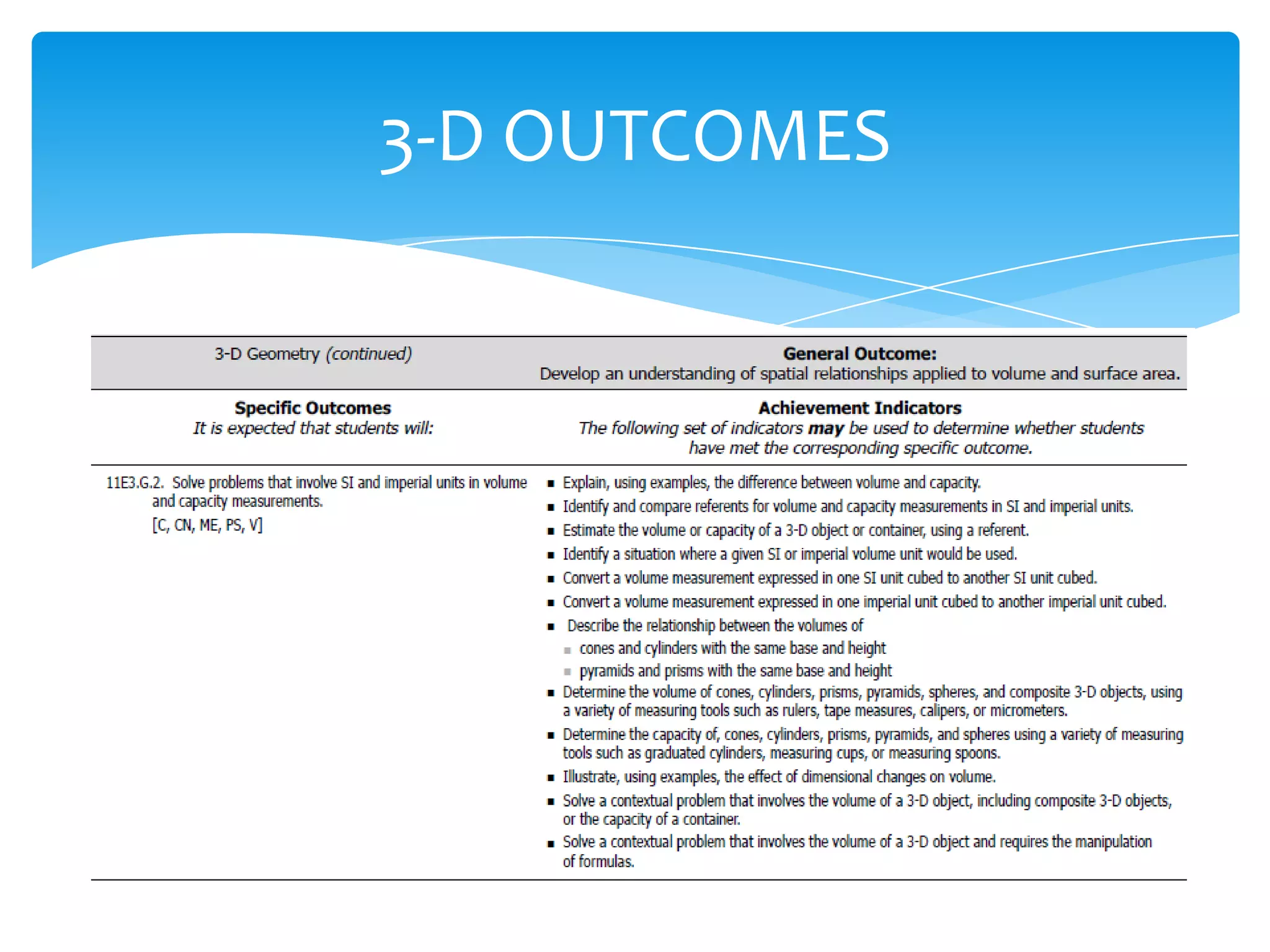
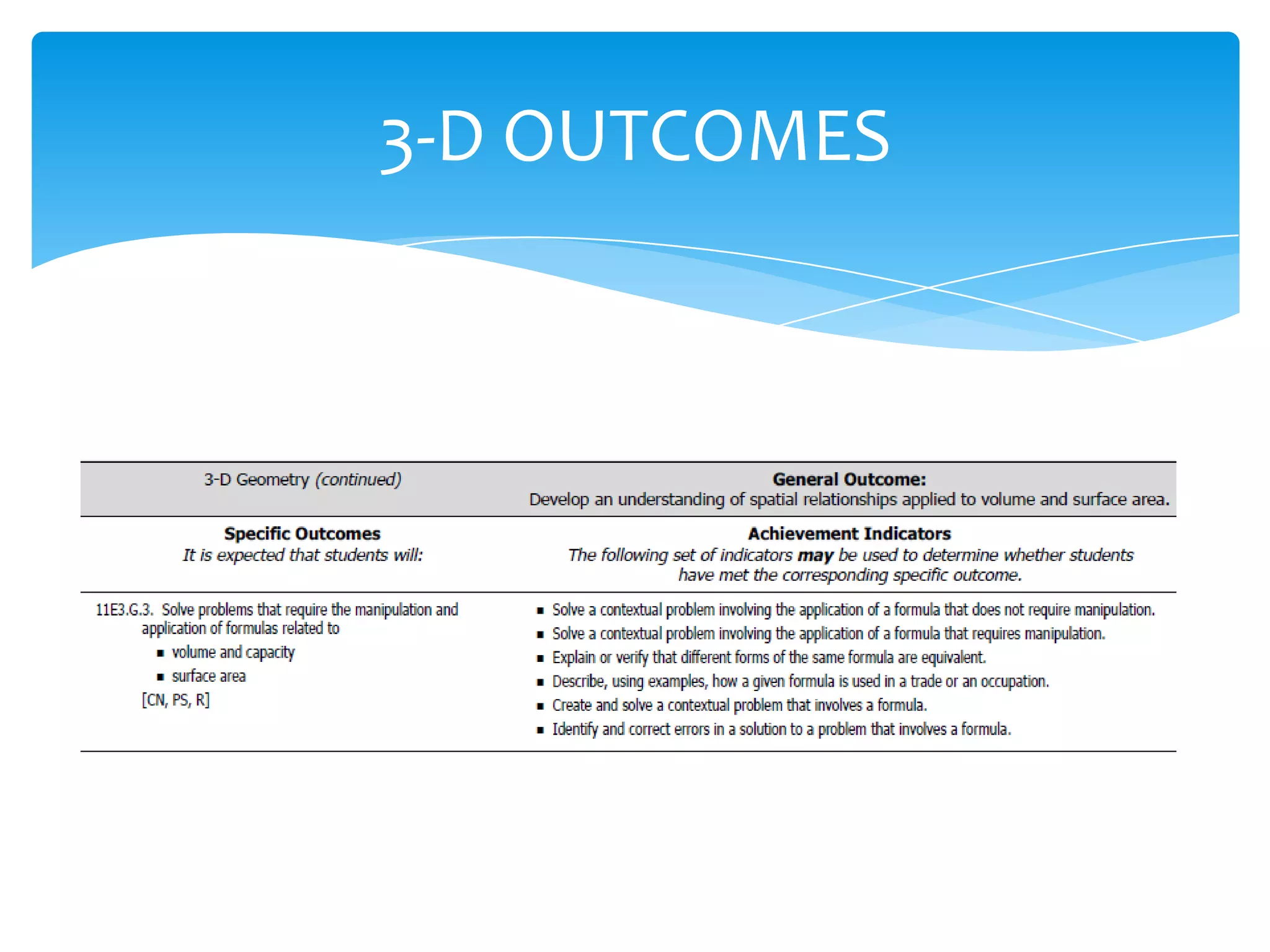
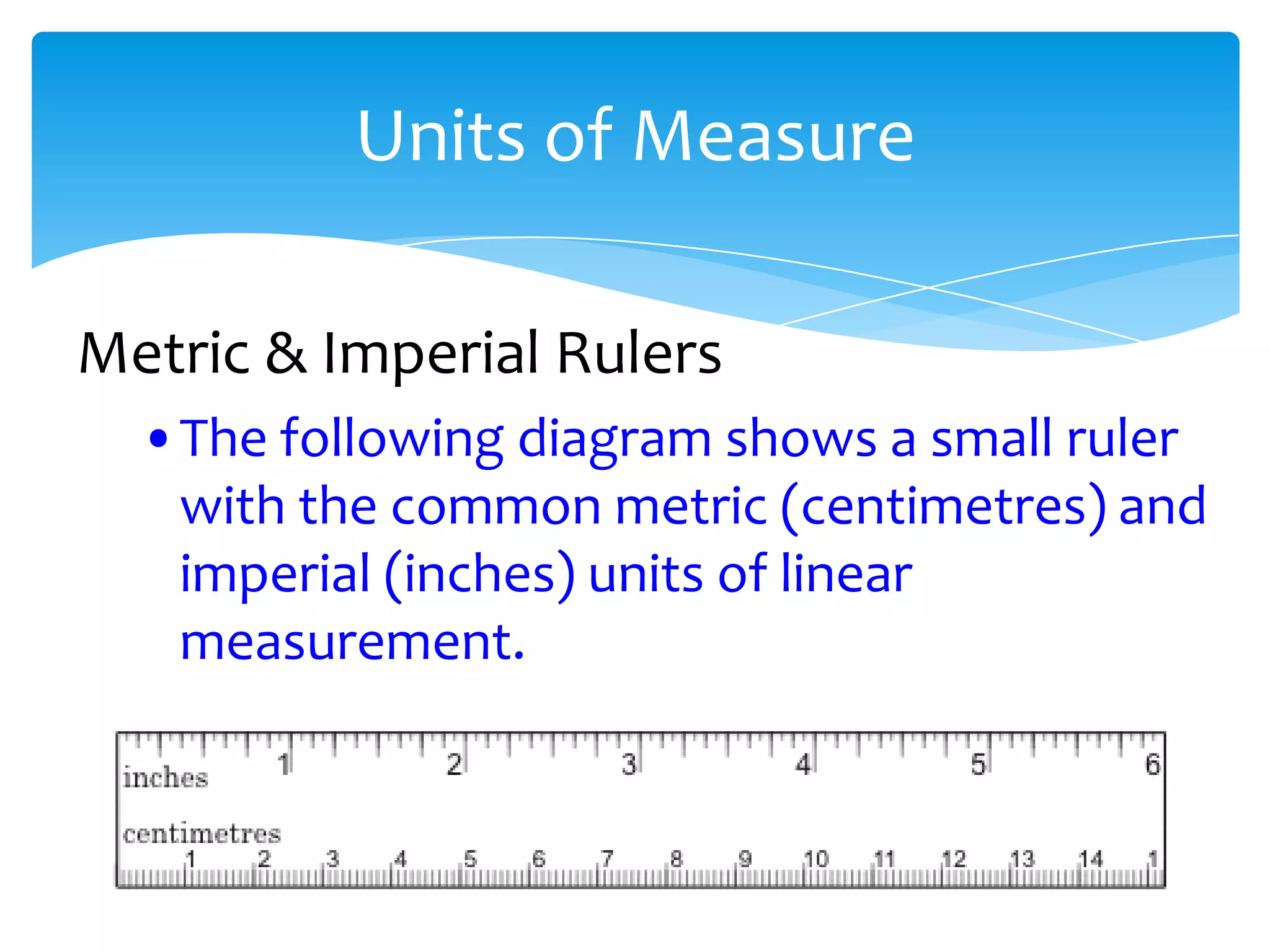
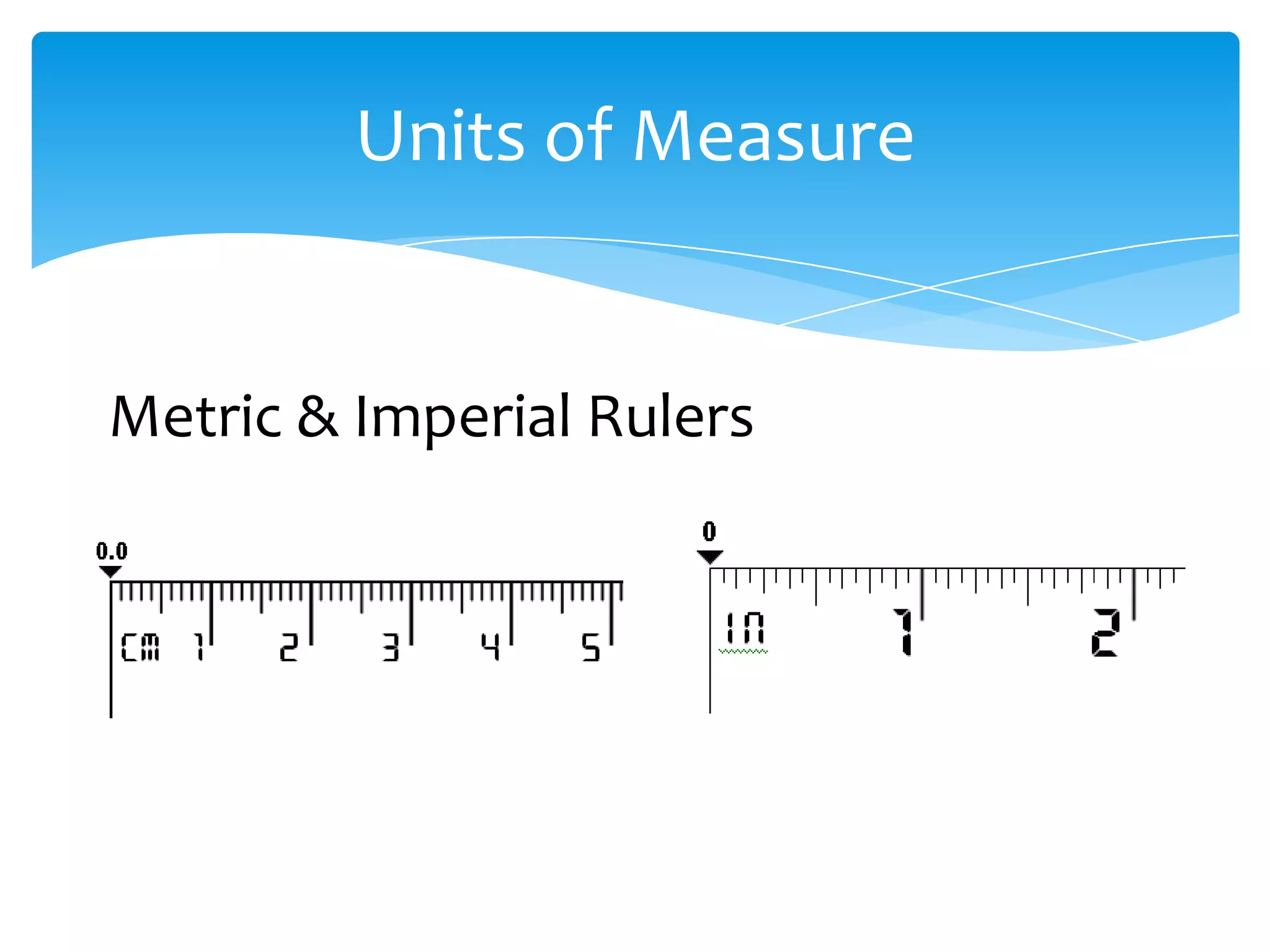
