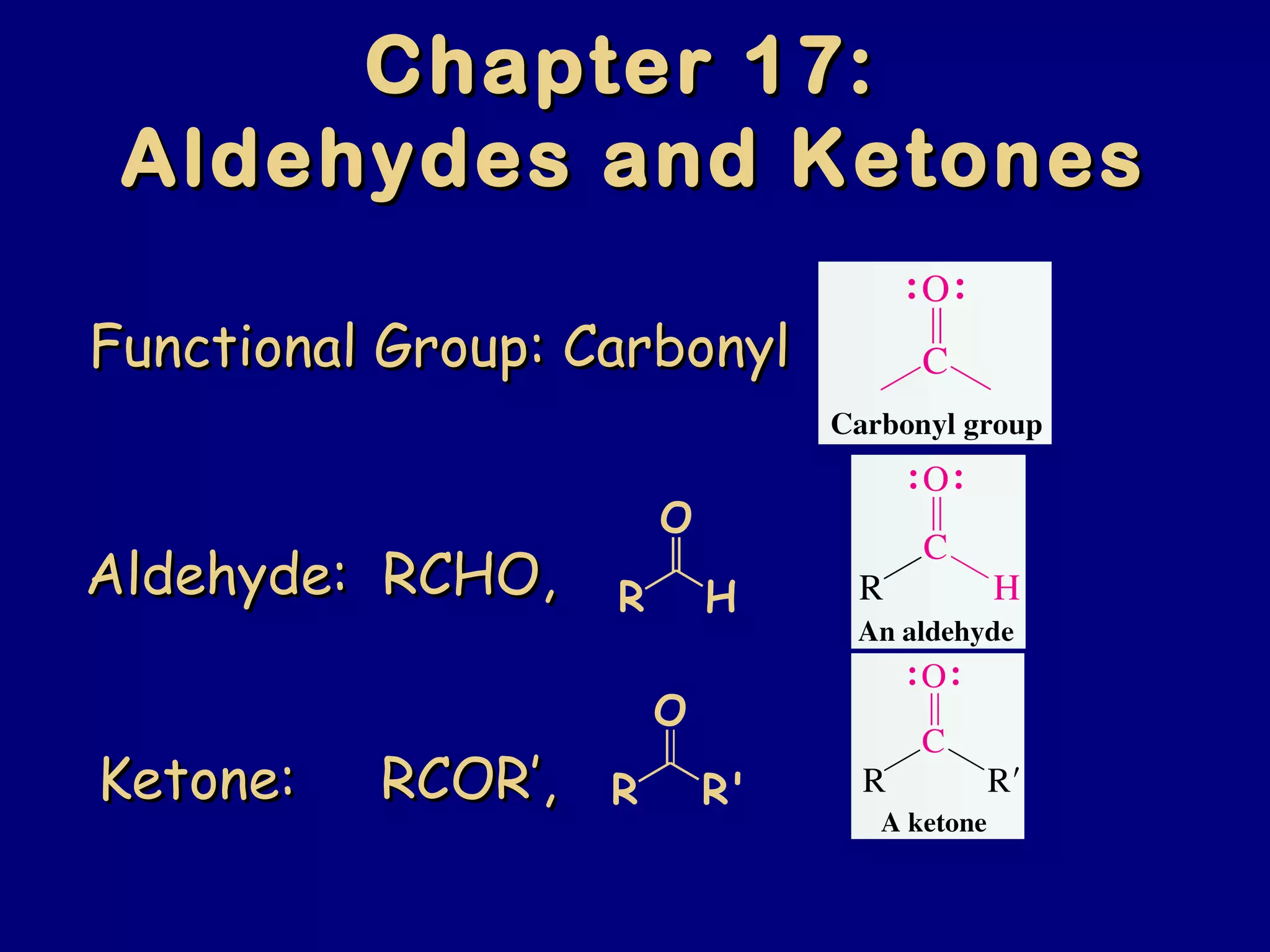
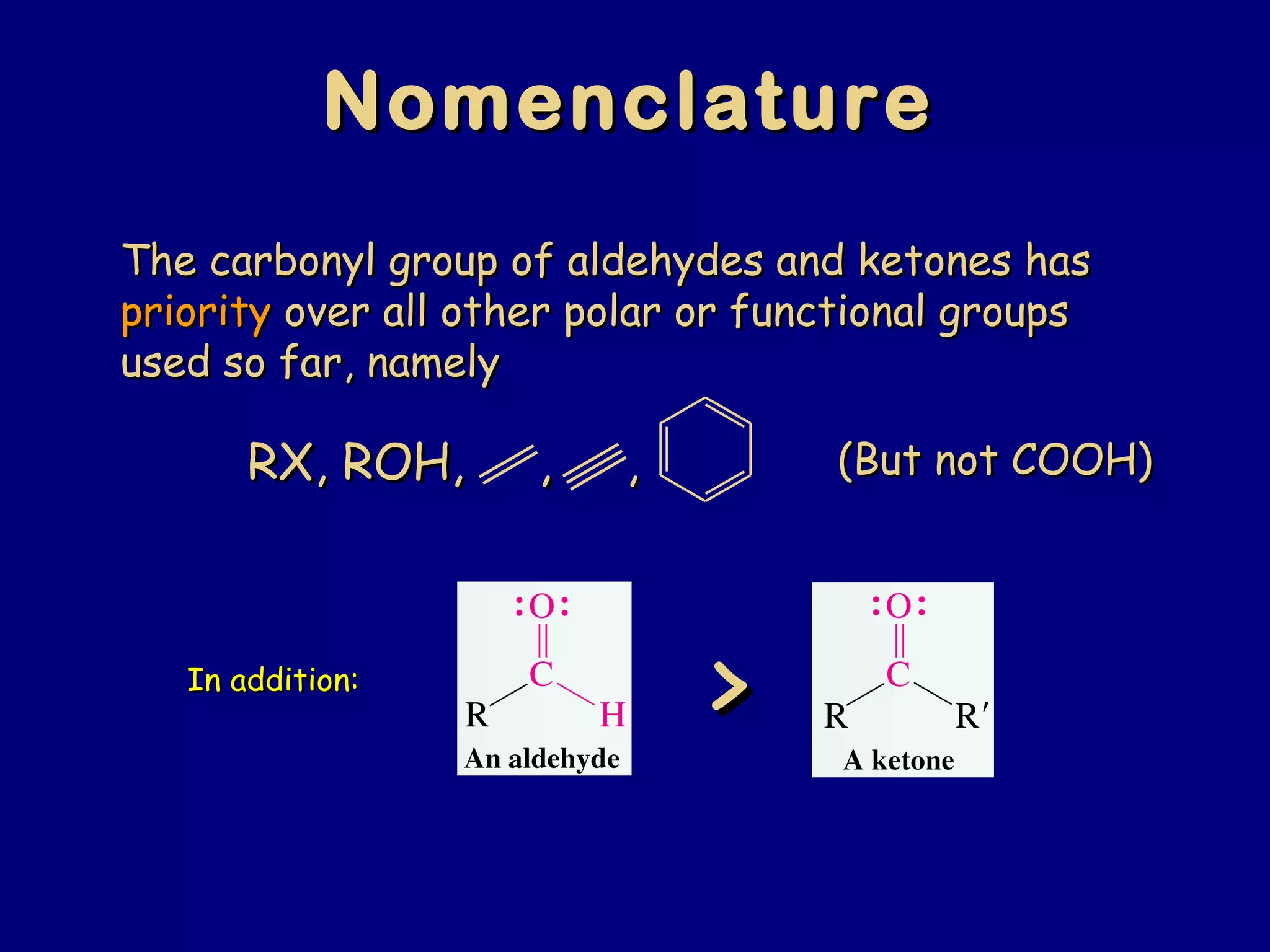
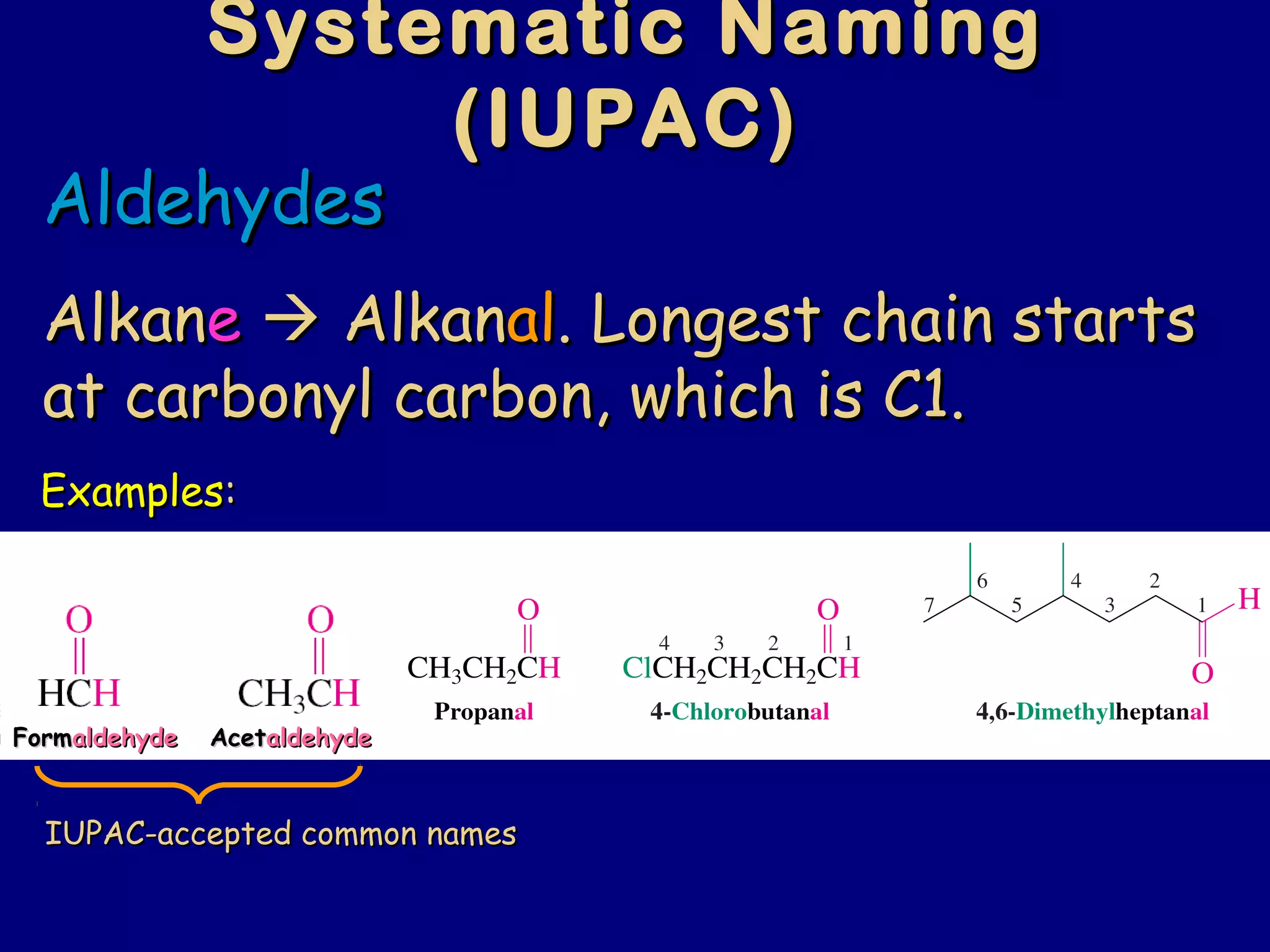
