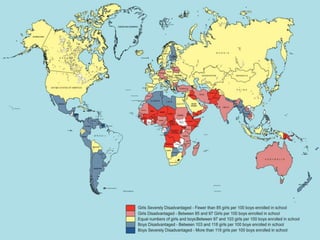
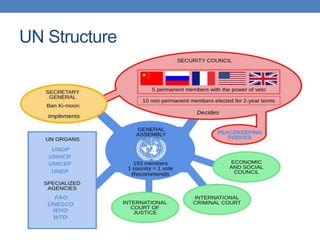
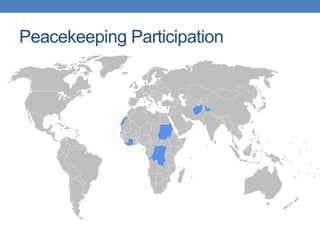
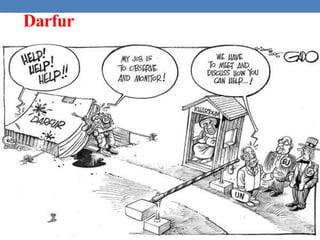
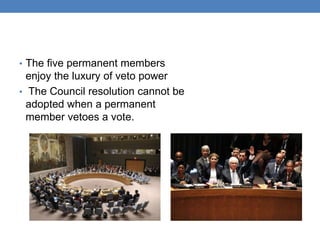
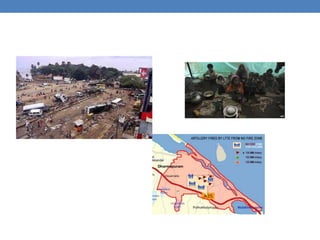
The United Nations was formed in 1945 to replace the League of Nations and promote international cooperation. It aims to maintain peace and security, protect human rights, deliver humanitarian aid, and uphold international law. However, the UN has faced criticisms over its handling of humanitarian crises and failures to prevent conflicts like the Rwandan genocide or stop human rights abuses in Darfur. Its security council has also been ineffective at times due to veto powers held by the five permanent members.