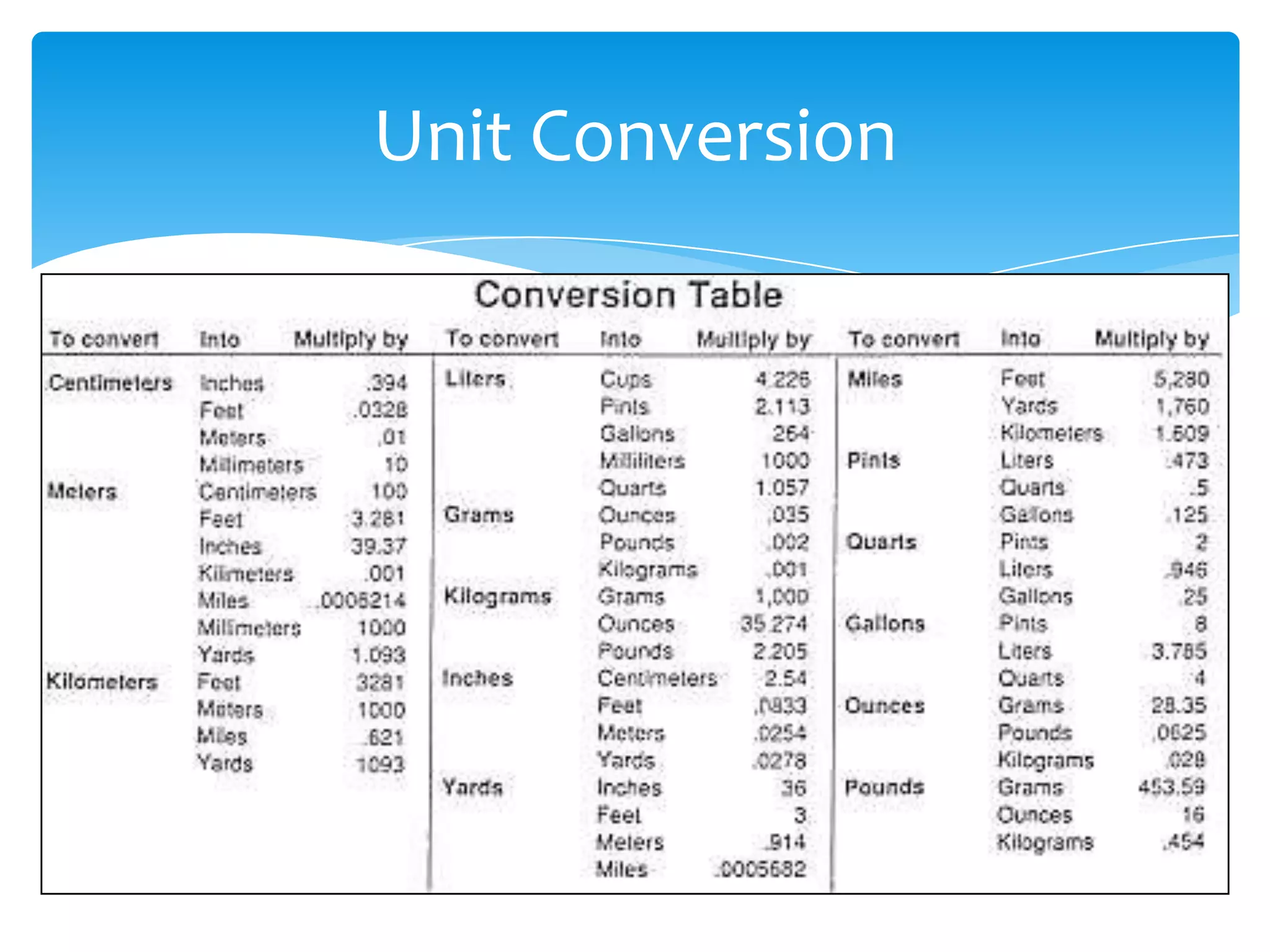
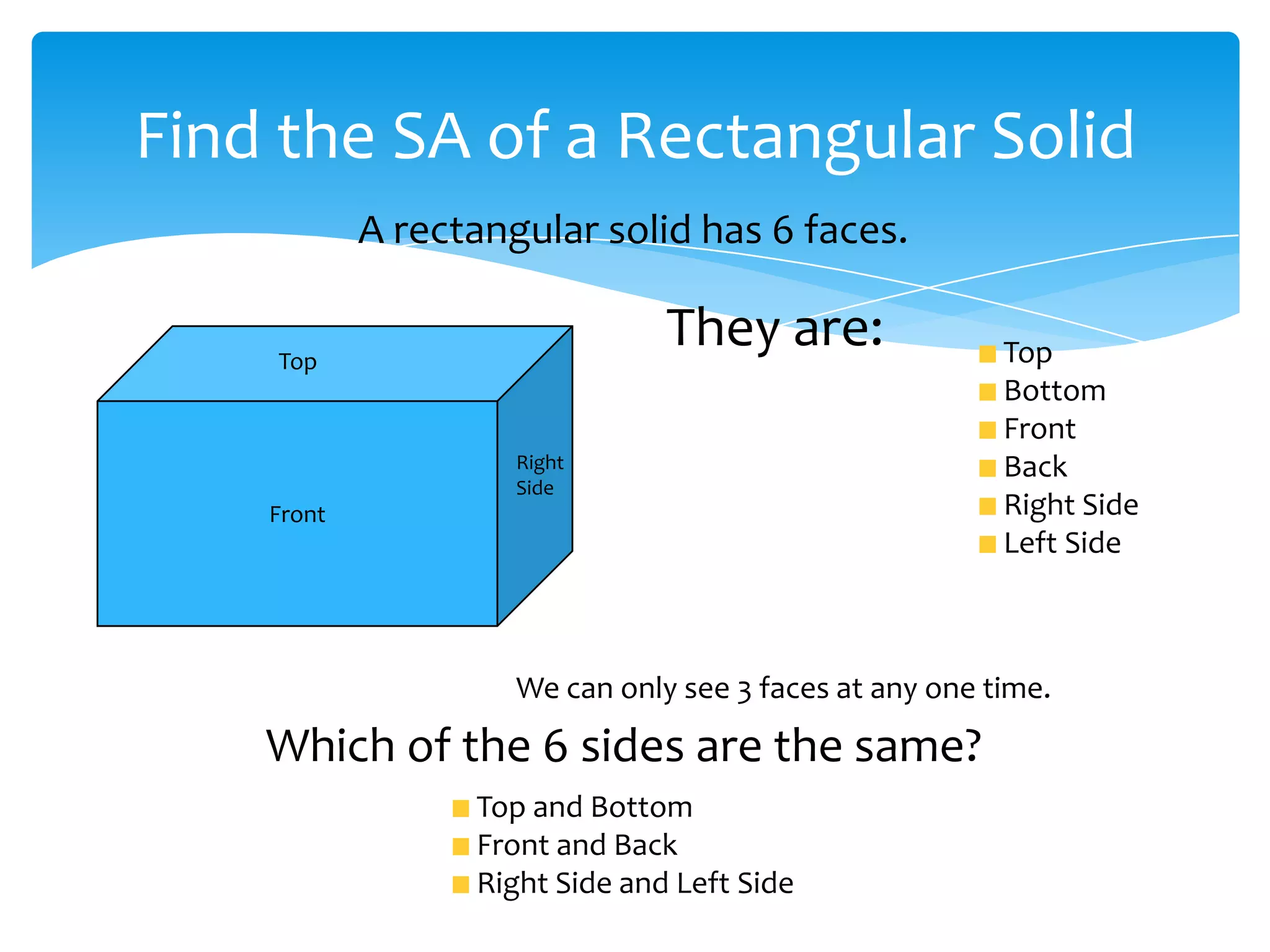
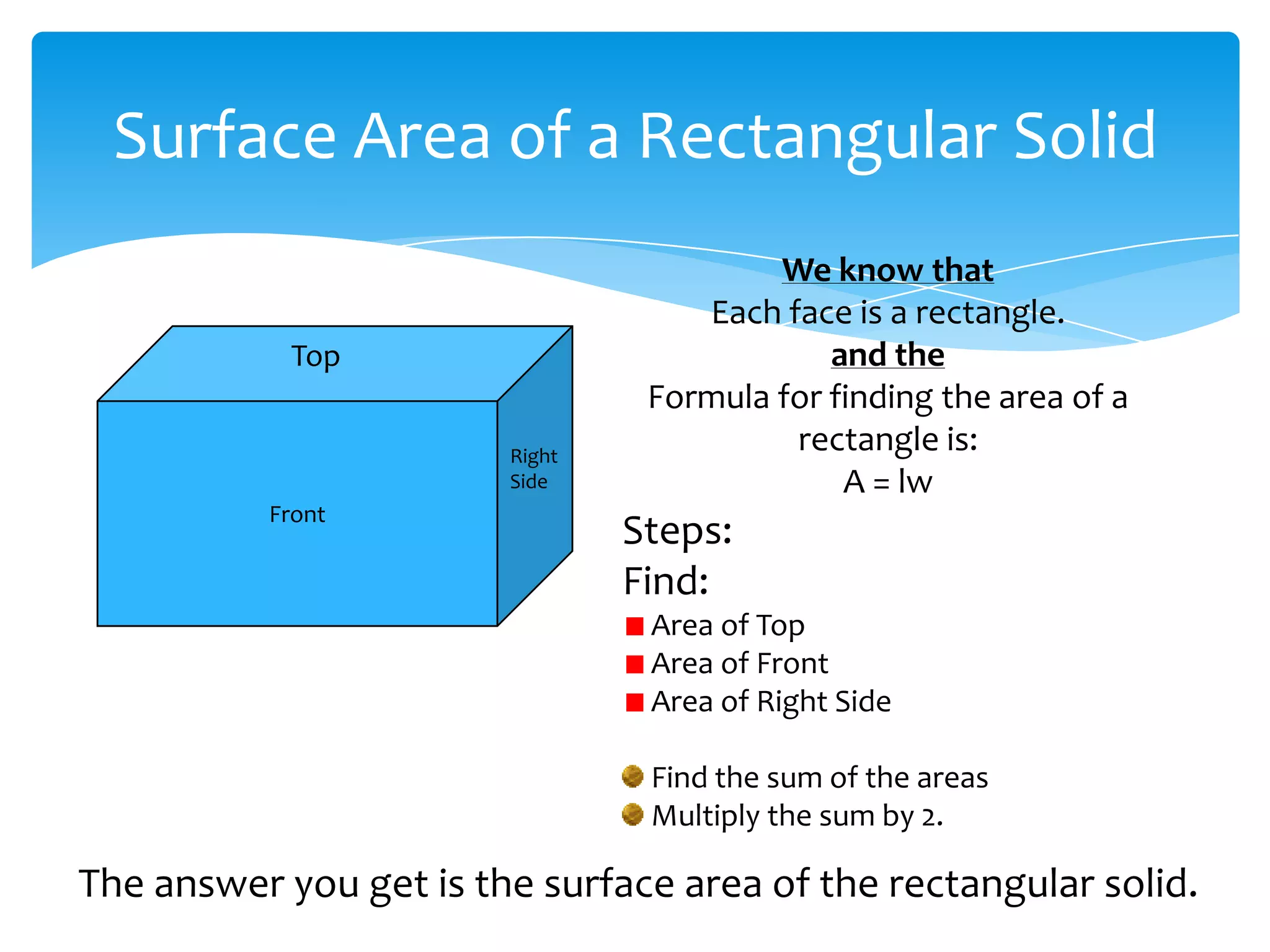
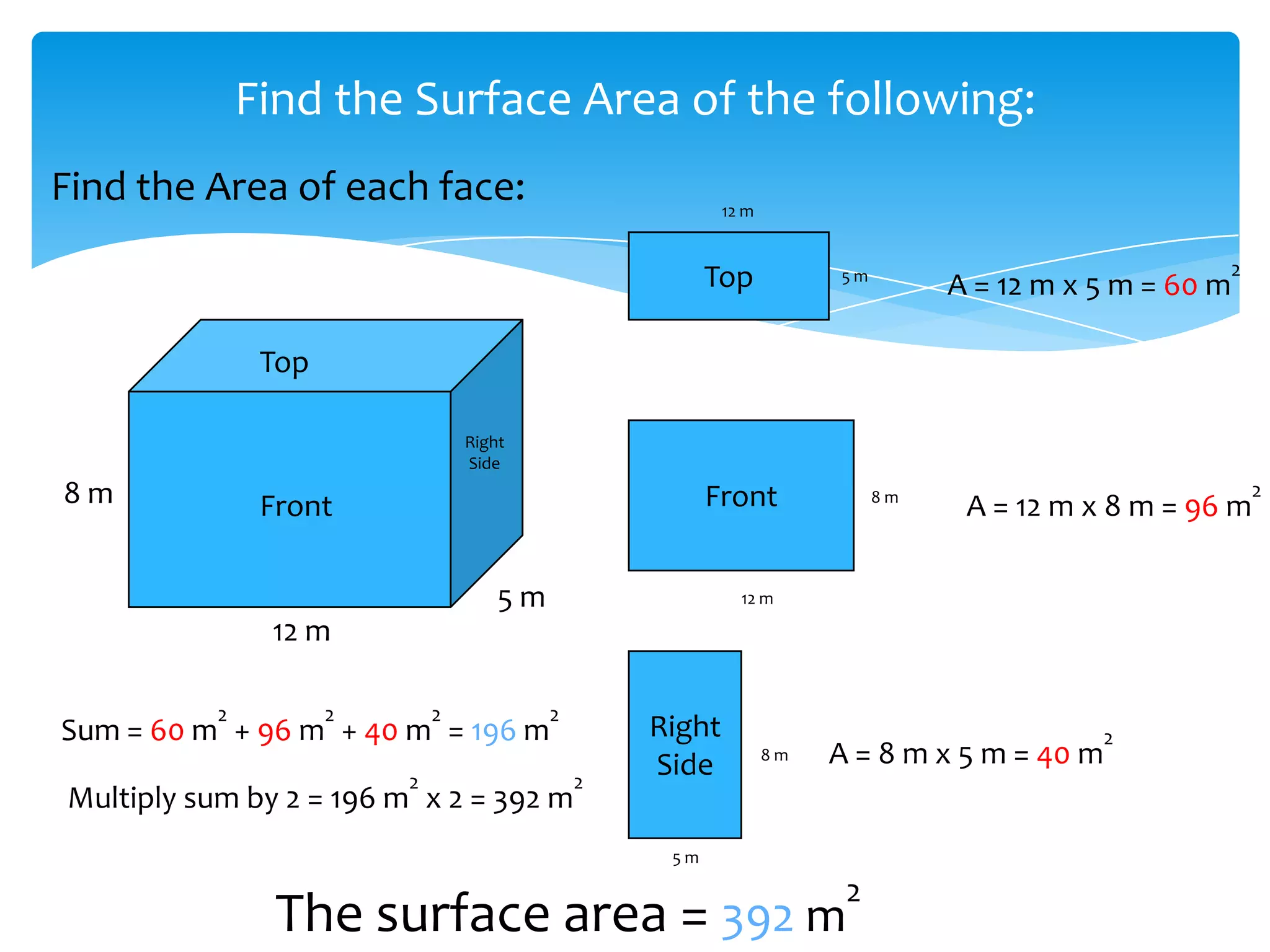