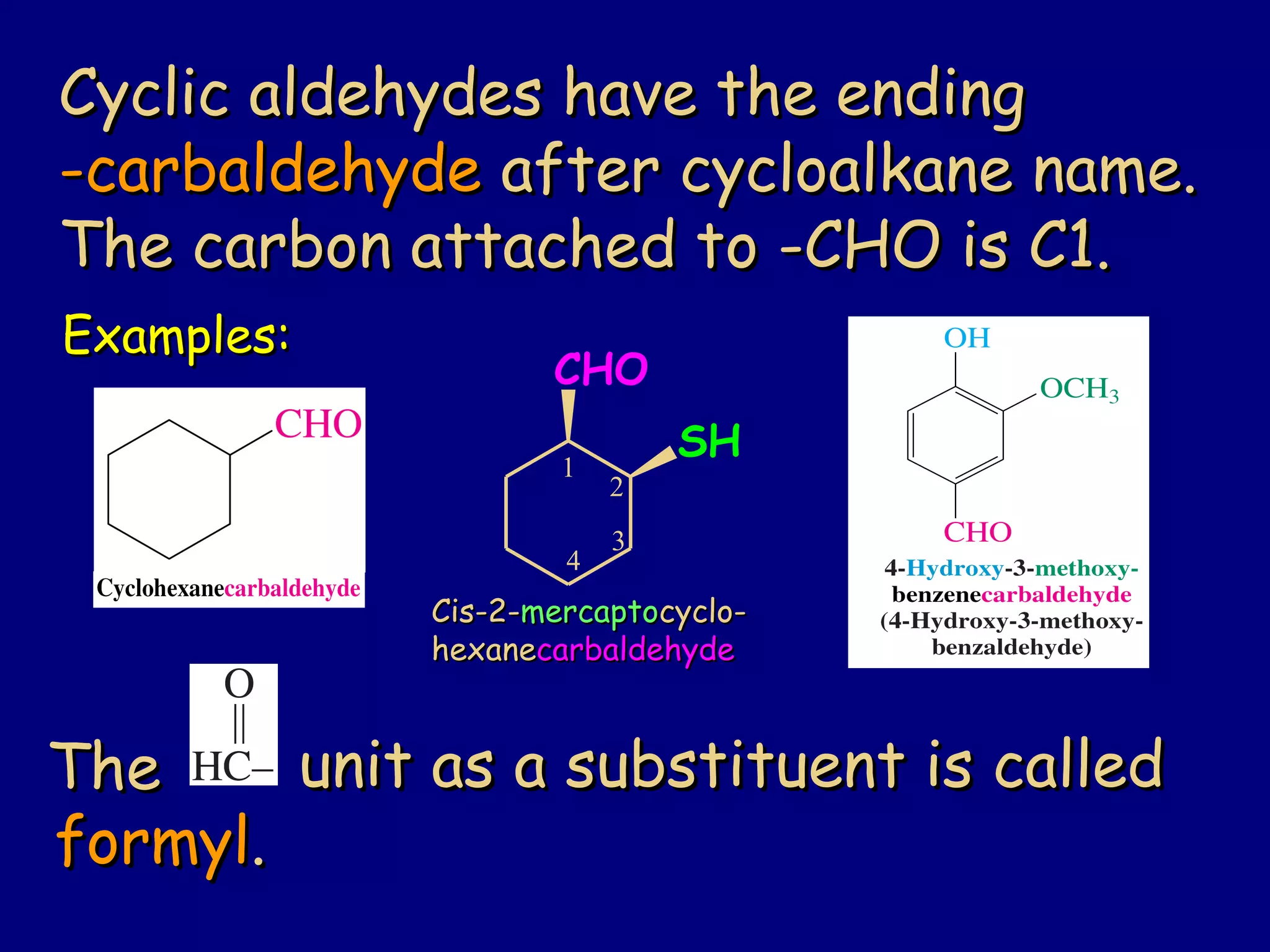
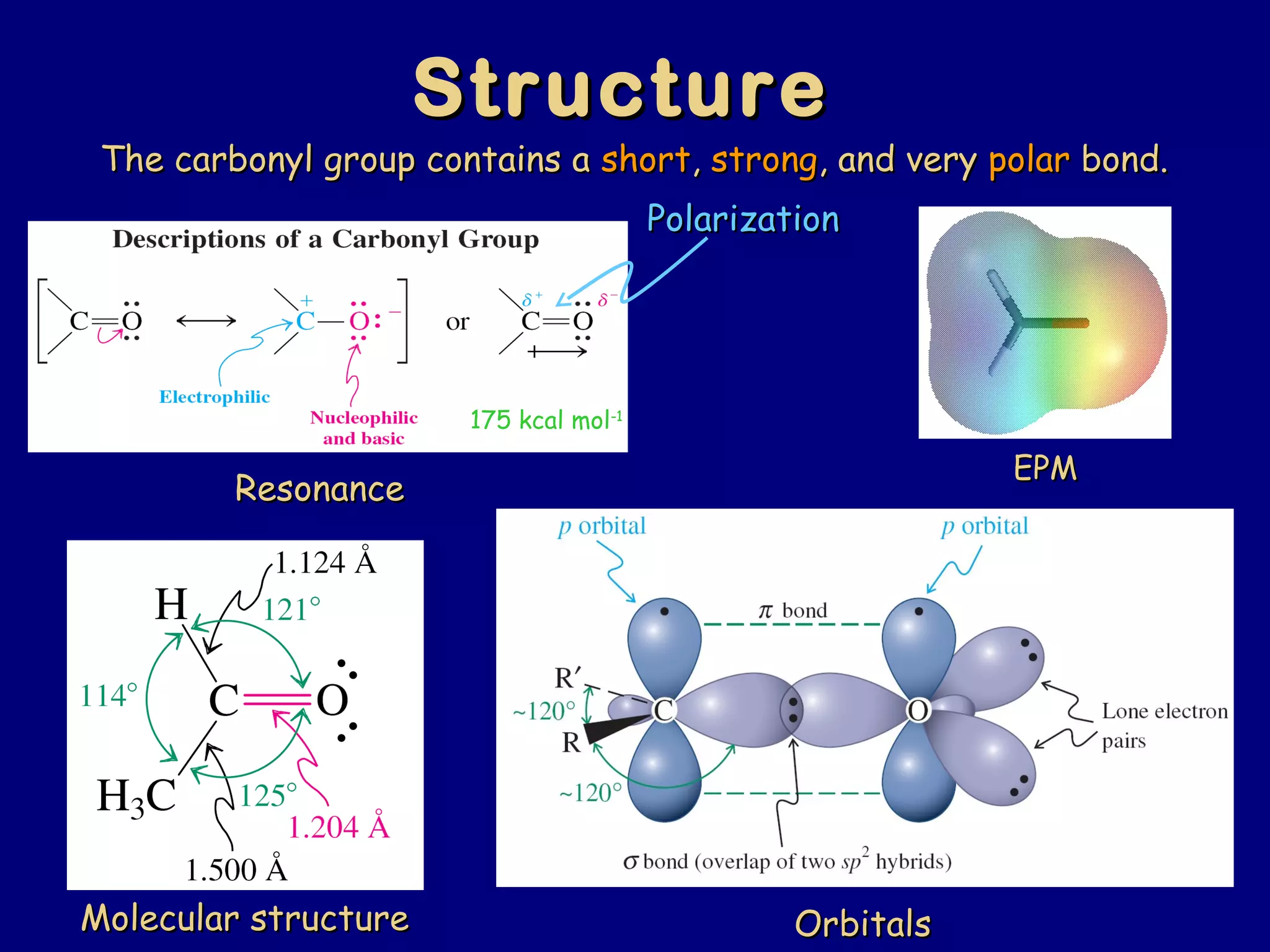
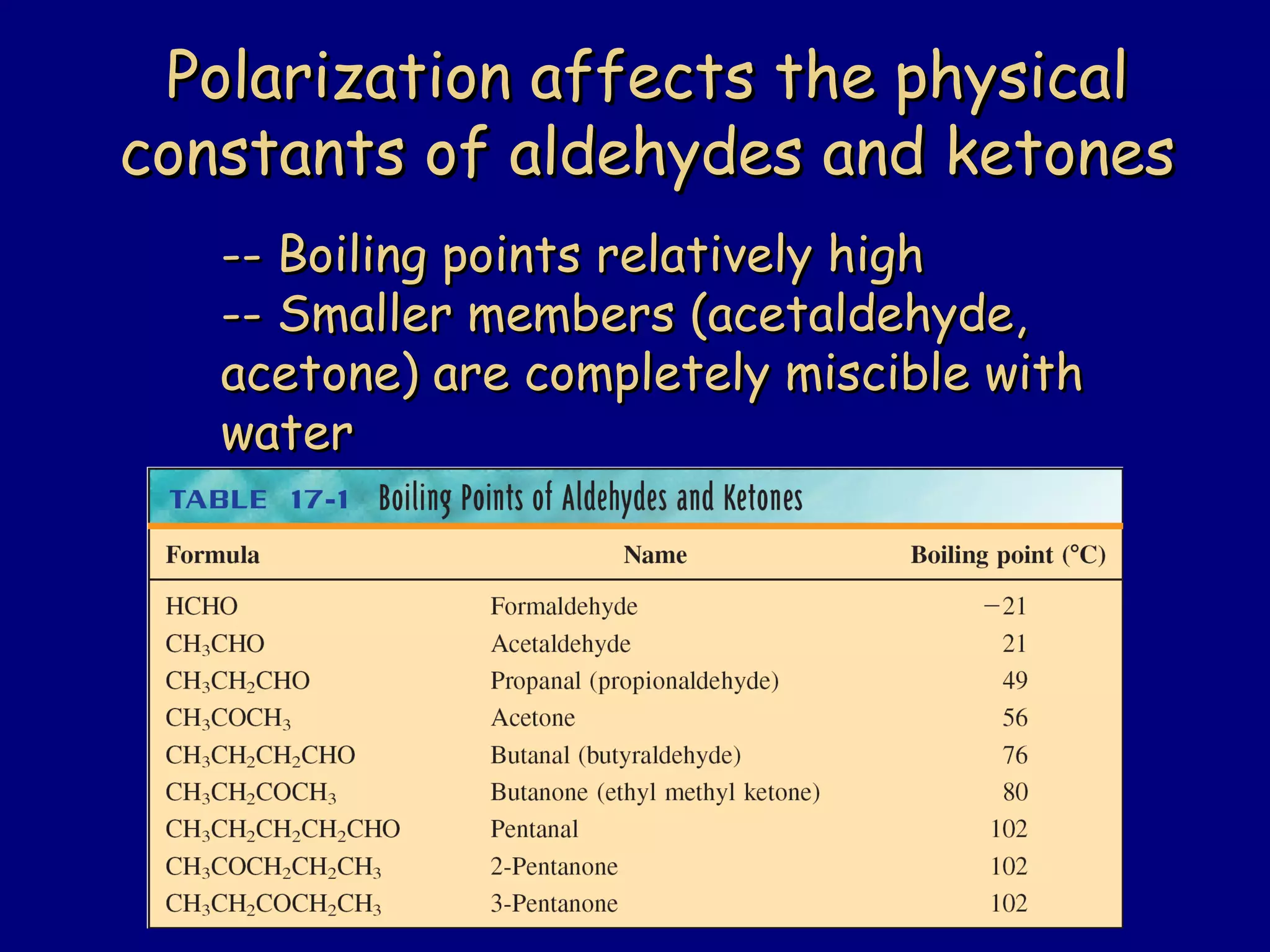
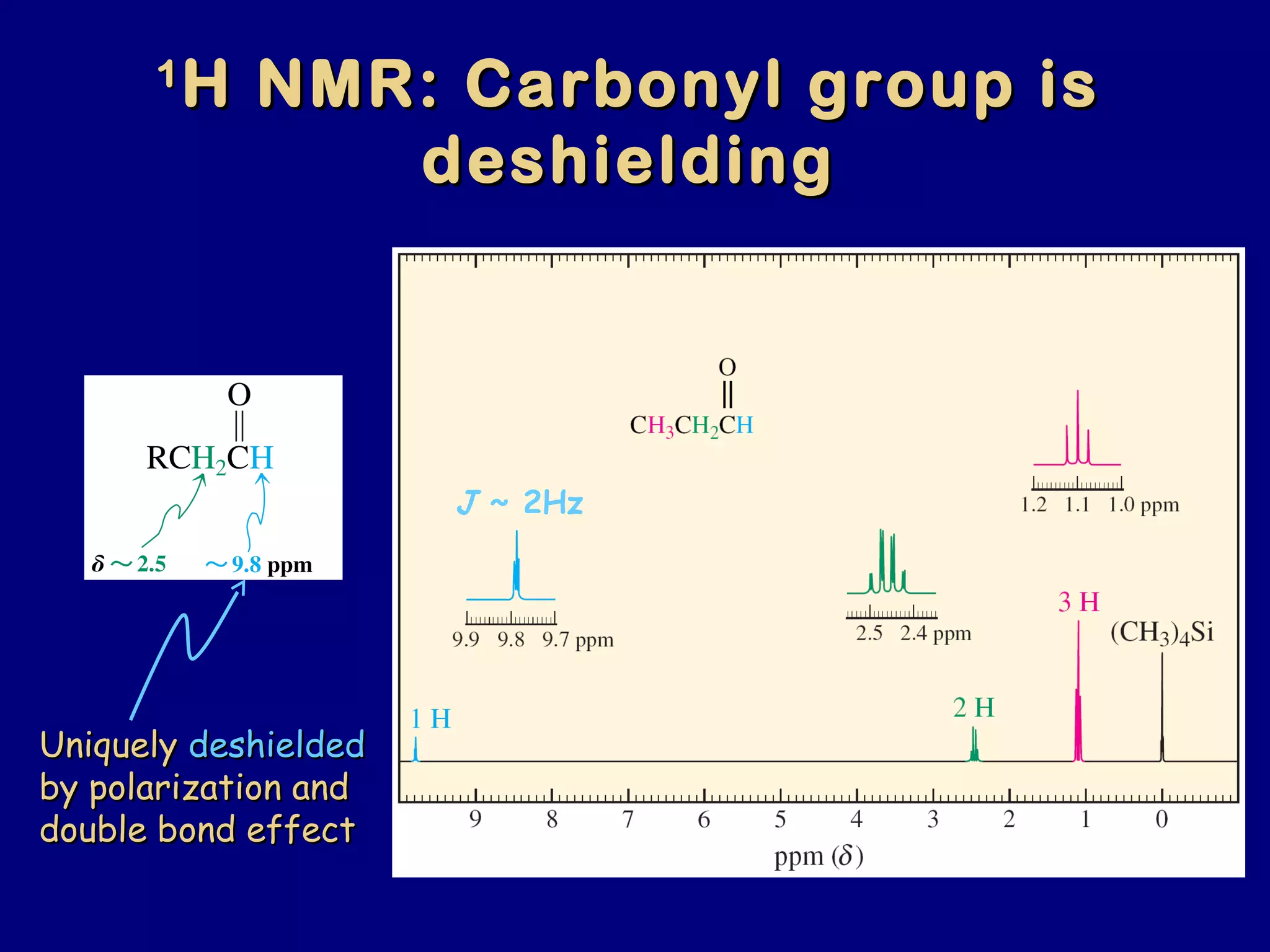
