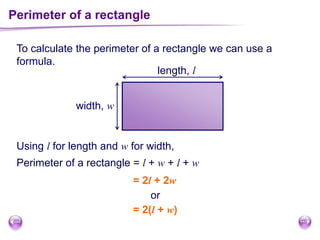
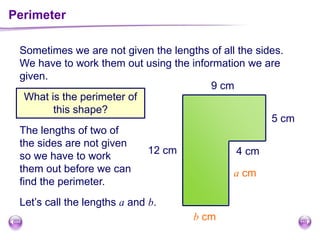
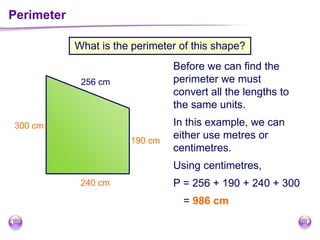
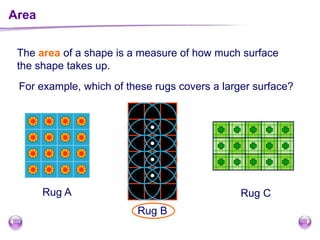
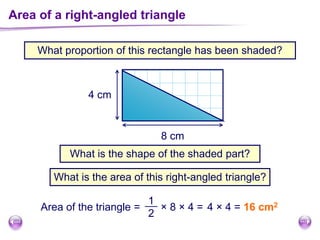
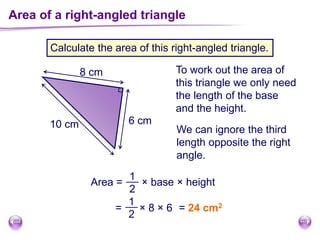
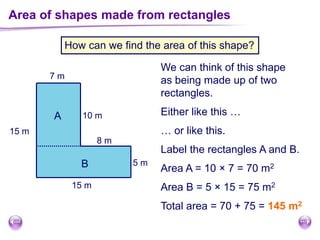
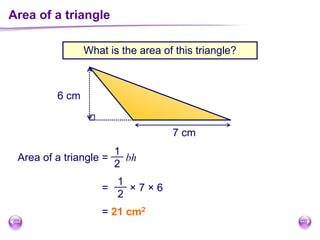
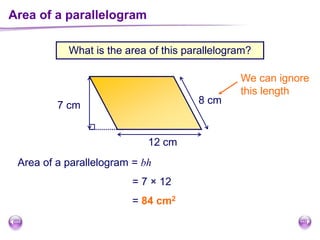
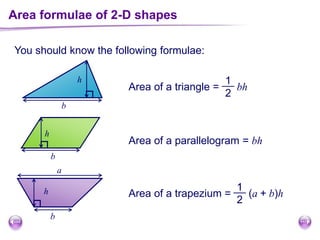
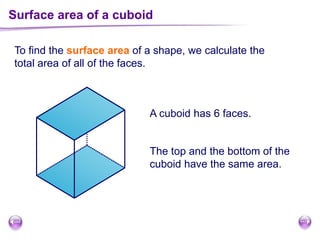
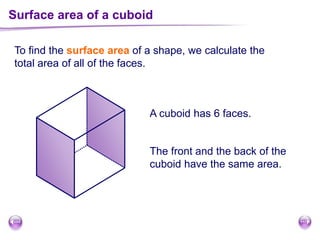
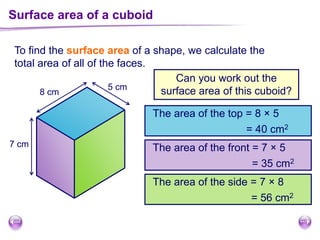
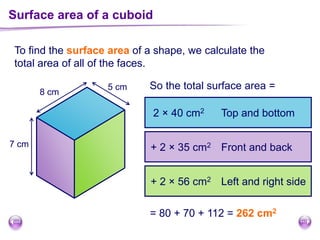
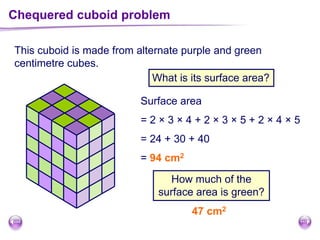
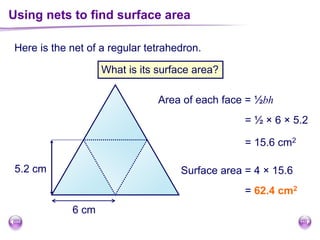
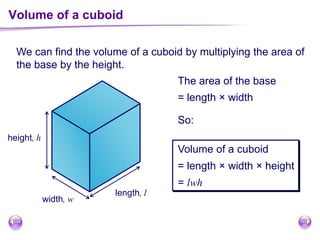
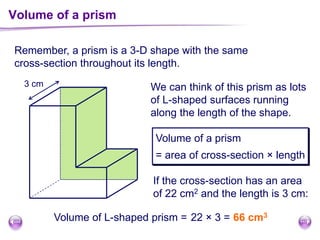
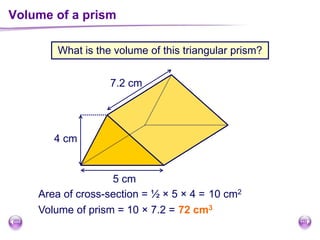
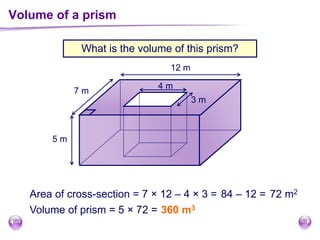
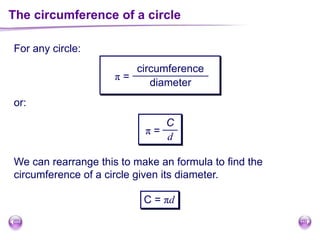
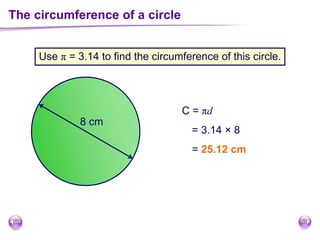