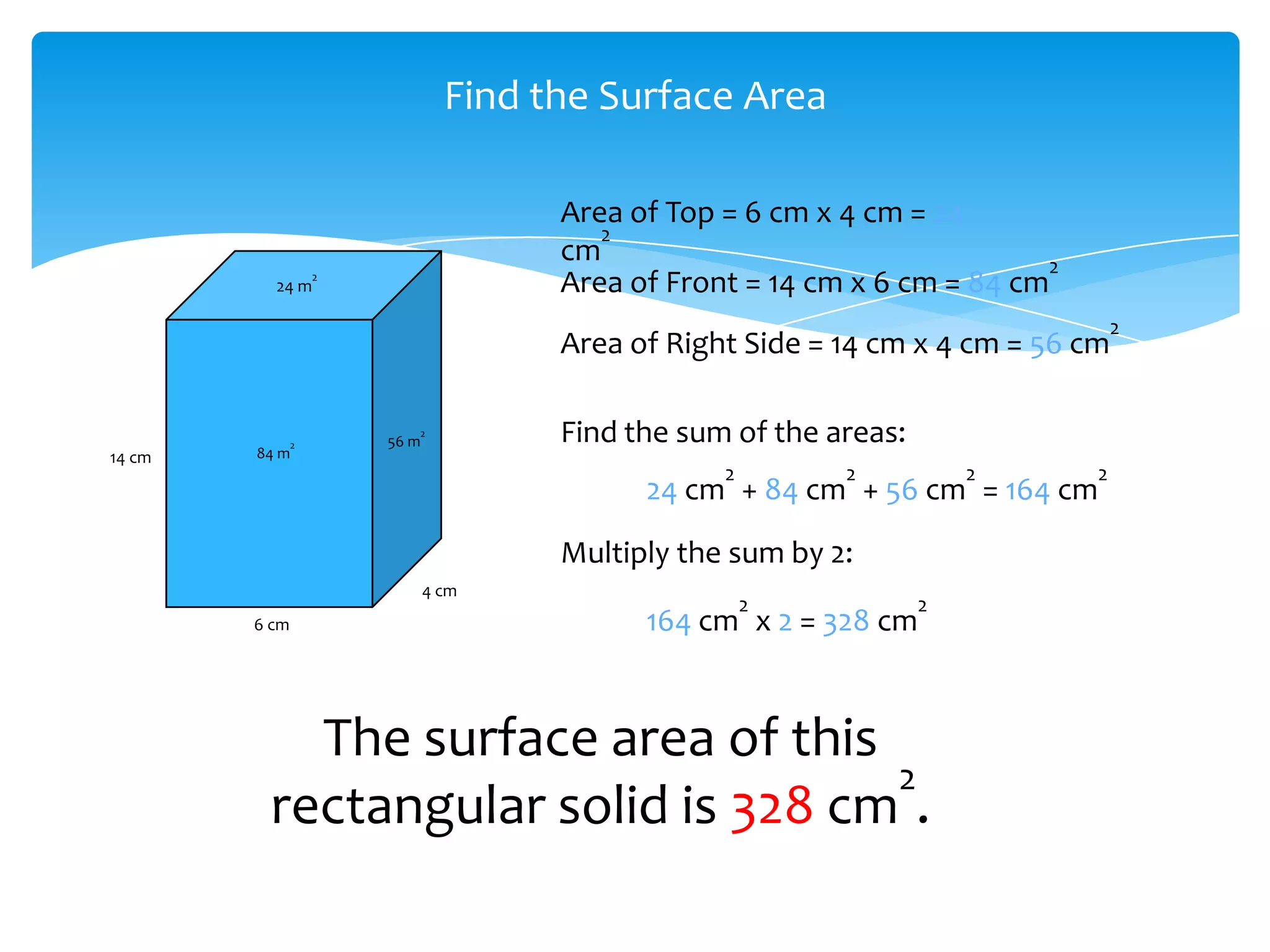
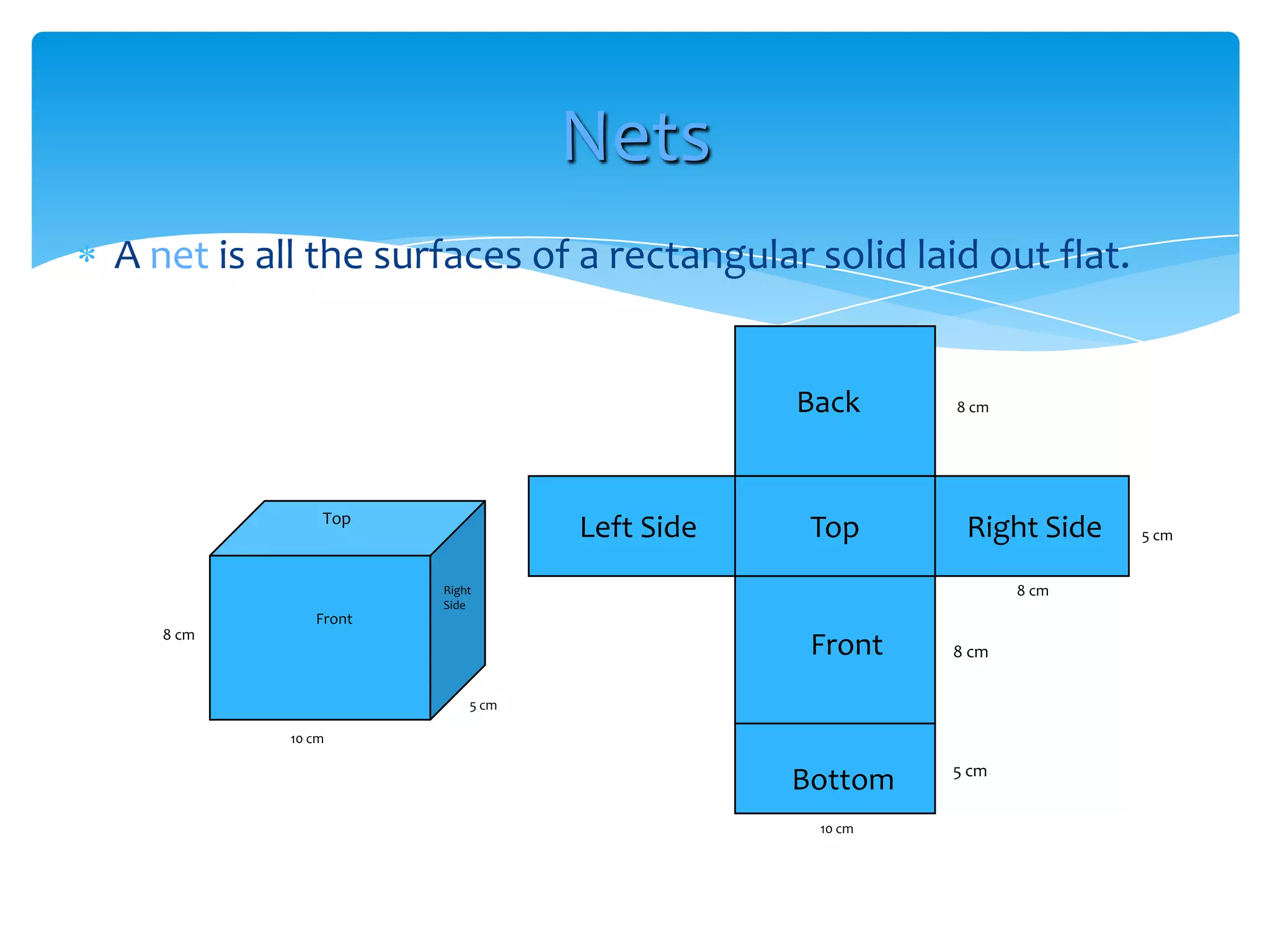
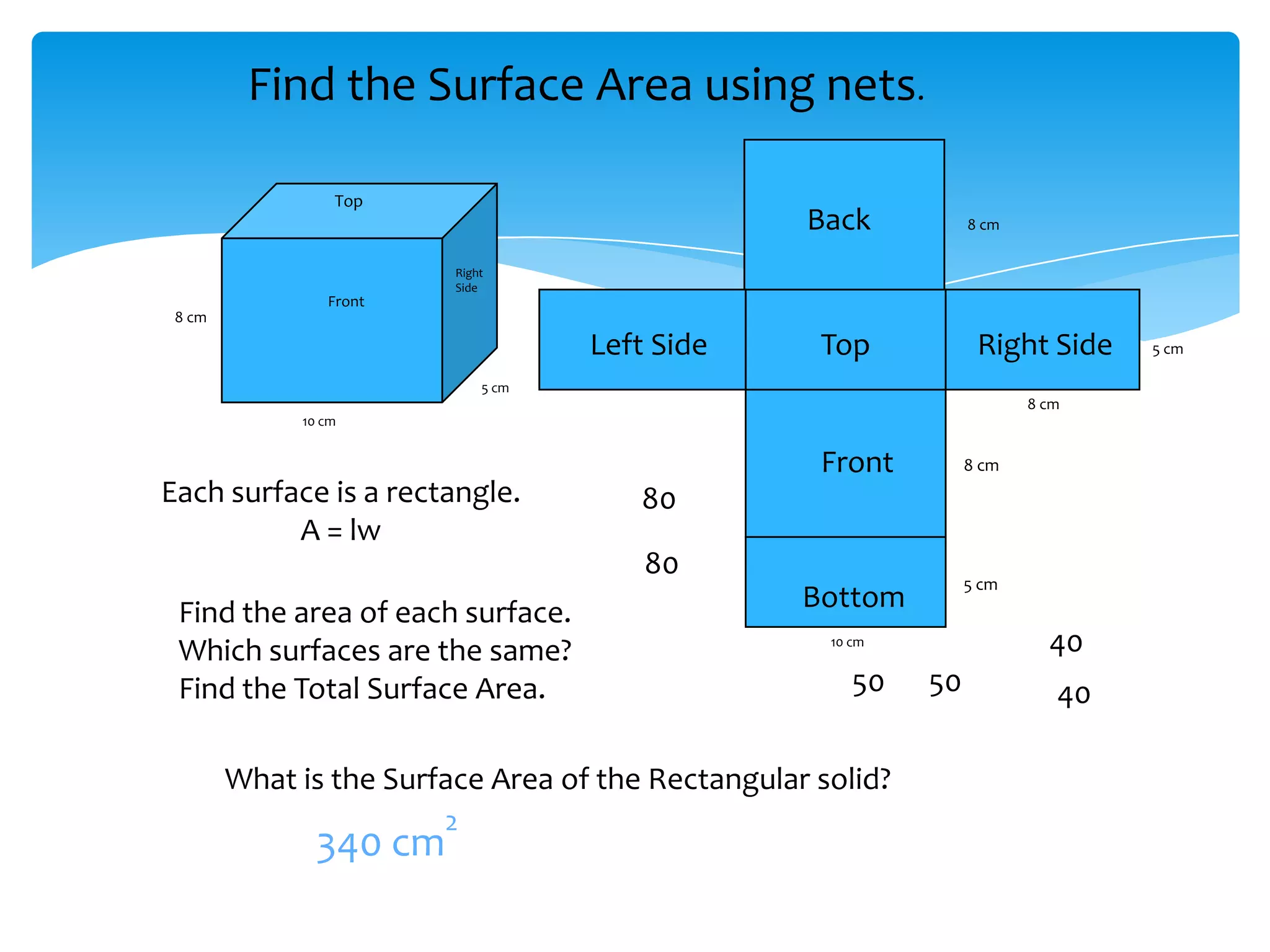