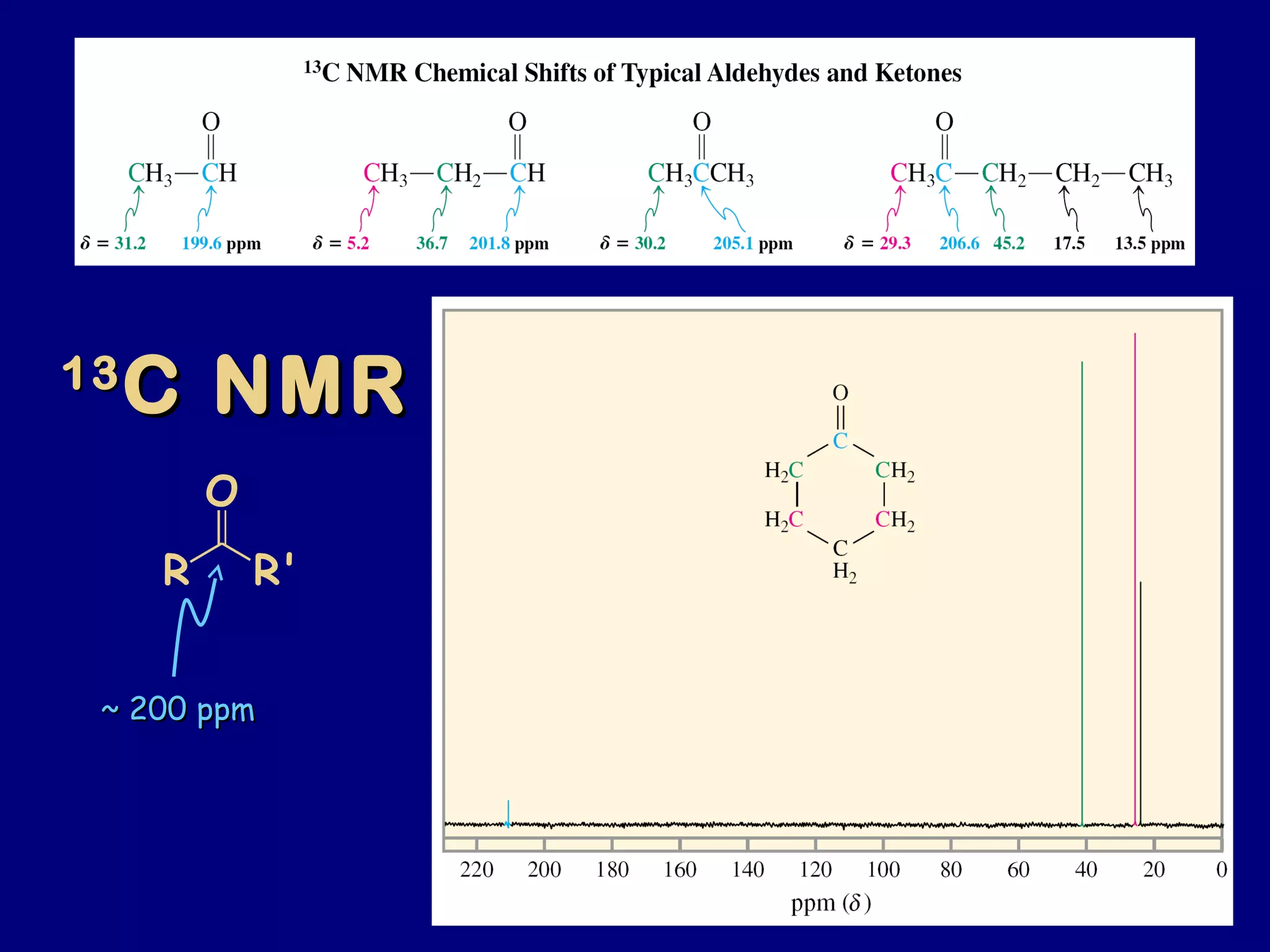
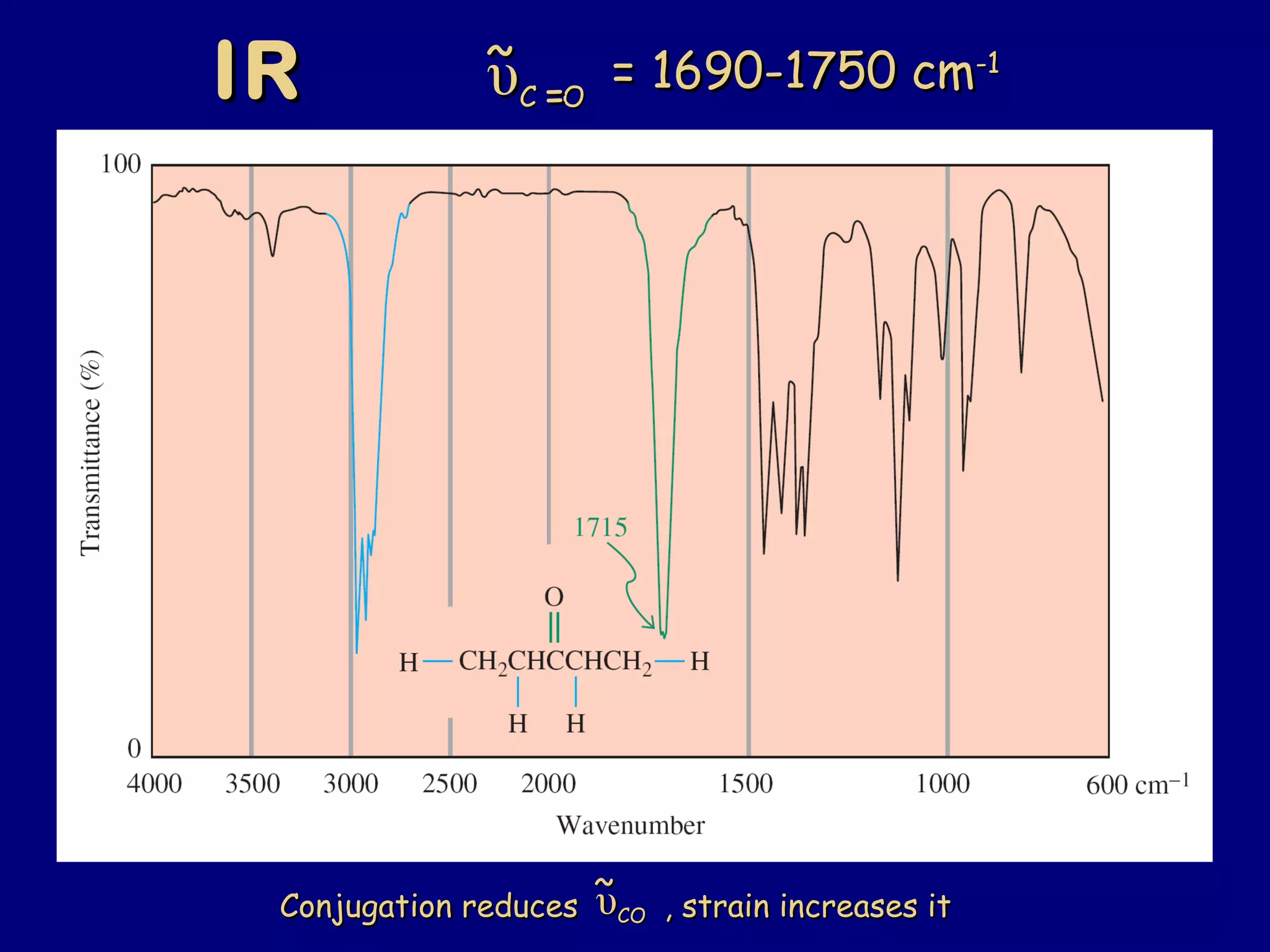
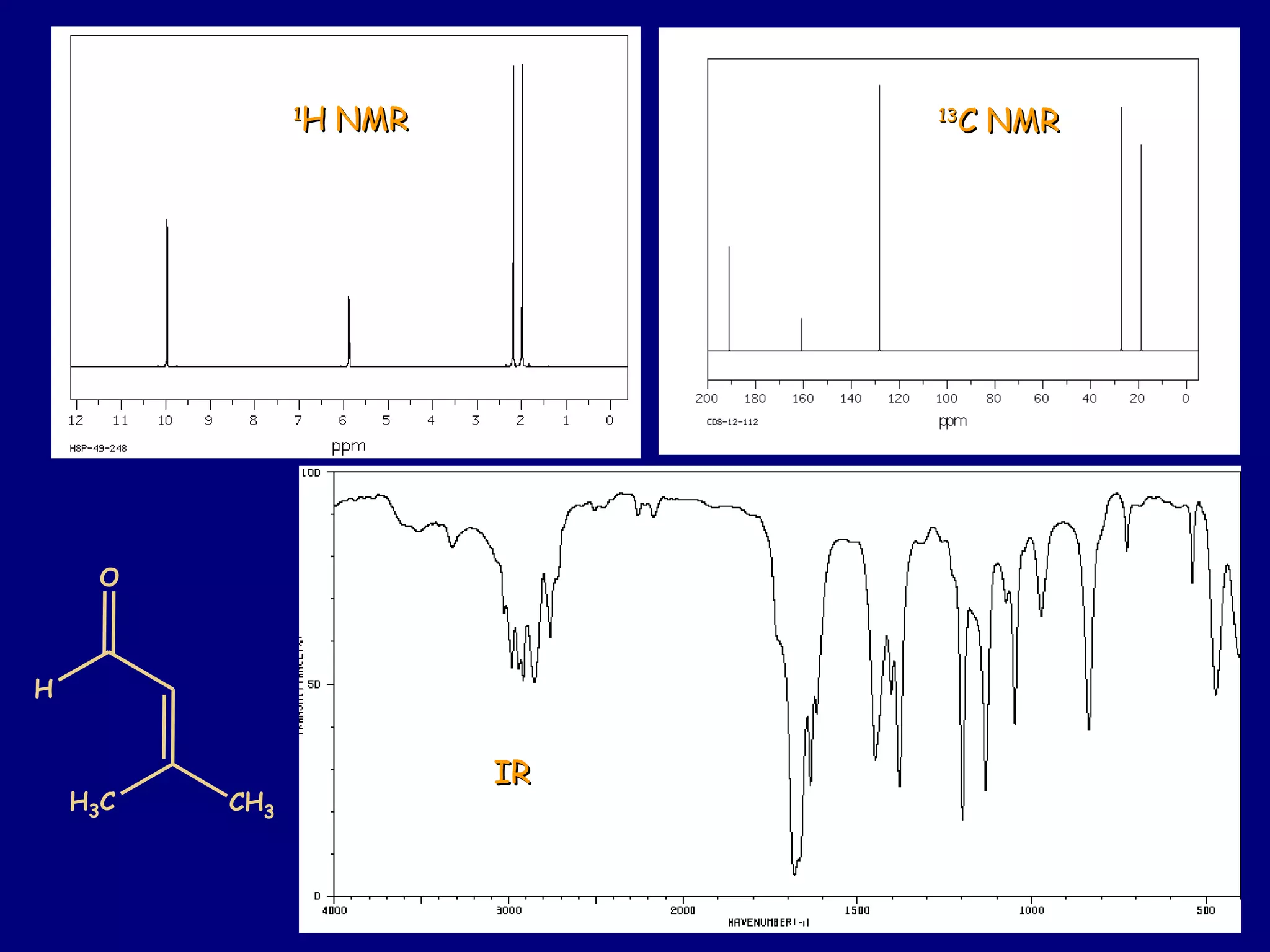