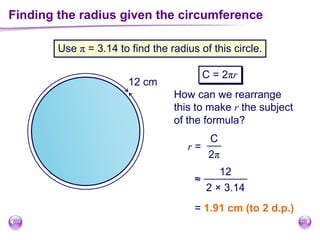
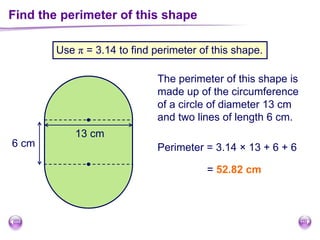
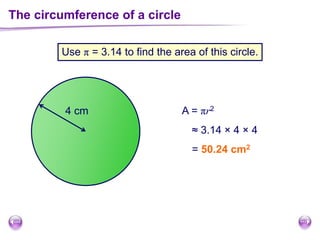
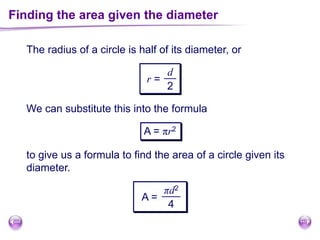
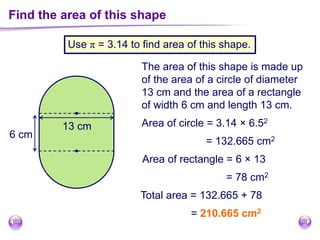
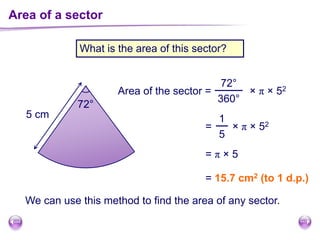
This document discusses perimeter, area, and volume. It begins by defining perimeter as the distance around a shape found by adding all the side lengths. It provides examples of calculating perimeters of rectangles, irregular shapes, and converting between units. It then defines area as a measure of how much surface a shape covers. It gives formulas and examples for finding the areas of rectangles, triangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and irregular shapes. Finally, it discusses surface area as the total area of all faces of a shape. It provides the surface area formulas and worked examples for cuboids and cubes.