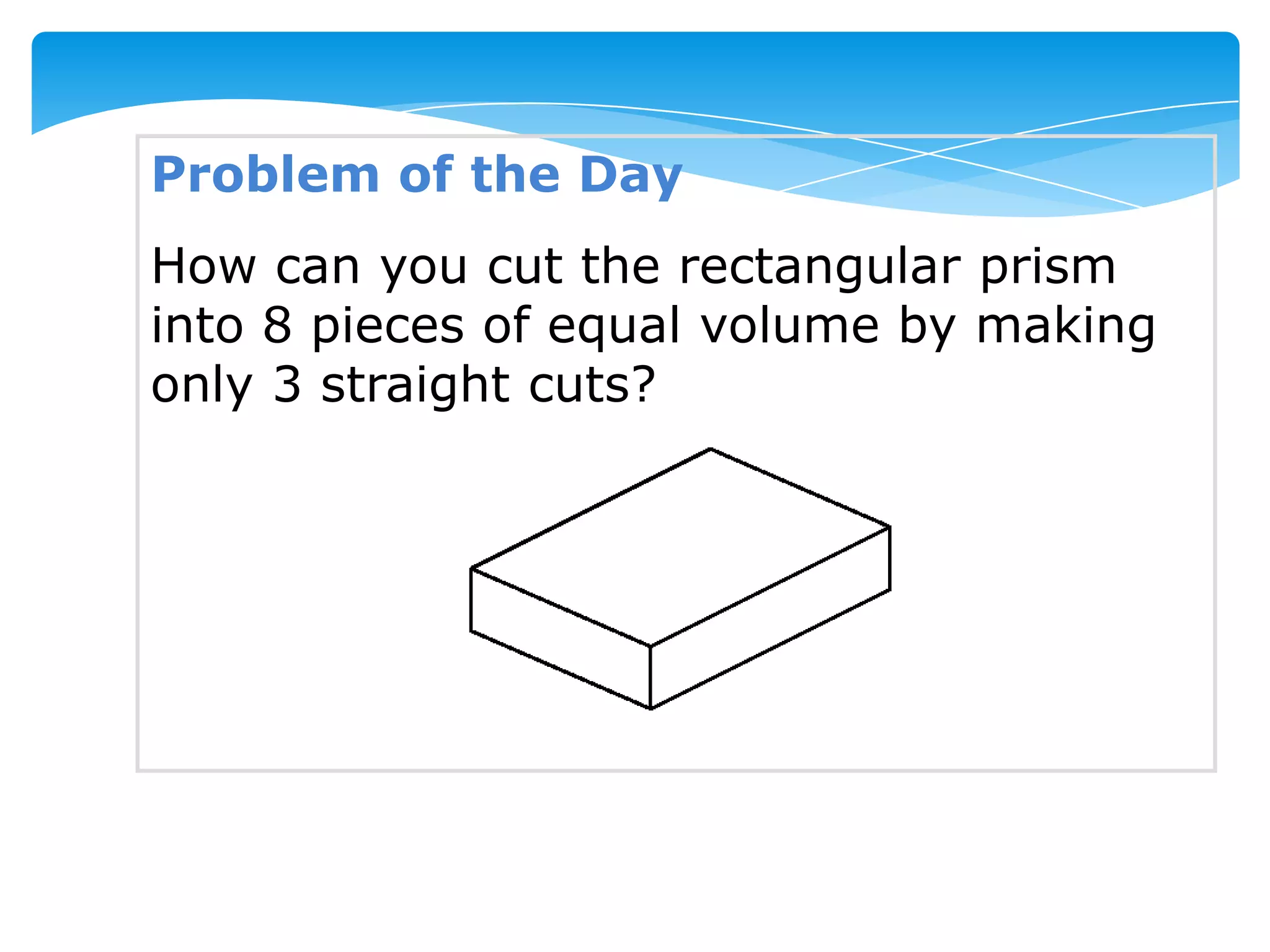
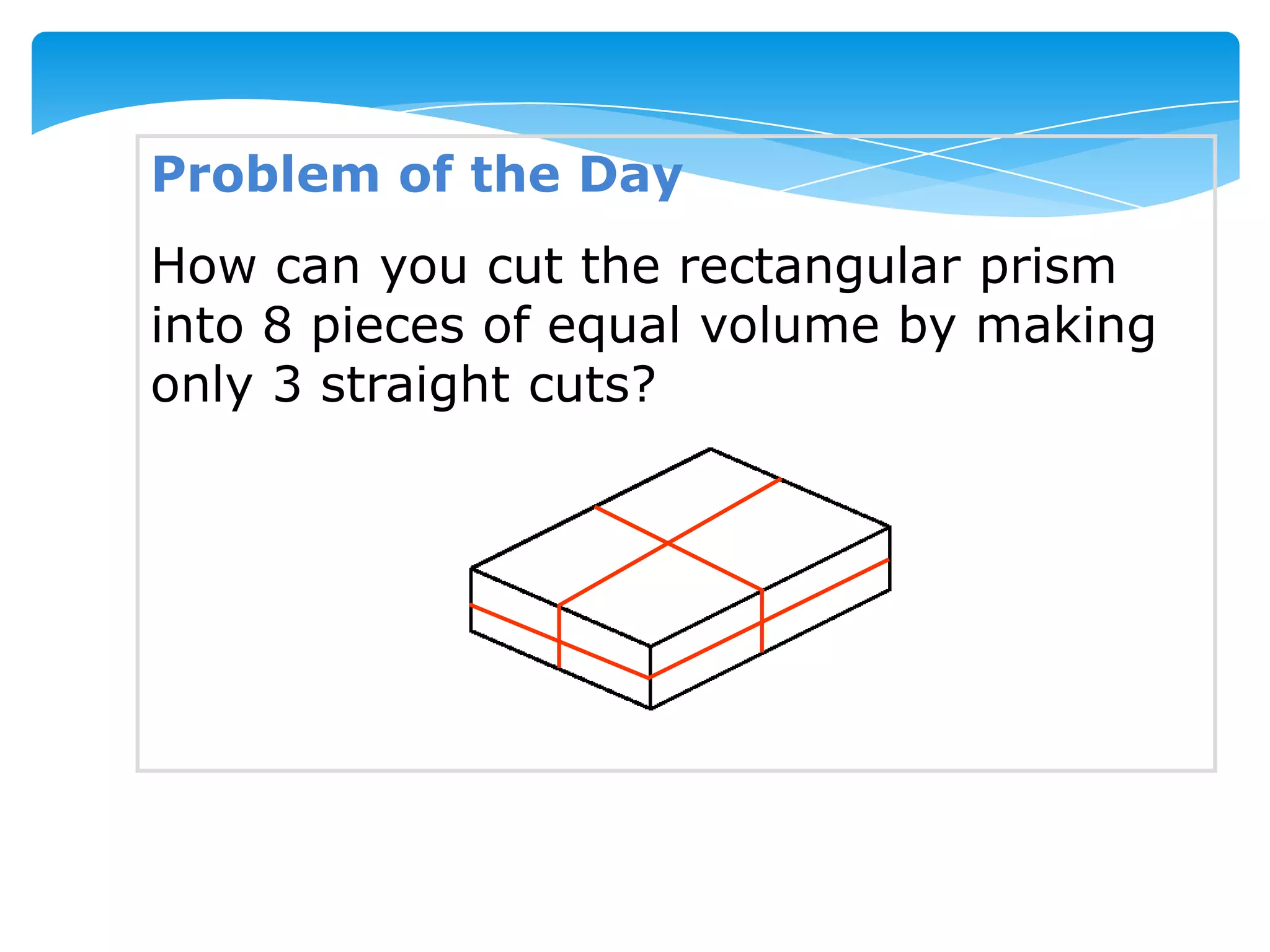
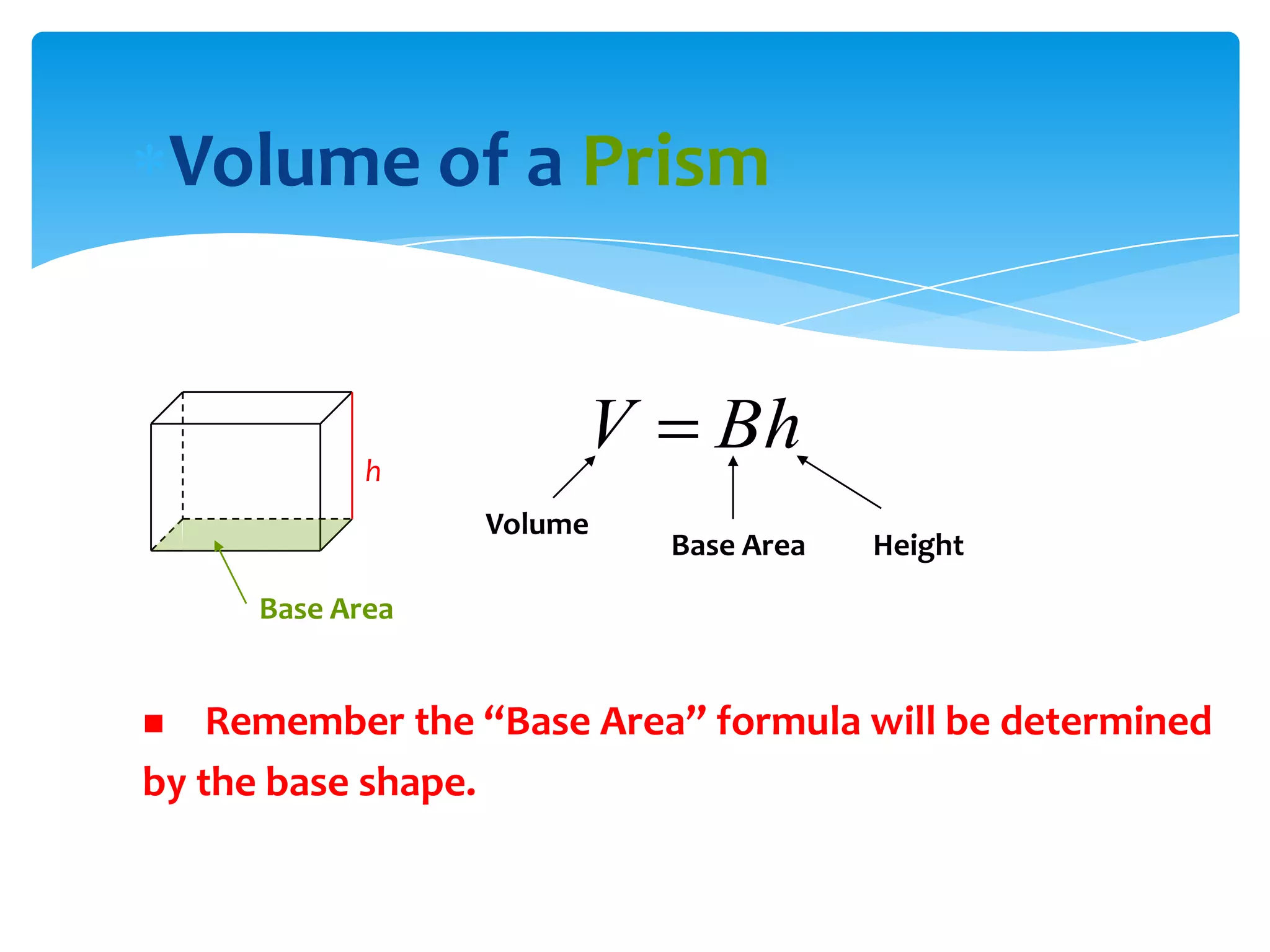
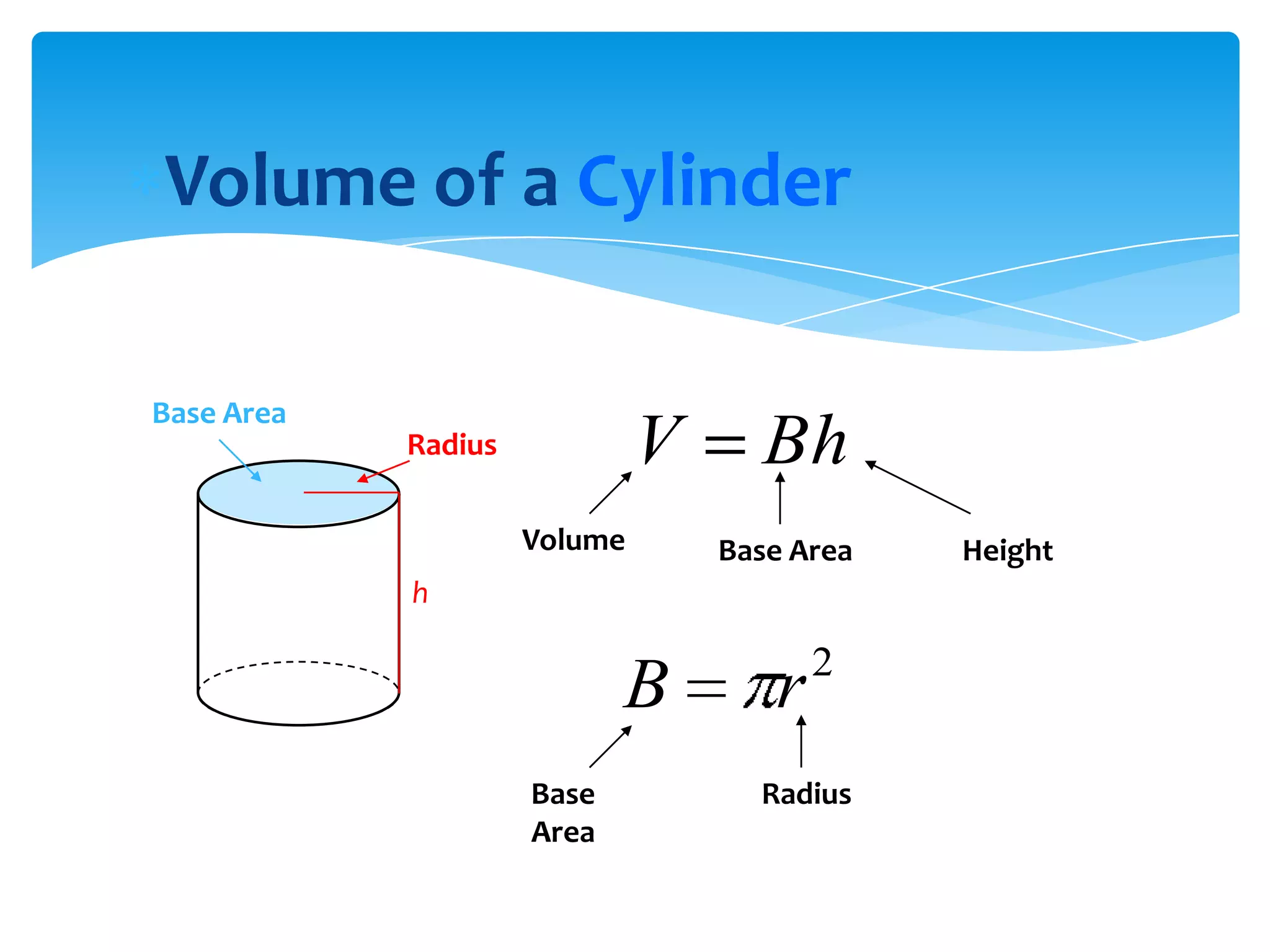