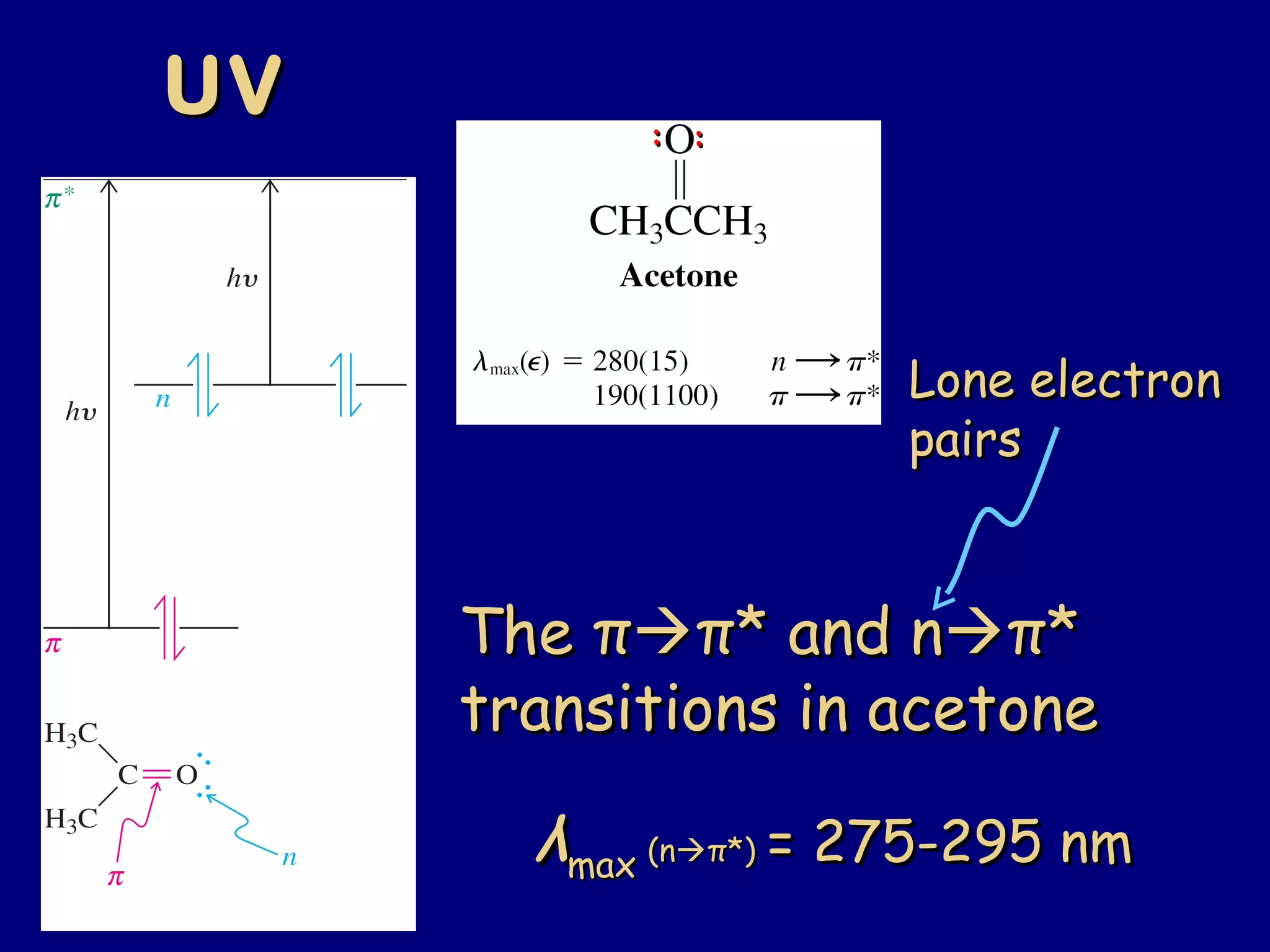
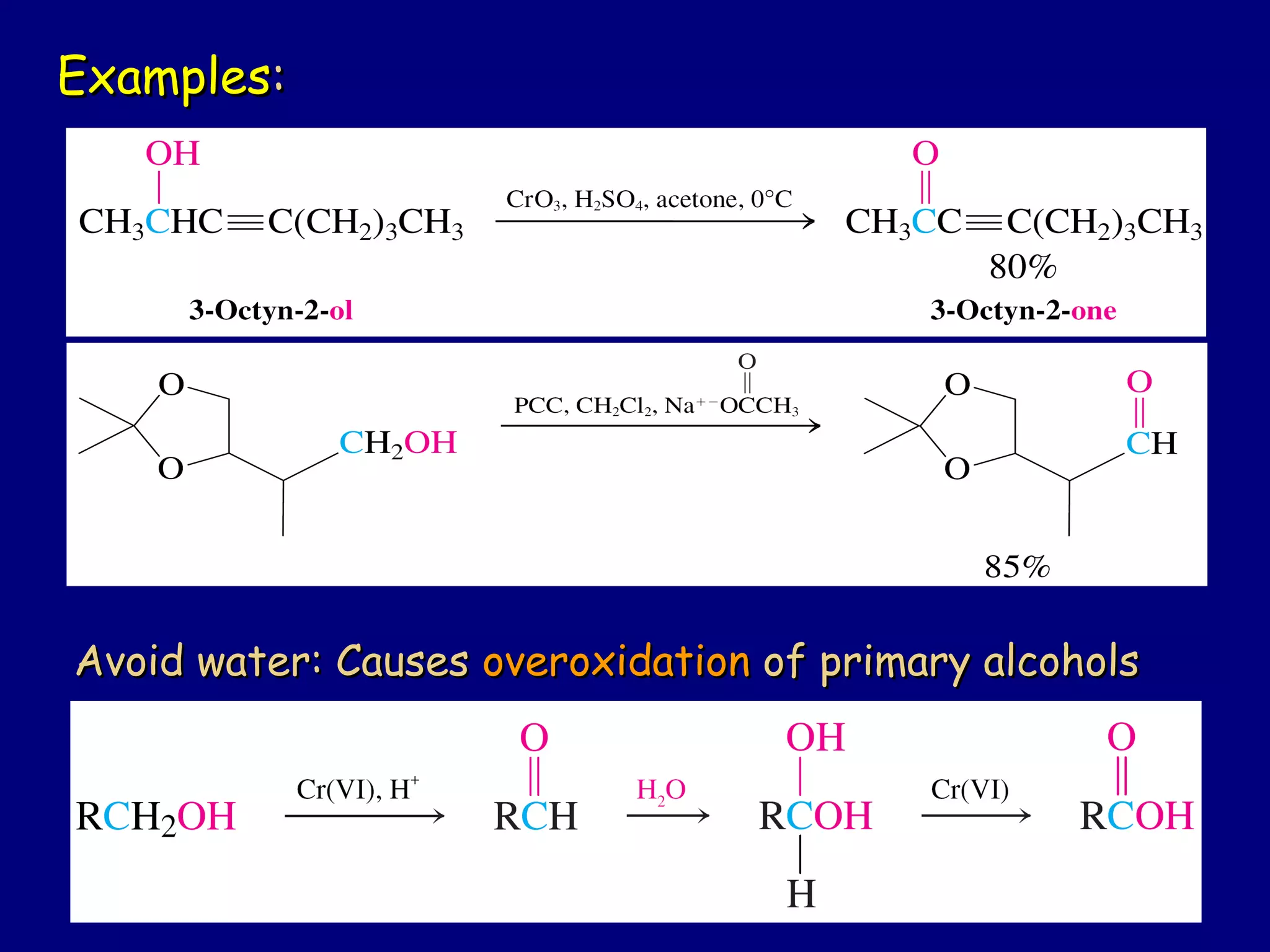
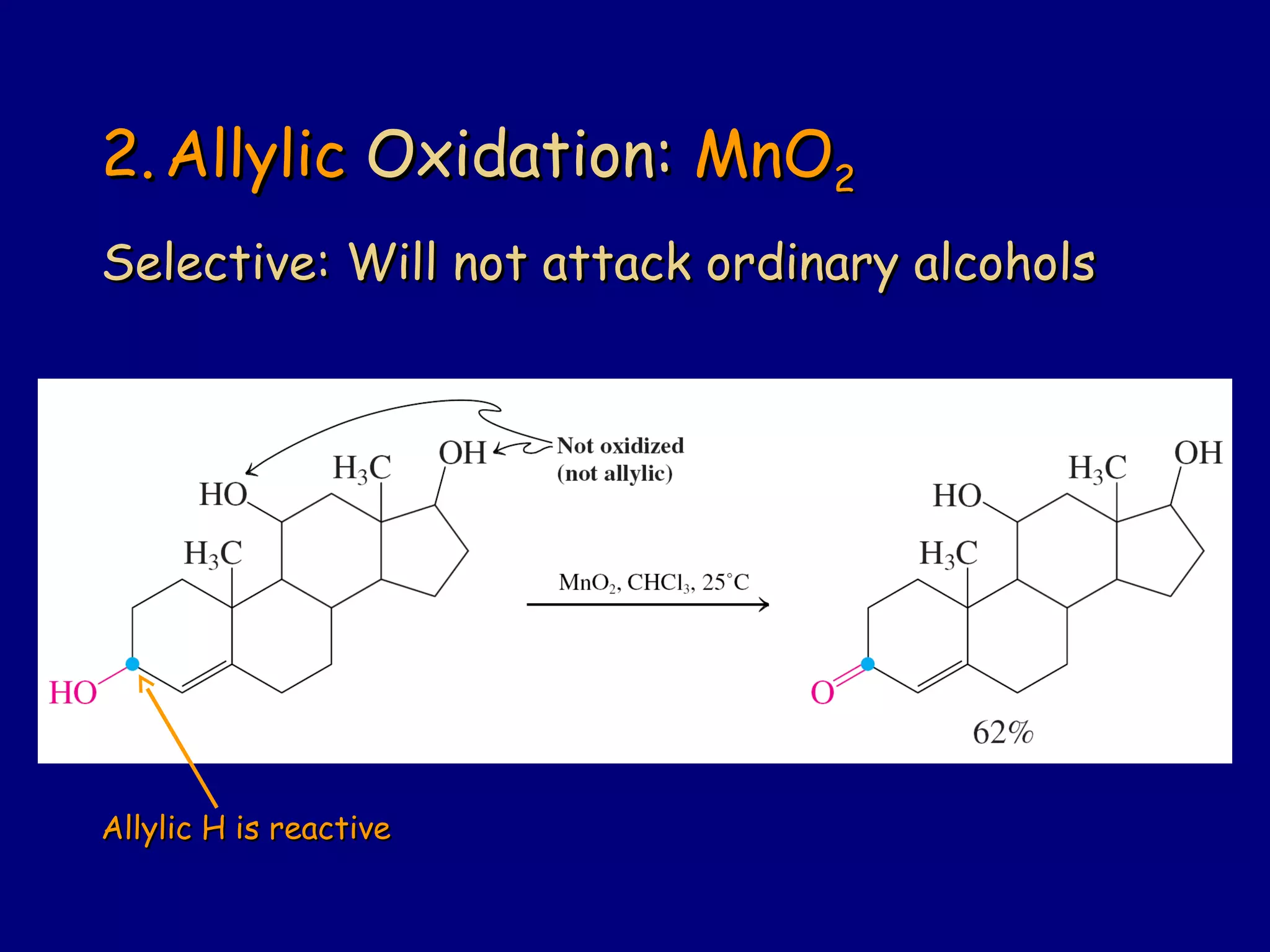
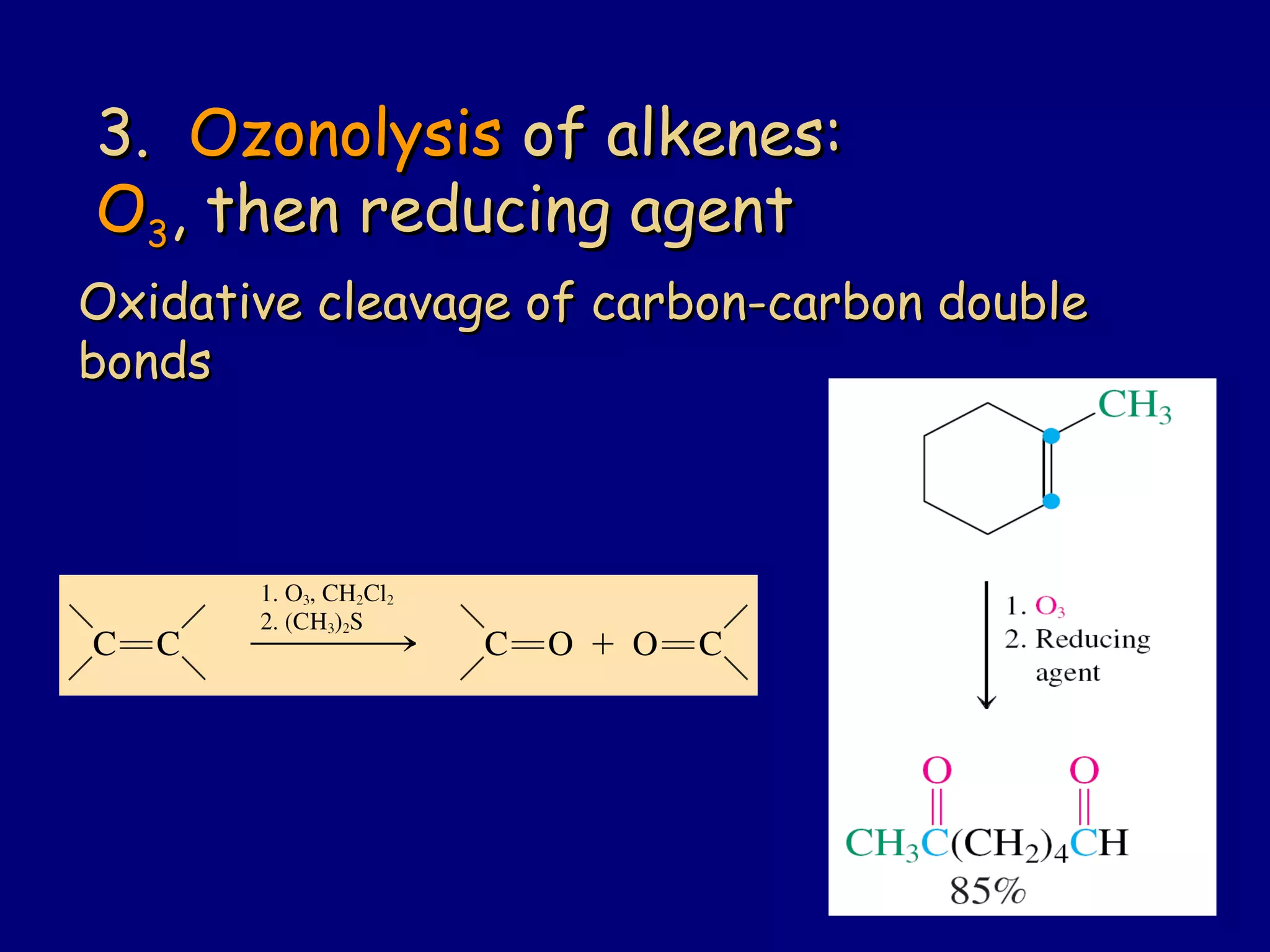
