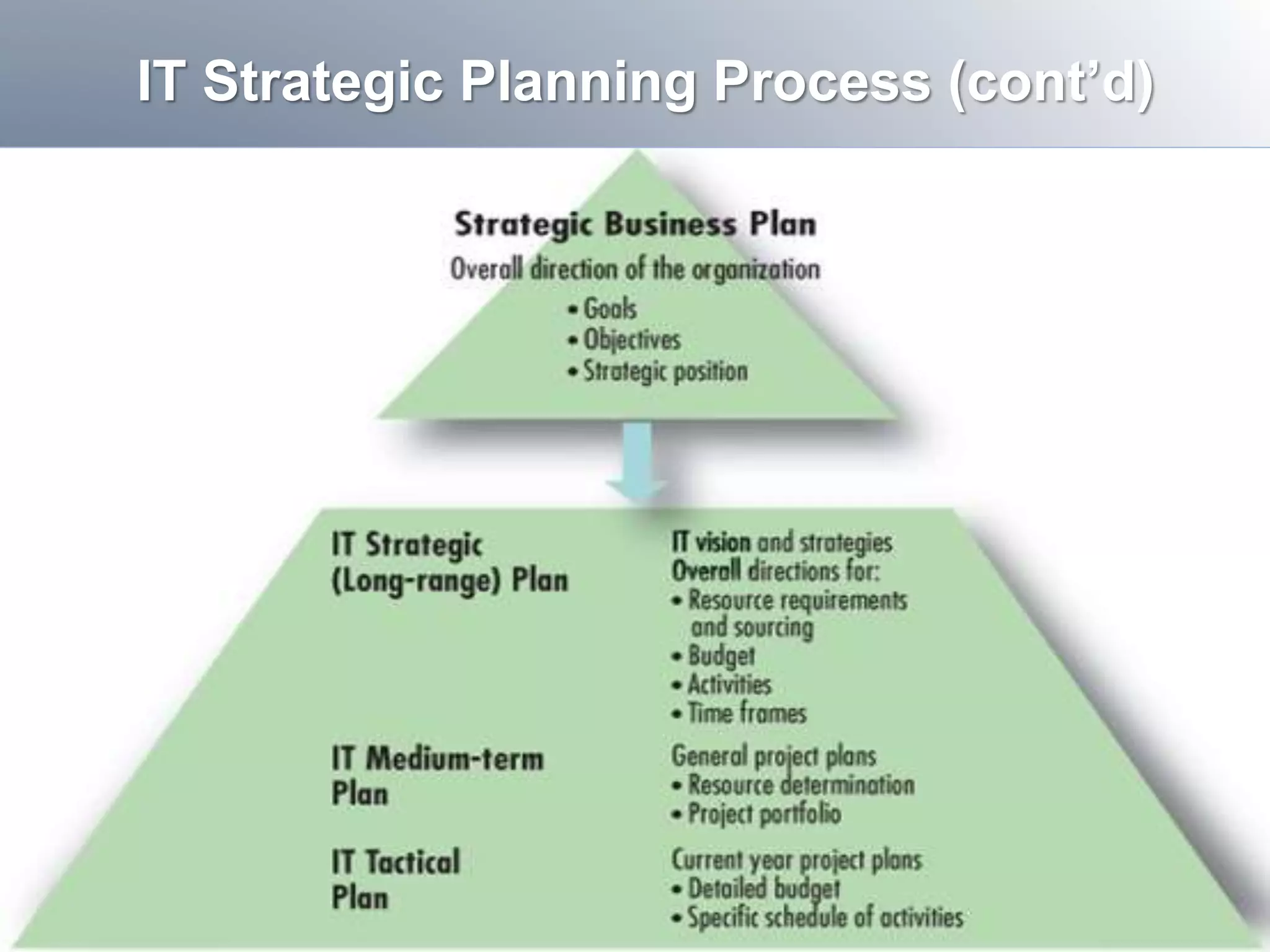
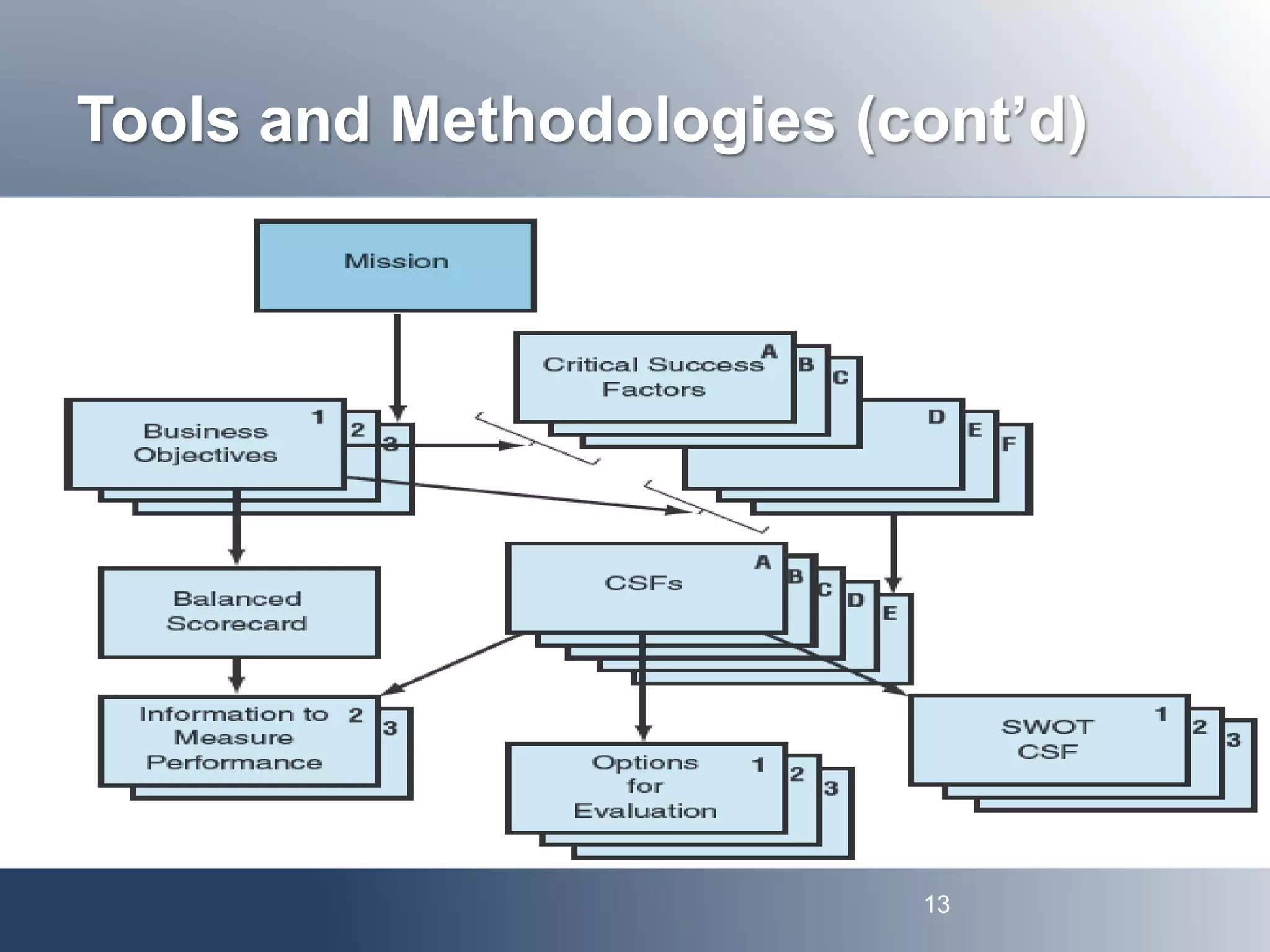
This document discusses IT strategy, sourcing, and vendor relationships. It covers key topics such as:
1. Aligning IT strategy with business strategy and exploring different IT governance models.
2. Examining IT operating plans and sourcing strategies, including discussions of outsourcing, offshoring, and the outsourcing lifecycle.
3. Important considerations for commencing relationships with IT vendors, including vendor selection, contracts, and financial stability.