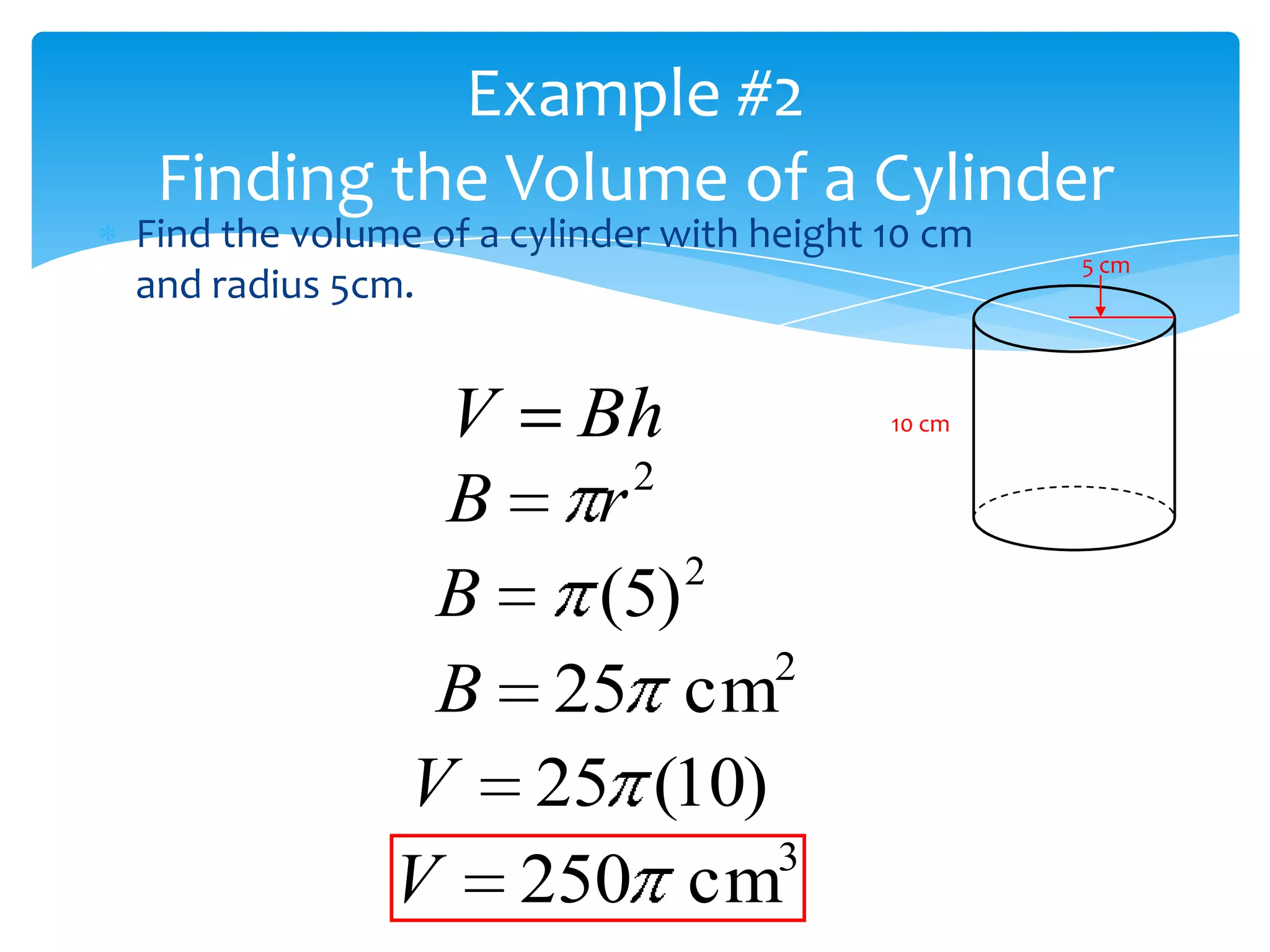
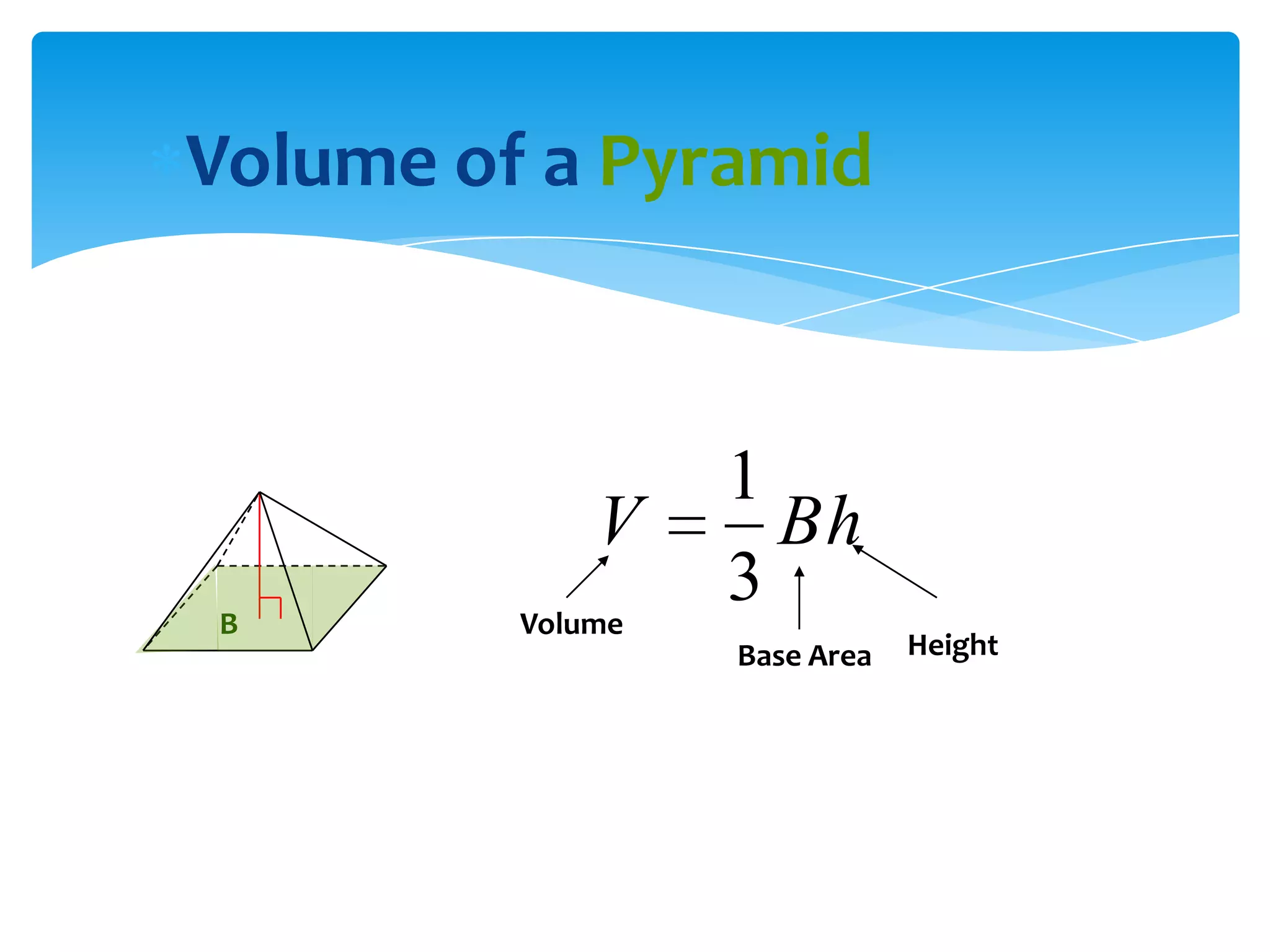
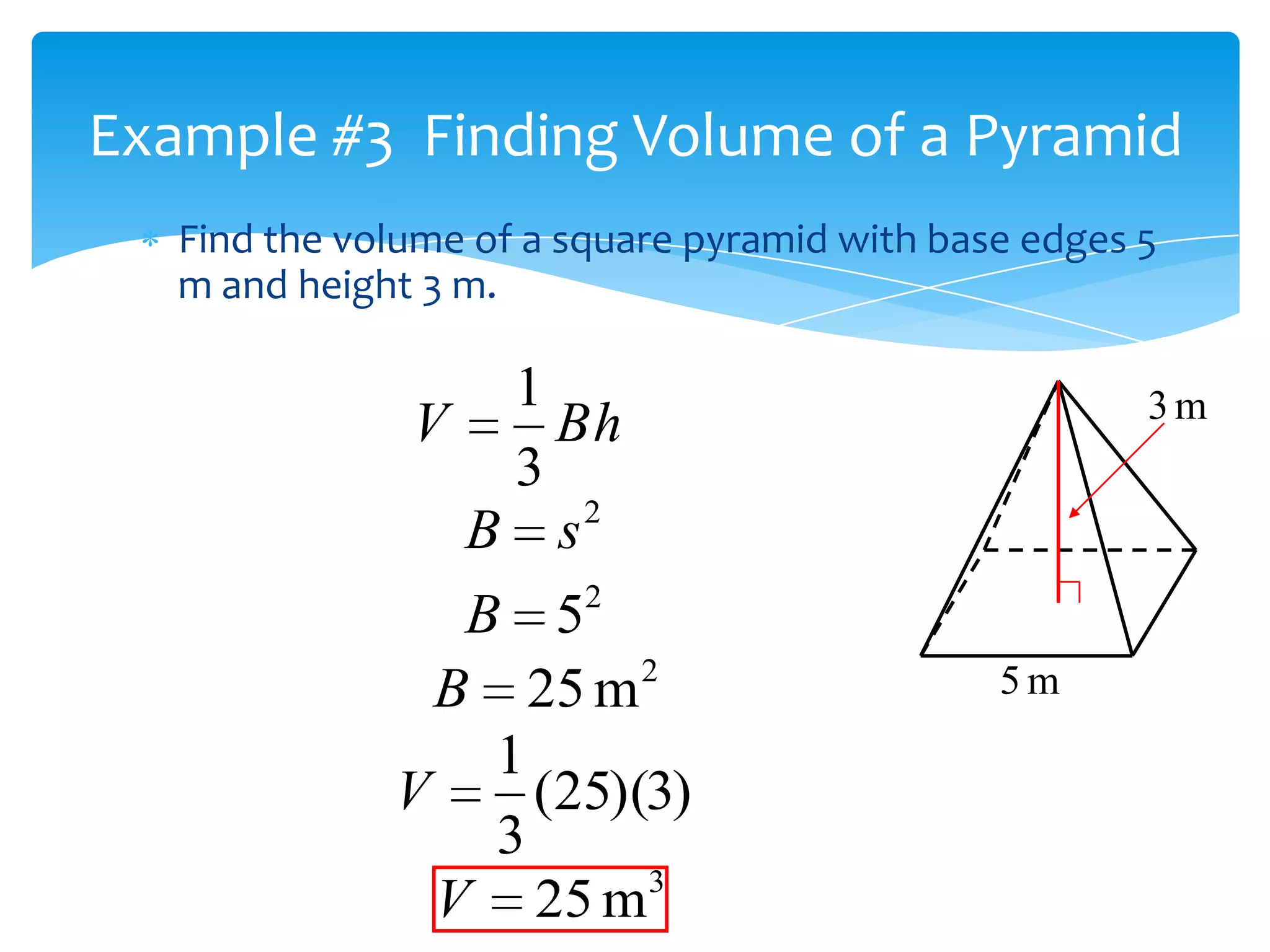
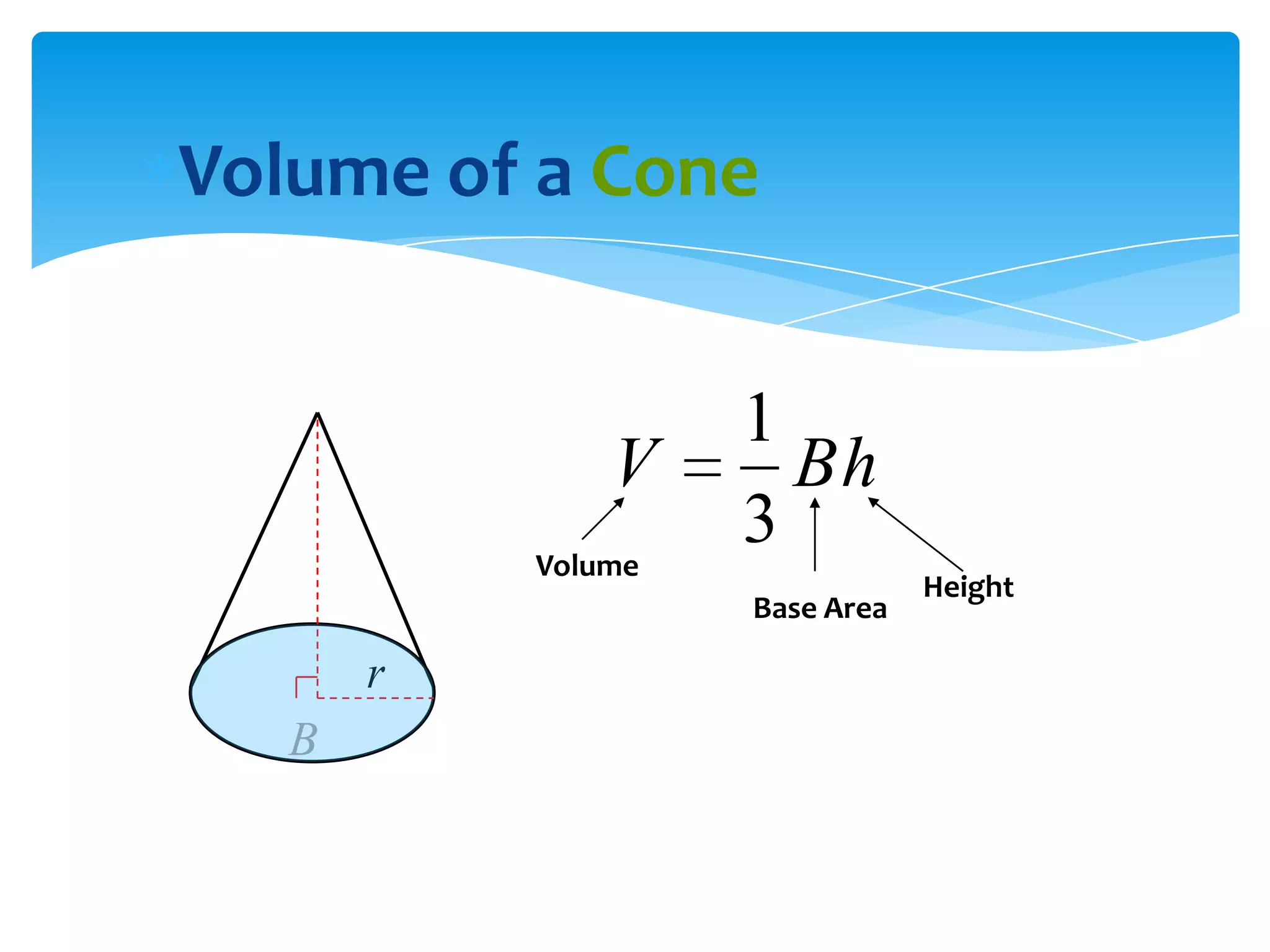