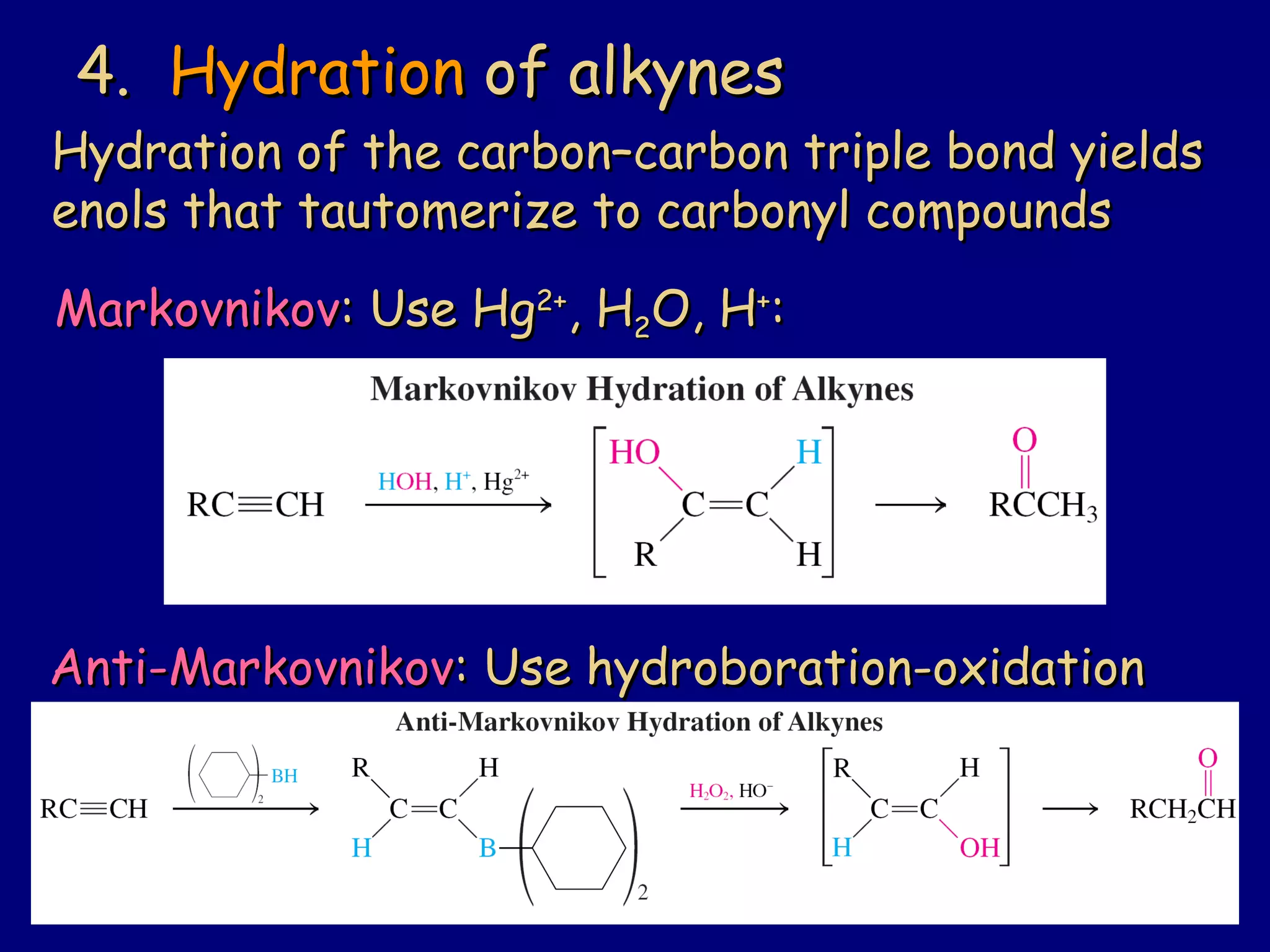
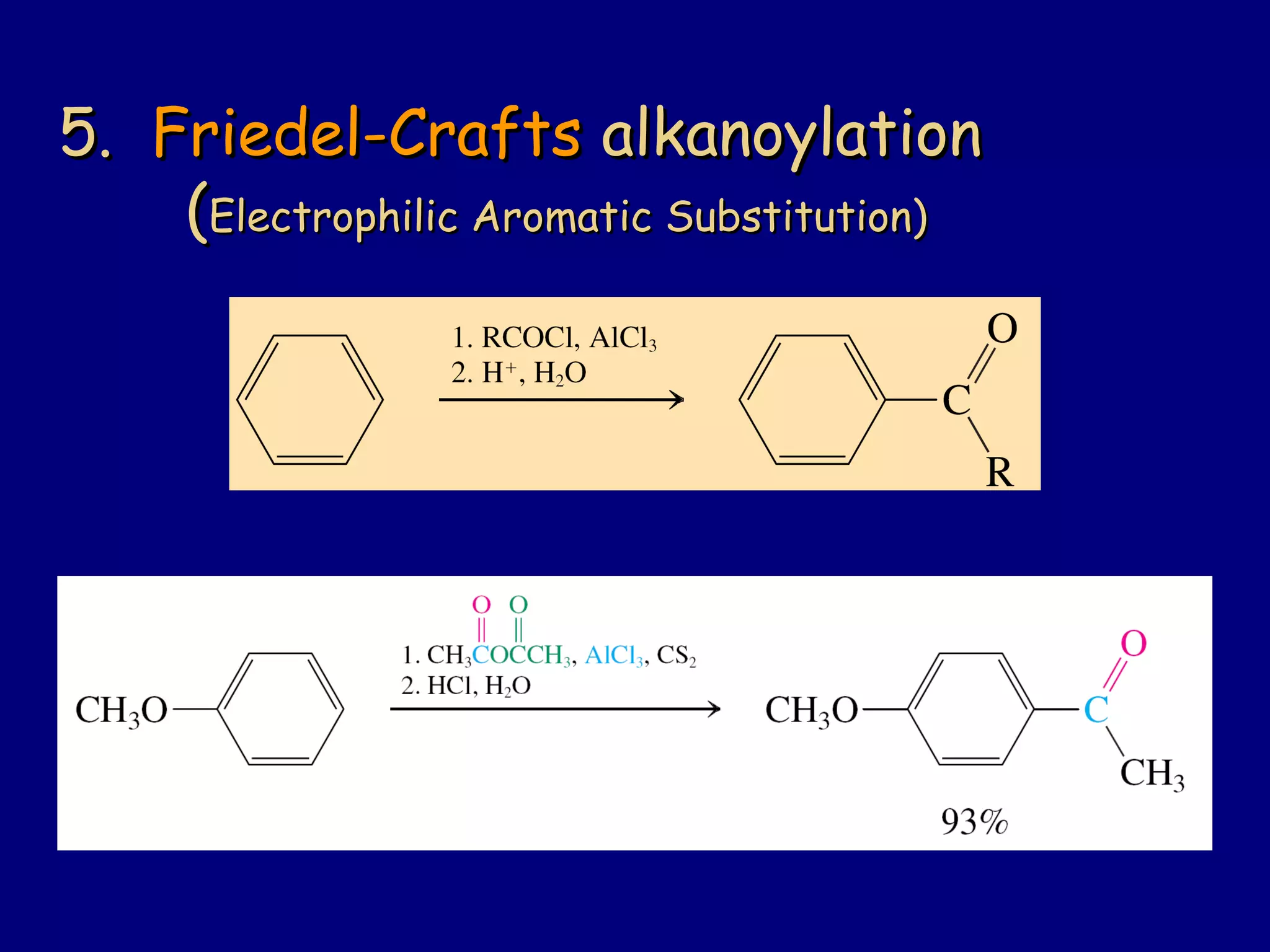
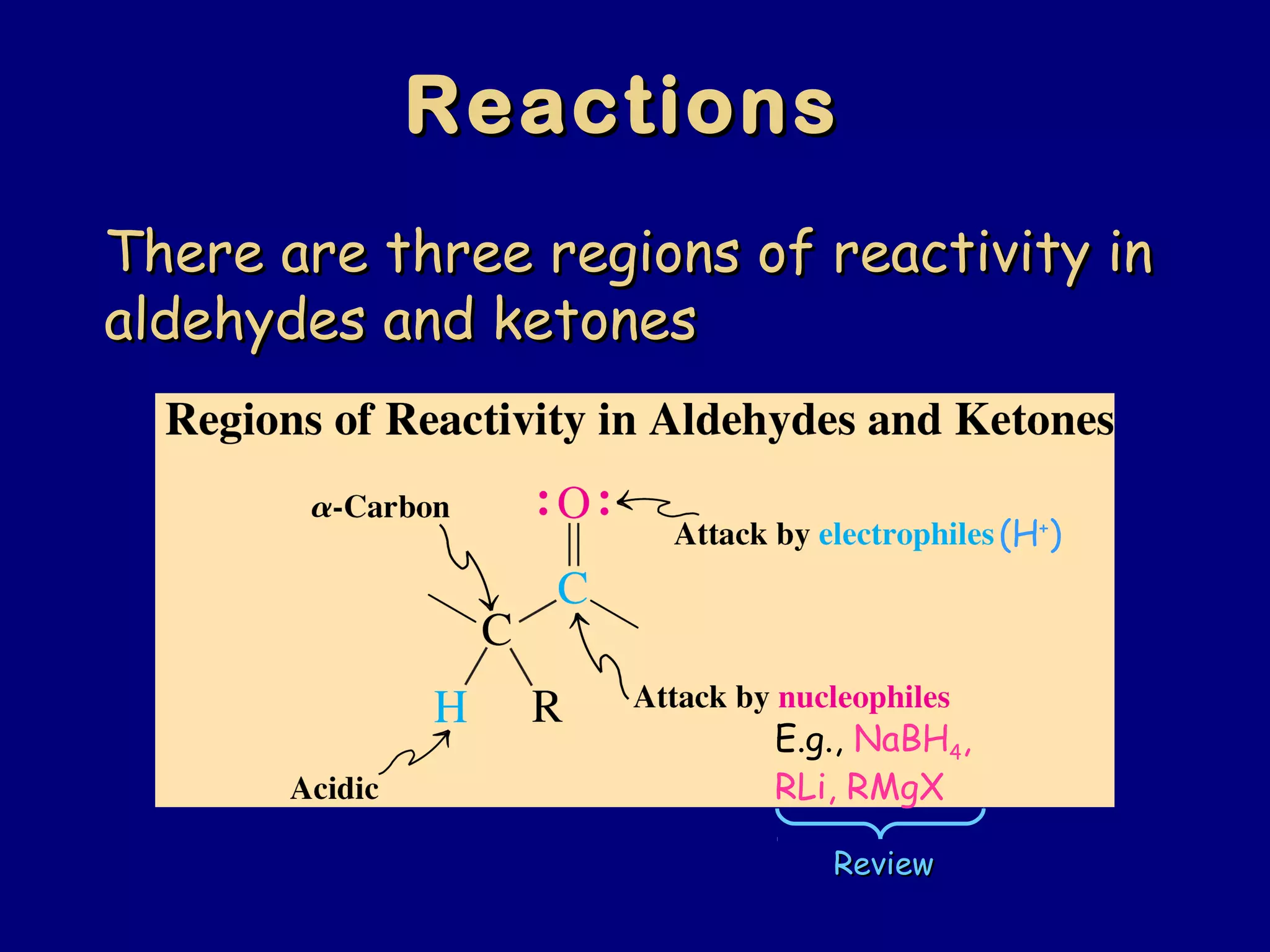
