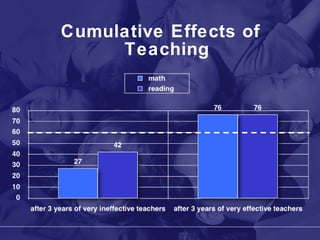
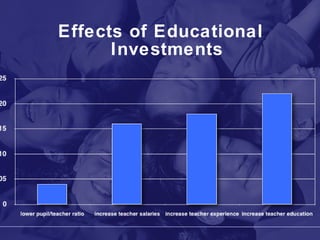
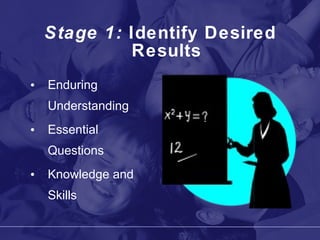
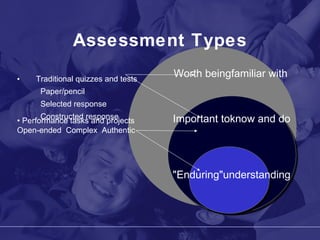
The document discusses the Utah Academy of Teachers and frameworks for quality teaching and student learning. It emphasizes that quality teaching is the most important factor in student achievement, and outlines four domains of teaching practice: planning and preparation, classroom environment, instruction, and professional responsibilities. It also discusses the backward design process of understanding by design curriculum development which begins with identifying desired learning outcomes and aligning standards, curriculum, instruction and assessment.












































![Who Dares to Teach Must Never Cease to Learn For more information: Rebecca Anderson [email_address] Carolee Coleman [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/understanding-091124154206-phpapp02/85/Understanding-PPT-50-320.jpg)