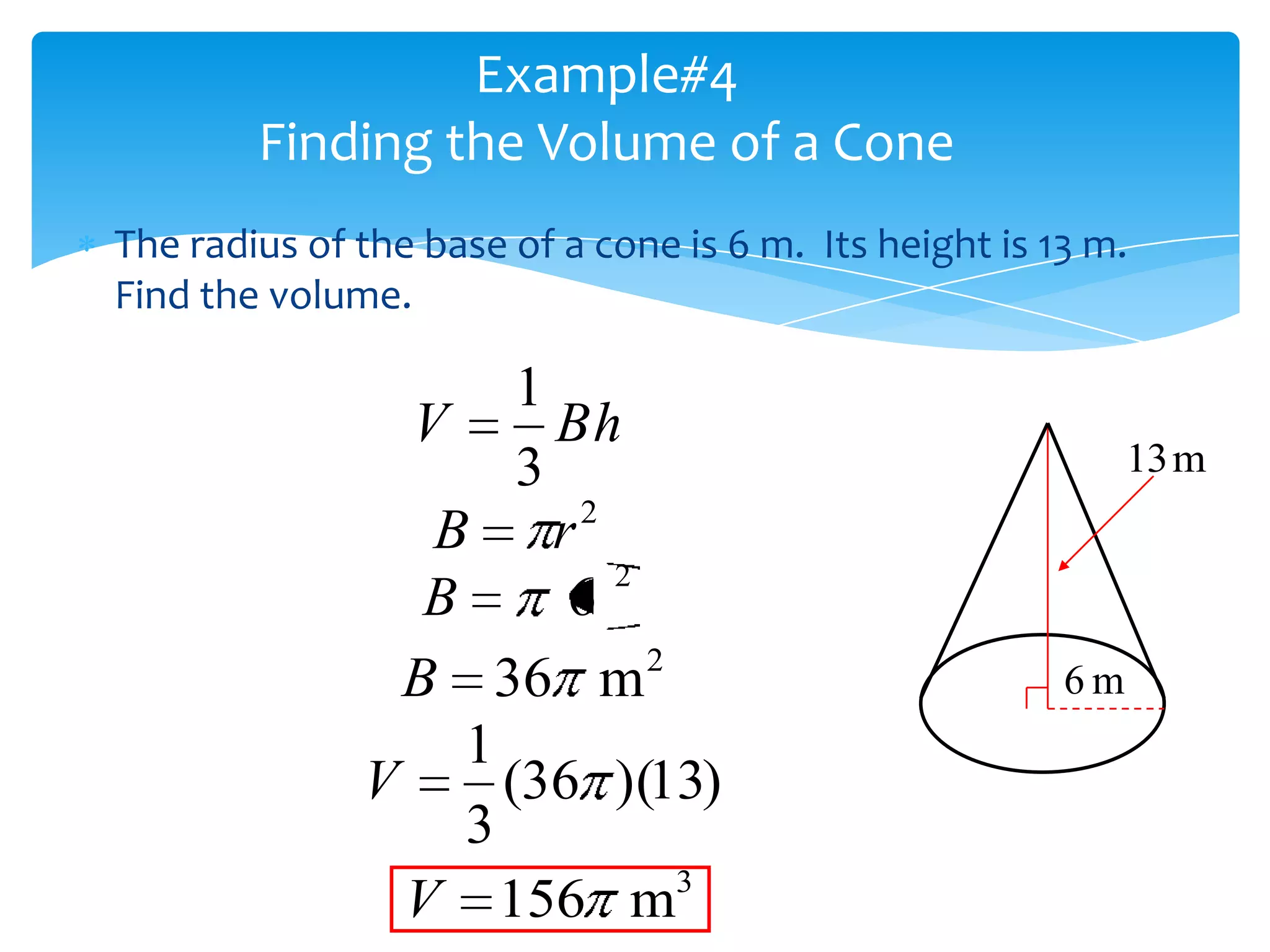
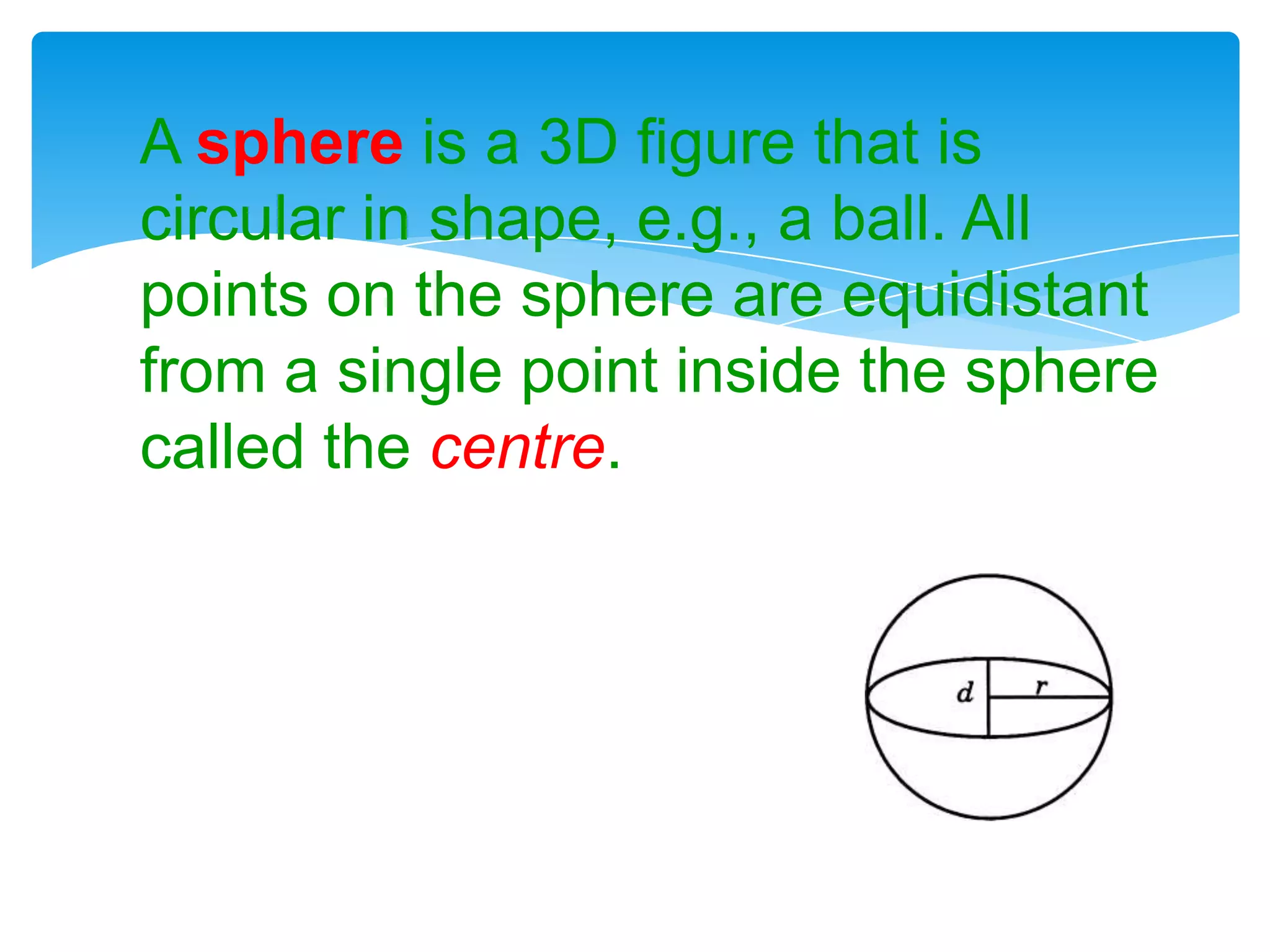
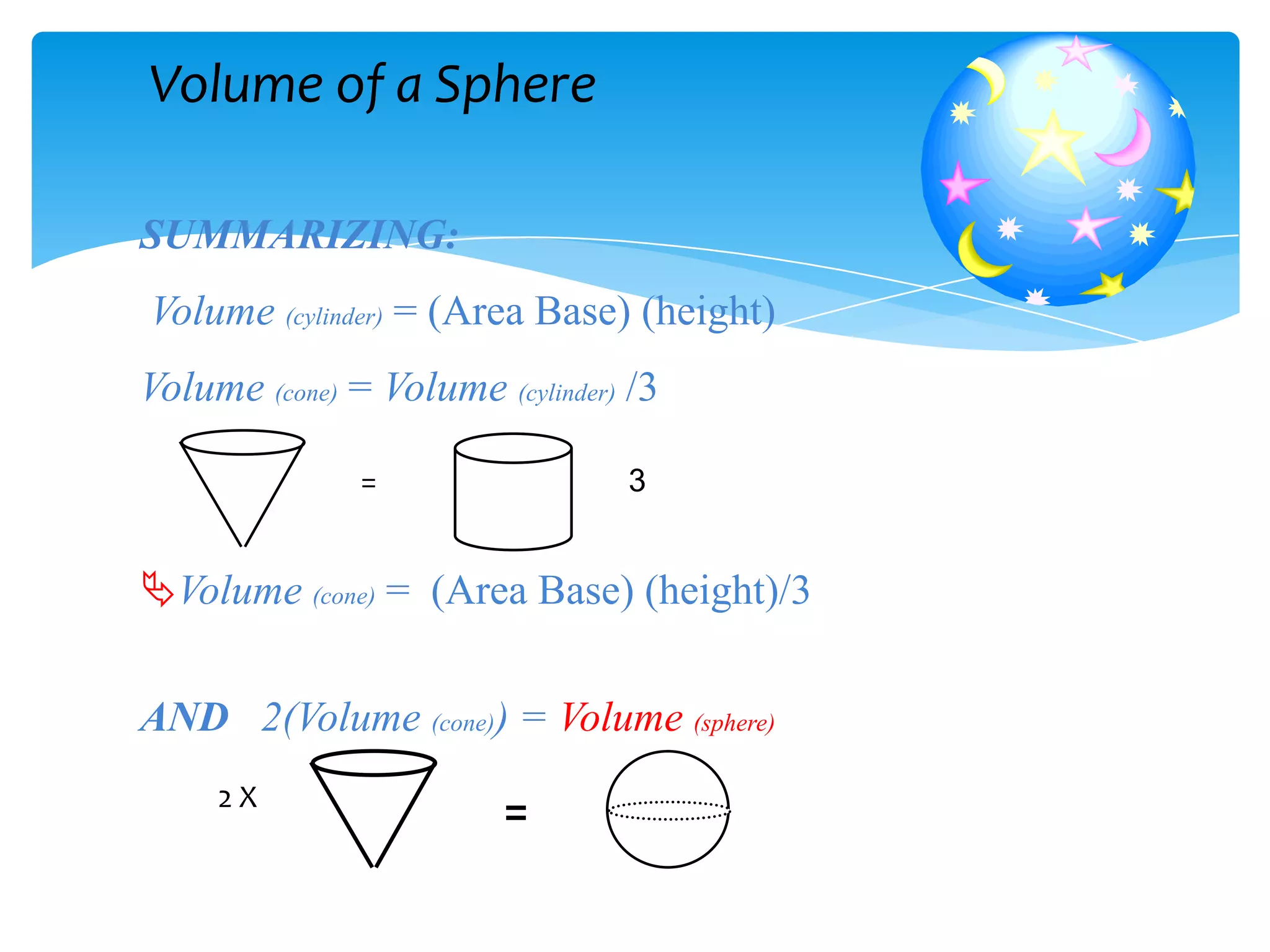
Okay, here are the steps:
Radius (r) = 12 cm
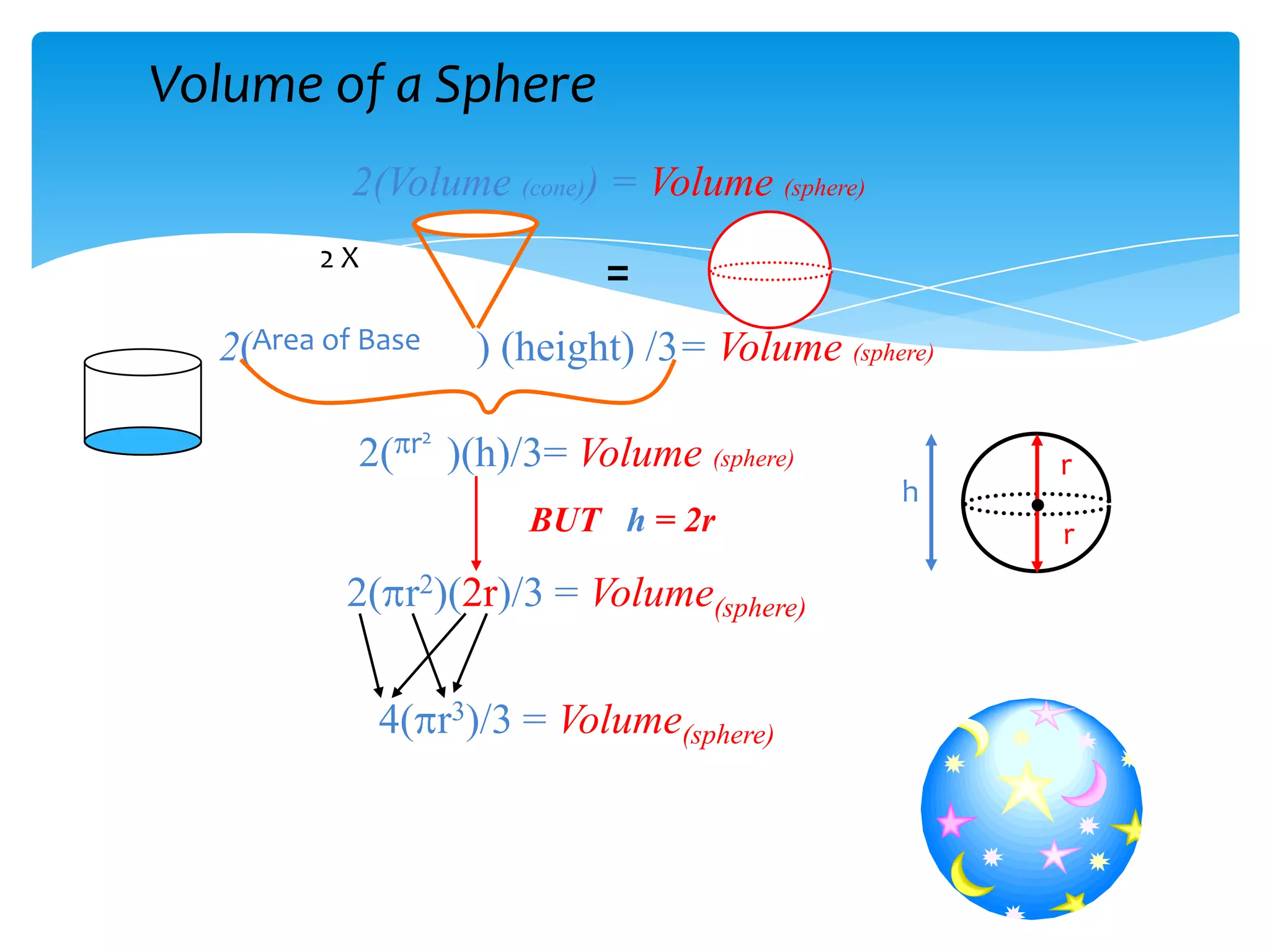
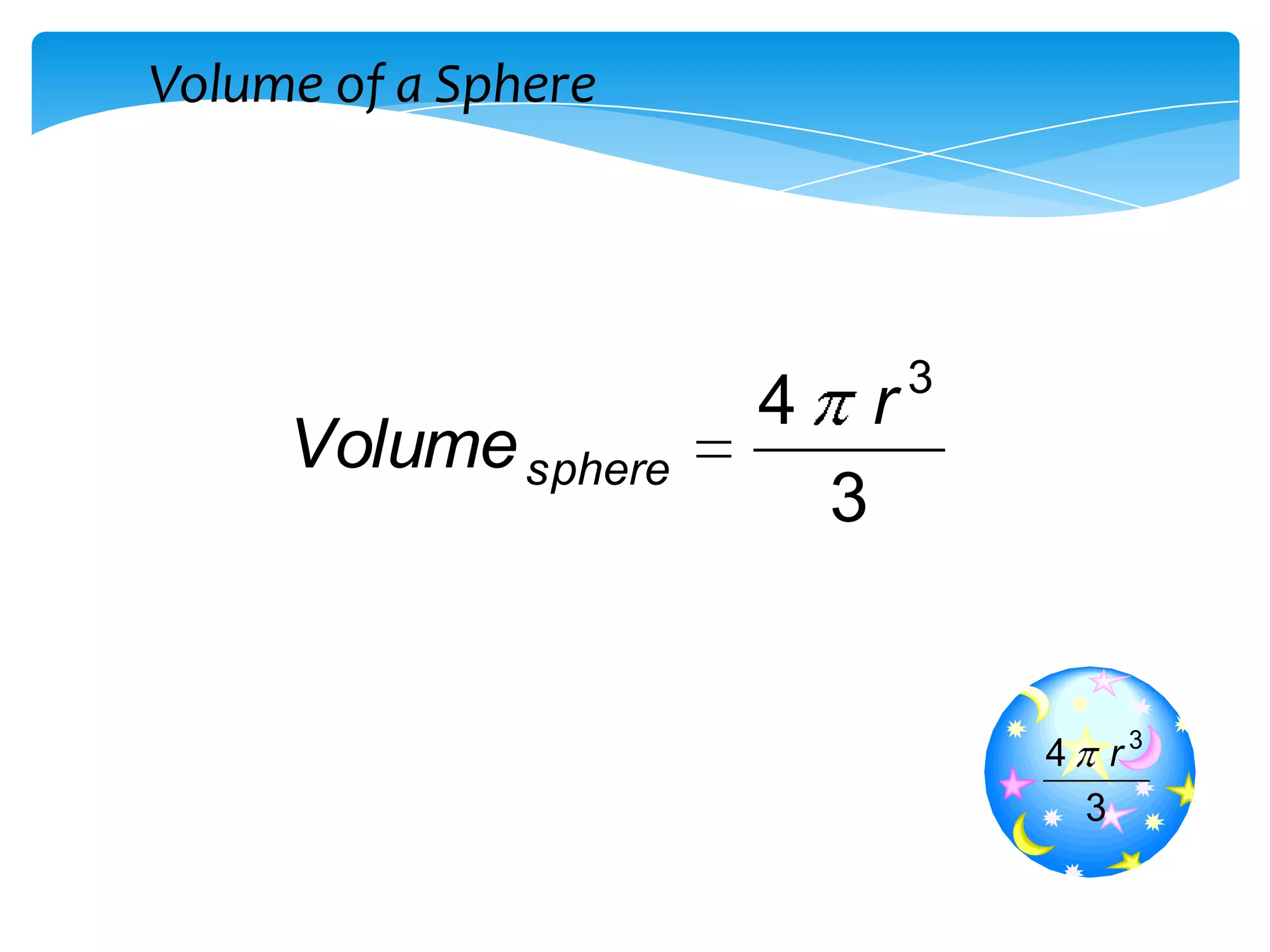
Volume of a sphere = (4/3)πr3
= (4/3)π(12cm)3
= (4/3)π × 13824 cm3
= 4488π cm3
Surface area of a sphere = 4πr2
= 4π(12cm)2
= 4π × 144 cm2
= 448π cm2
So the volume is 4488π cm3 and the surface area is 448π cm2.