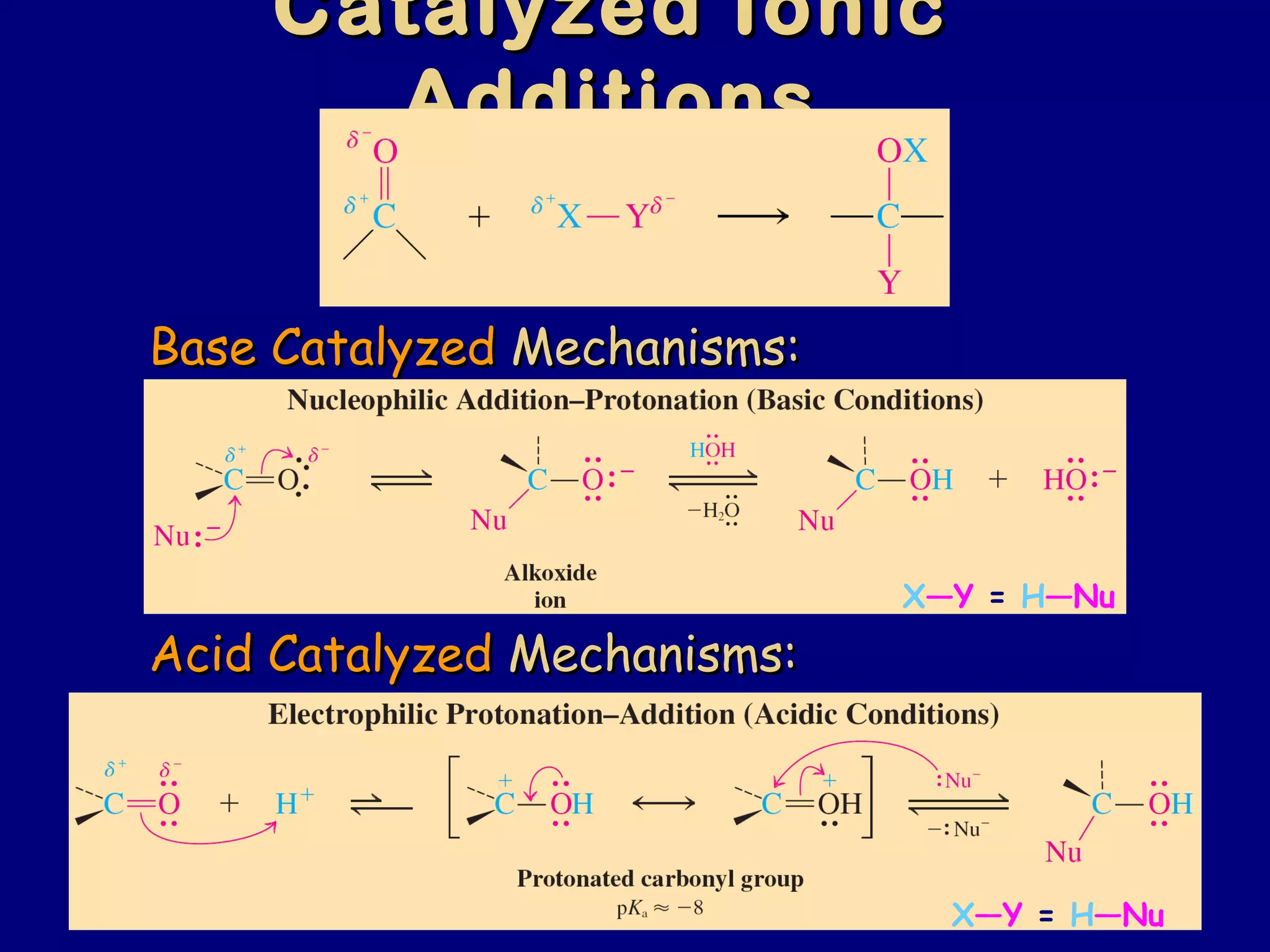
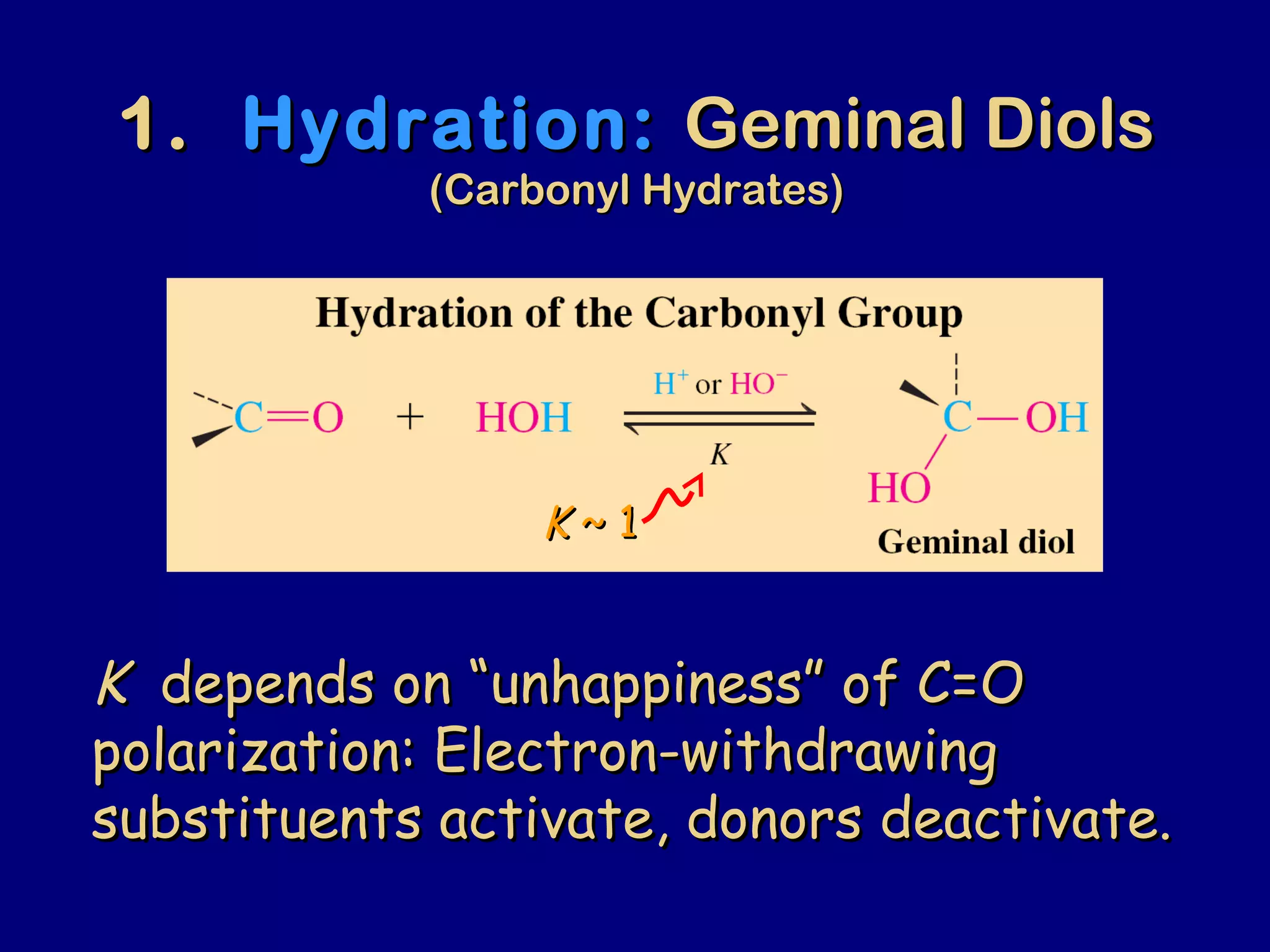
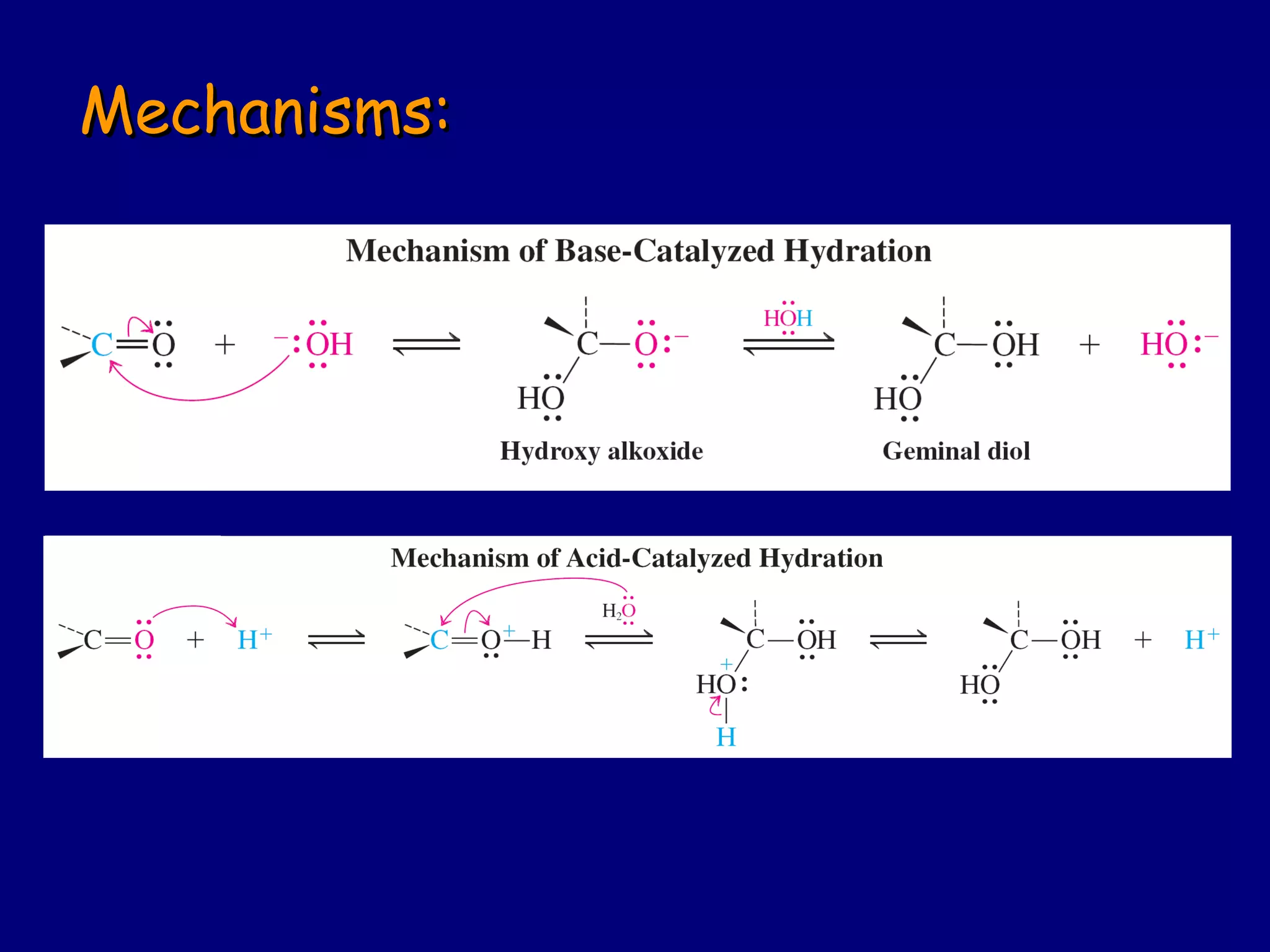
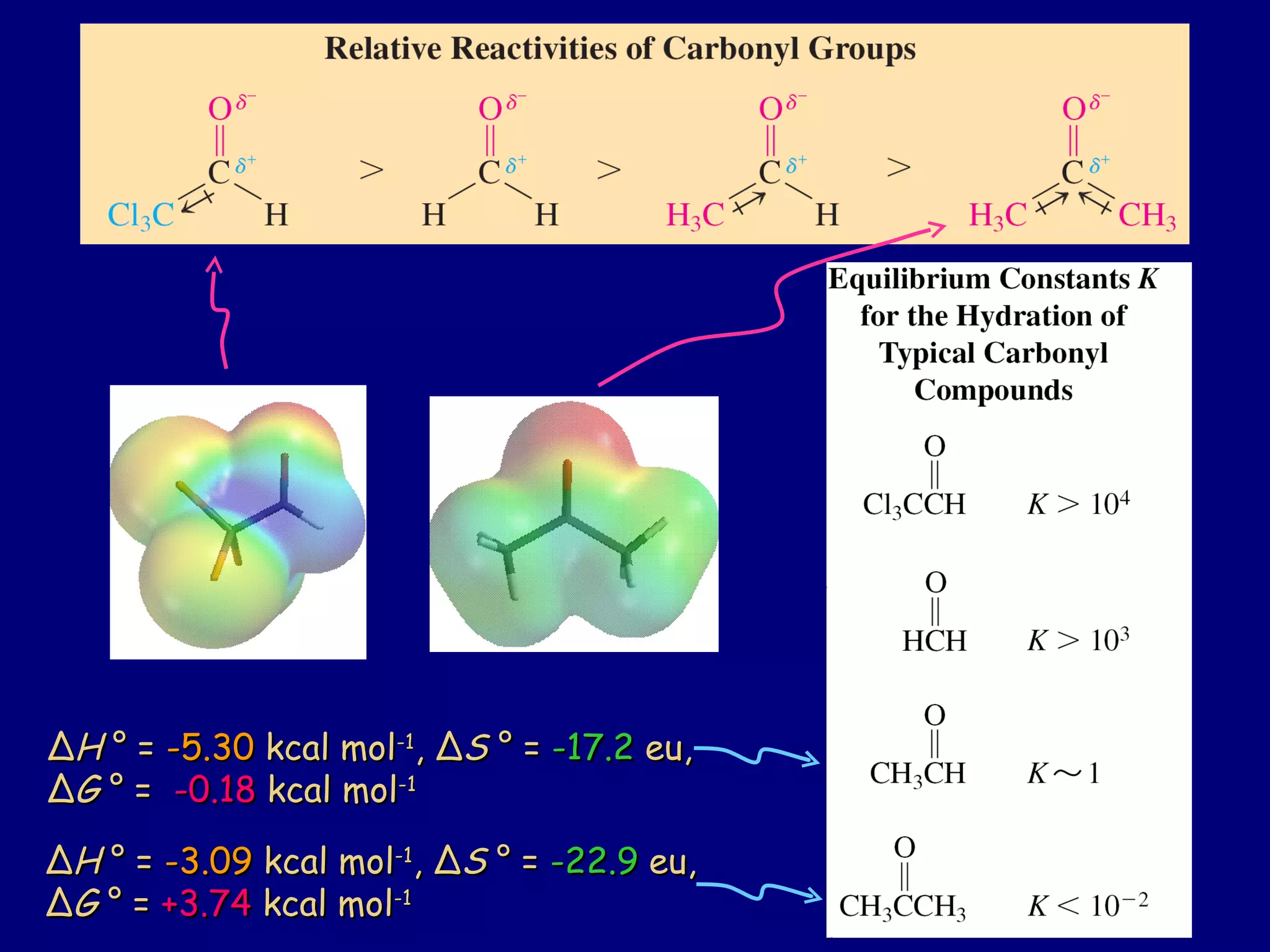
