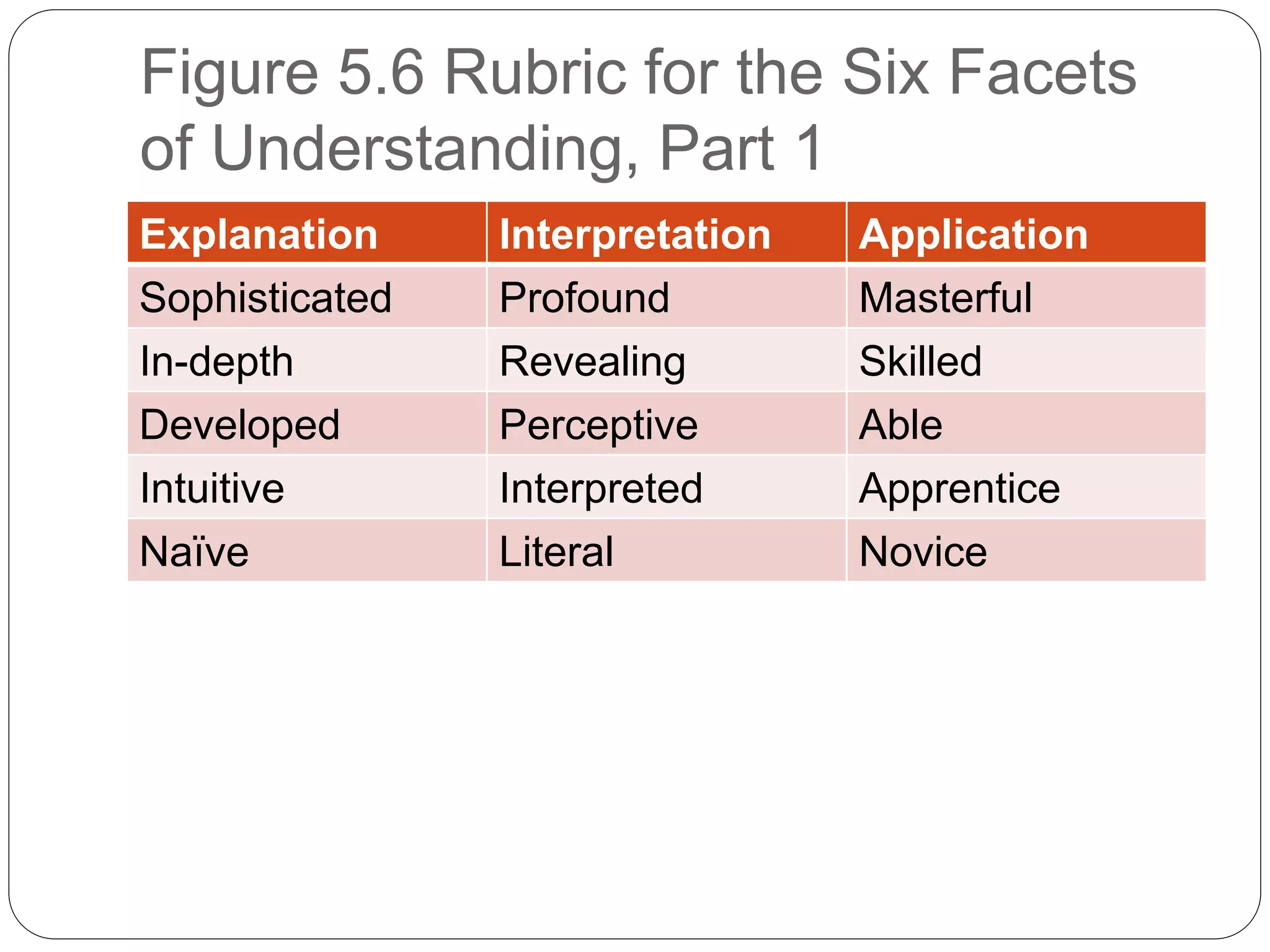
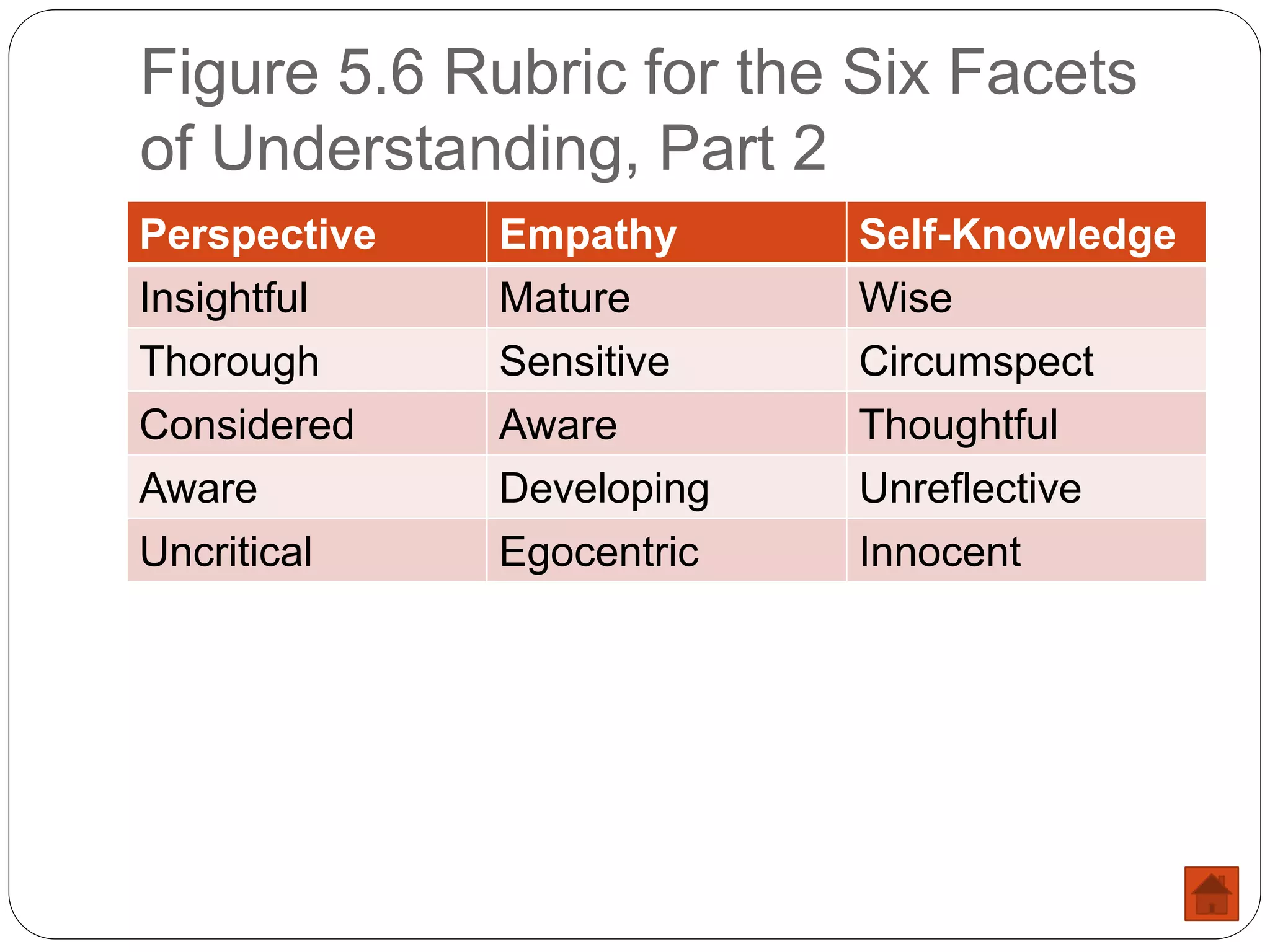
The document outlines six facets of understanding essential for student assessment: explain, interpret, apply, have perspective, empathize, and self-knowledge. It emphasizes the need for assessments that go beyond mere facts, focusing on students' ability to articulate their understanding, interpret data meaningfully, and apply knowledge in real-world contexts. The document also discusses the importance of perspective-taking and self-reflection, introducing assessment methods like oral exams, contextualized performance tasks, and rubrics to evaluate students' depth of understanding.