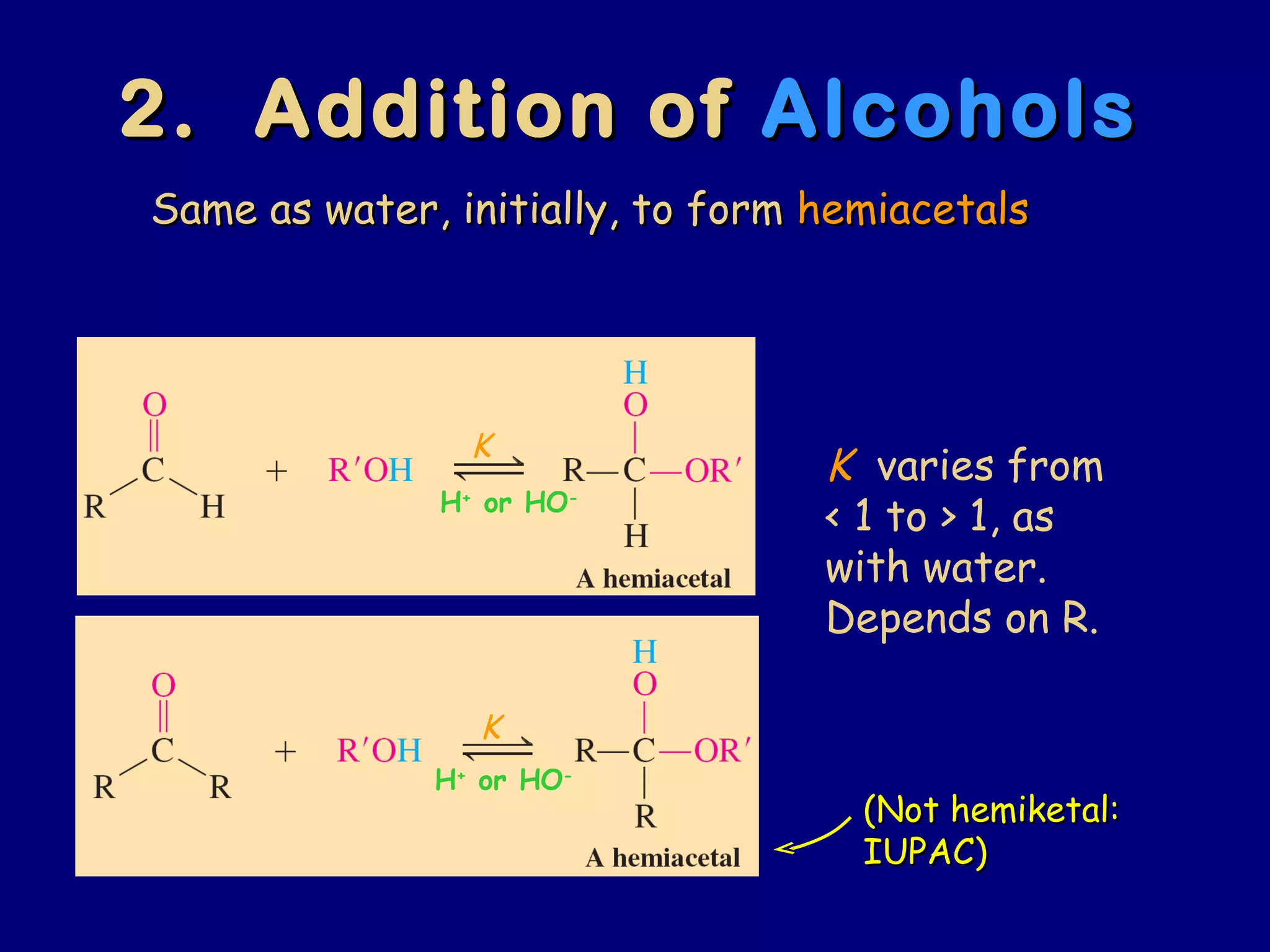
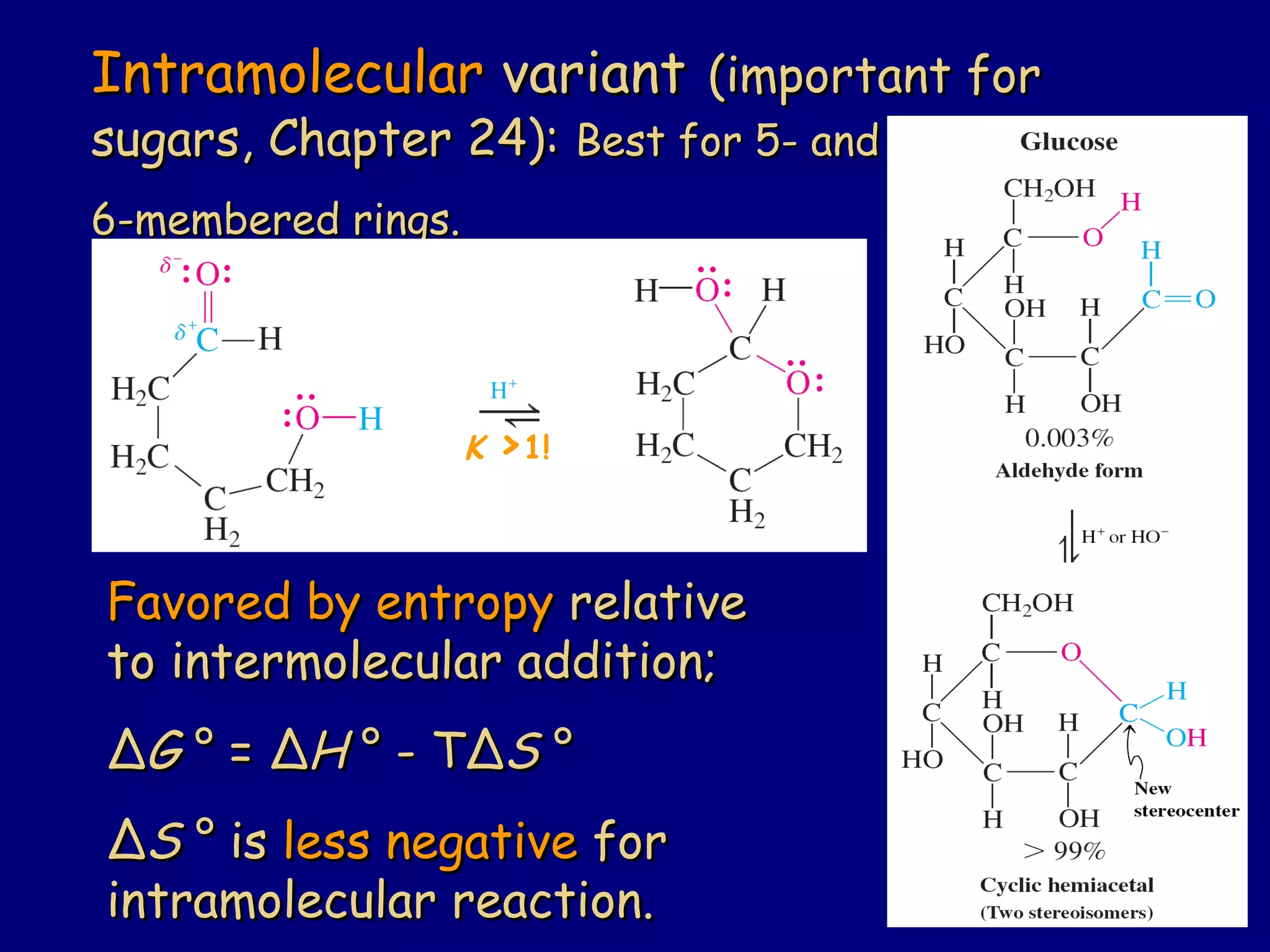
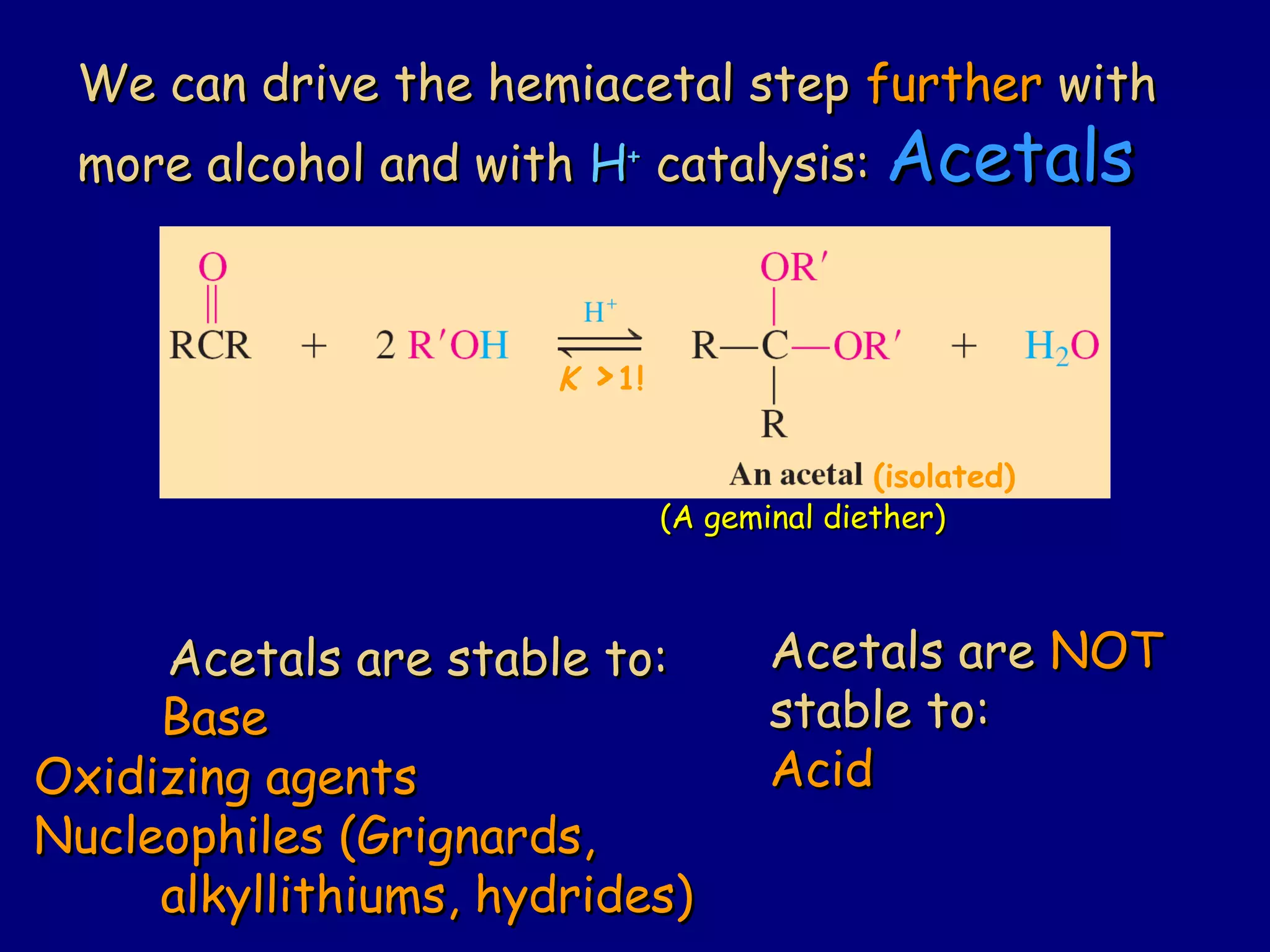
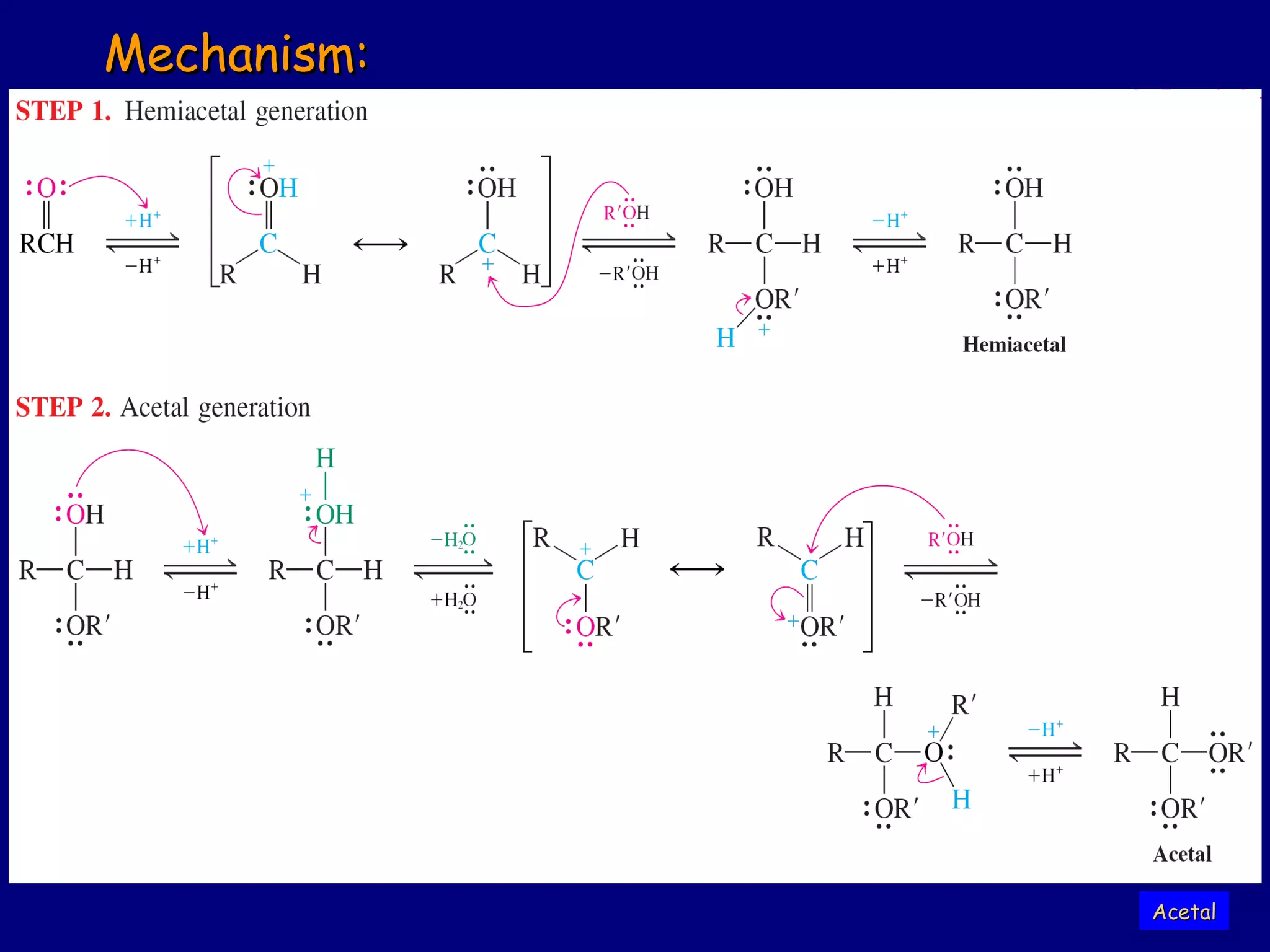
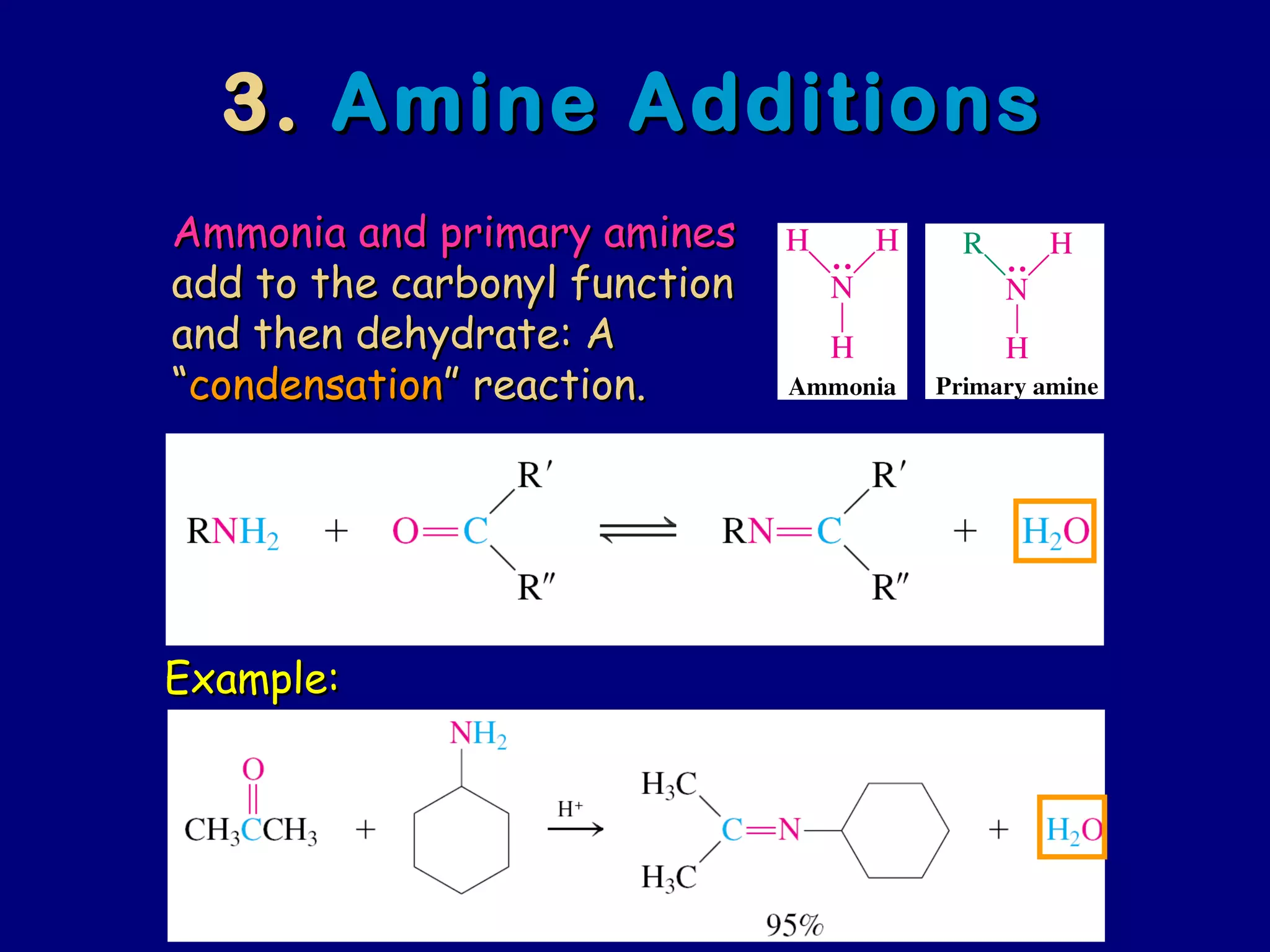
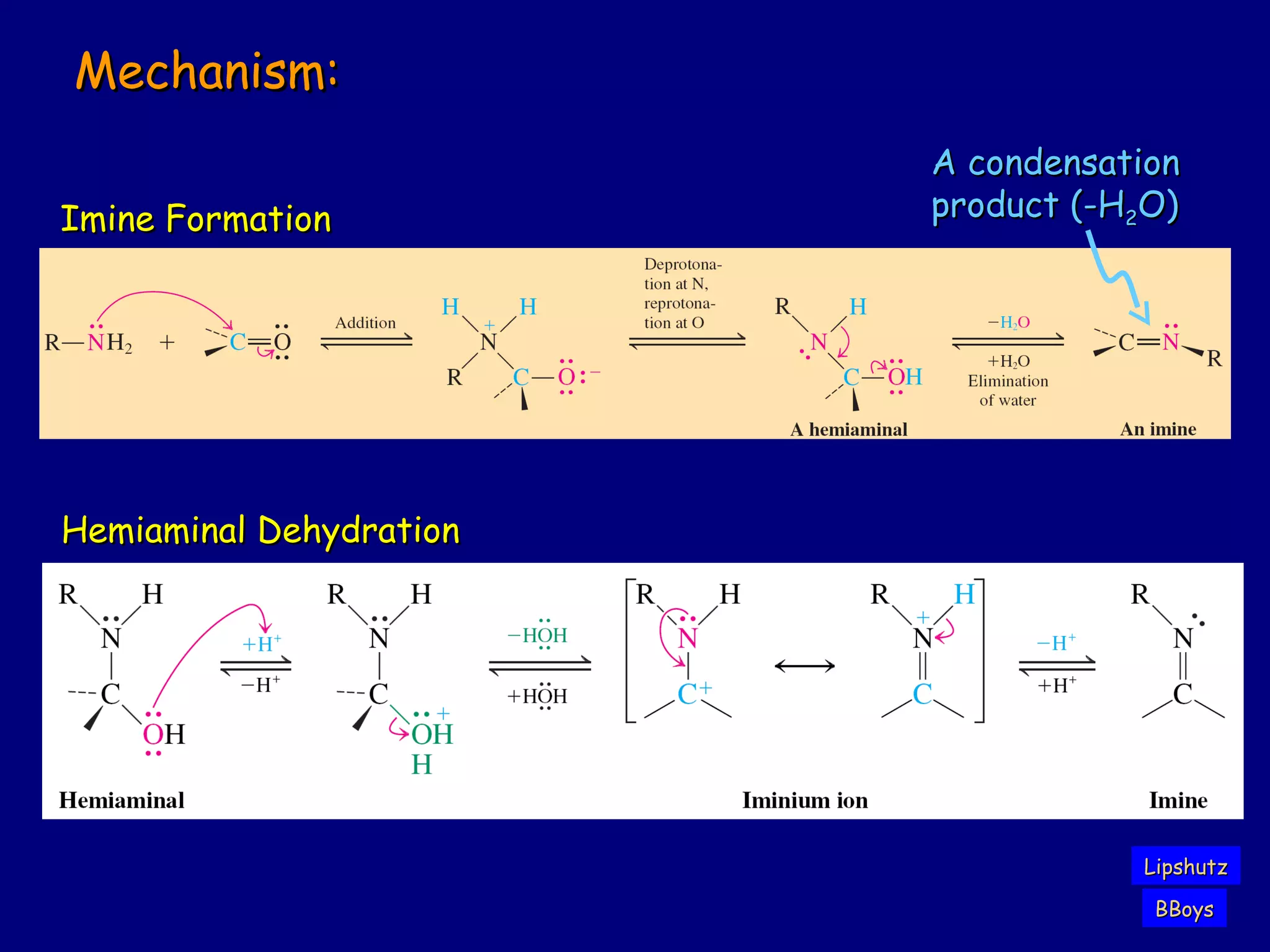
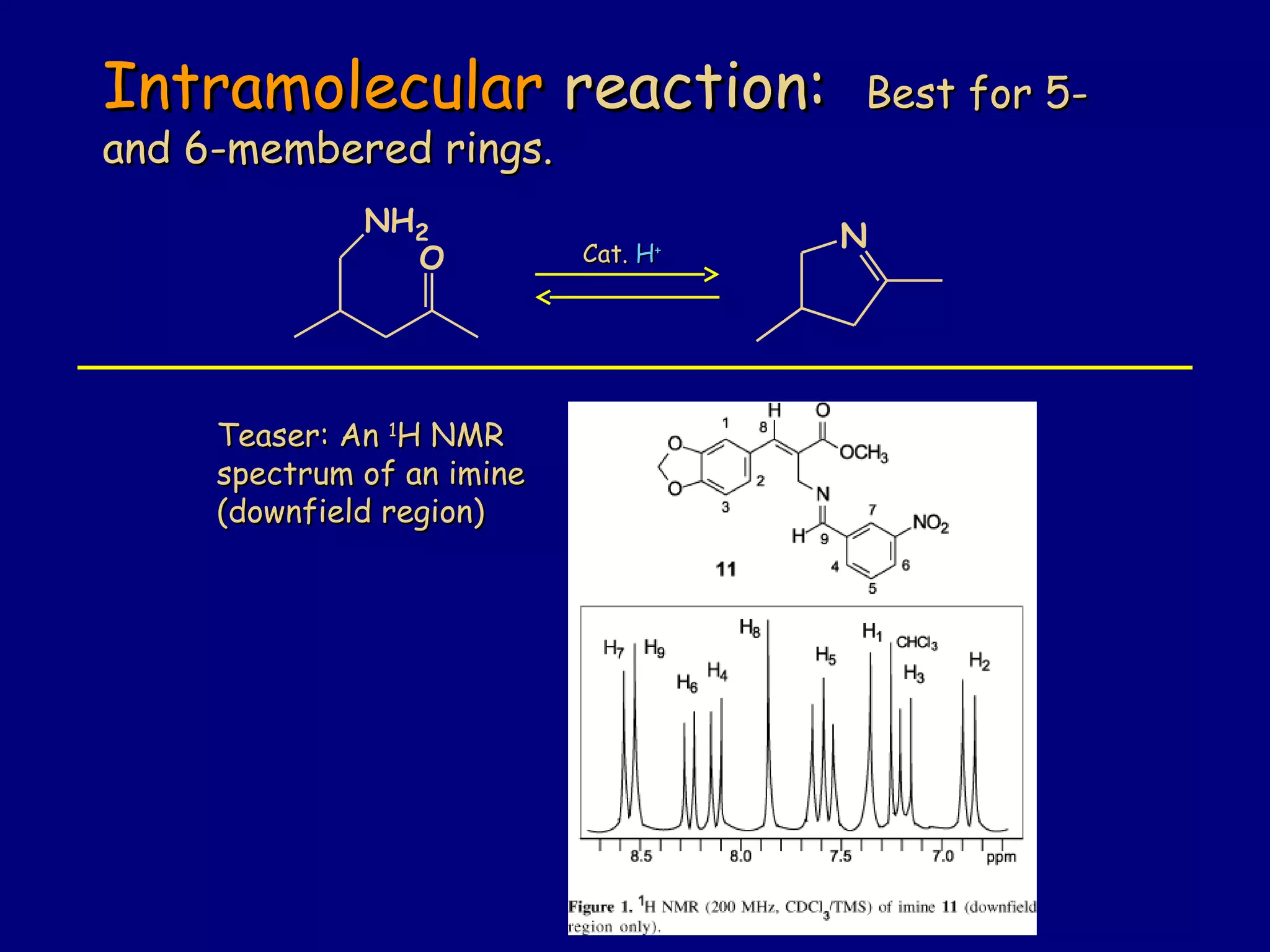
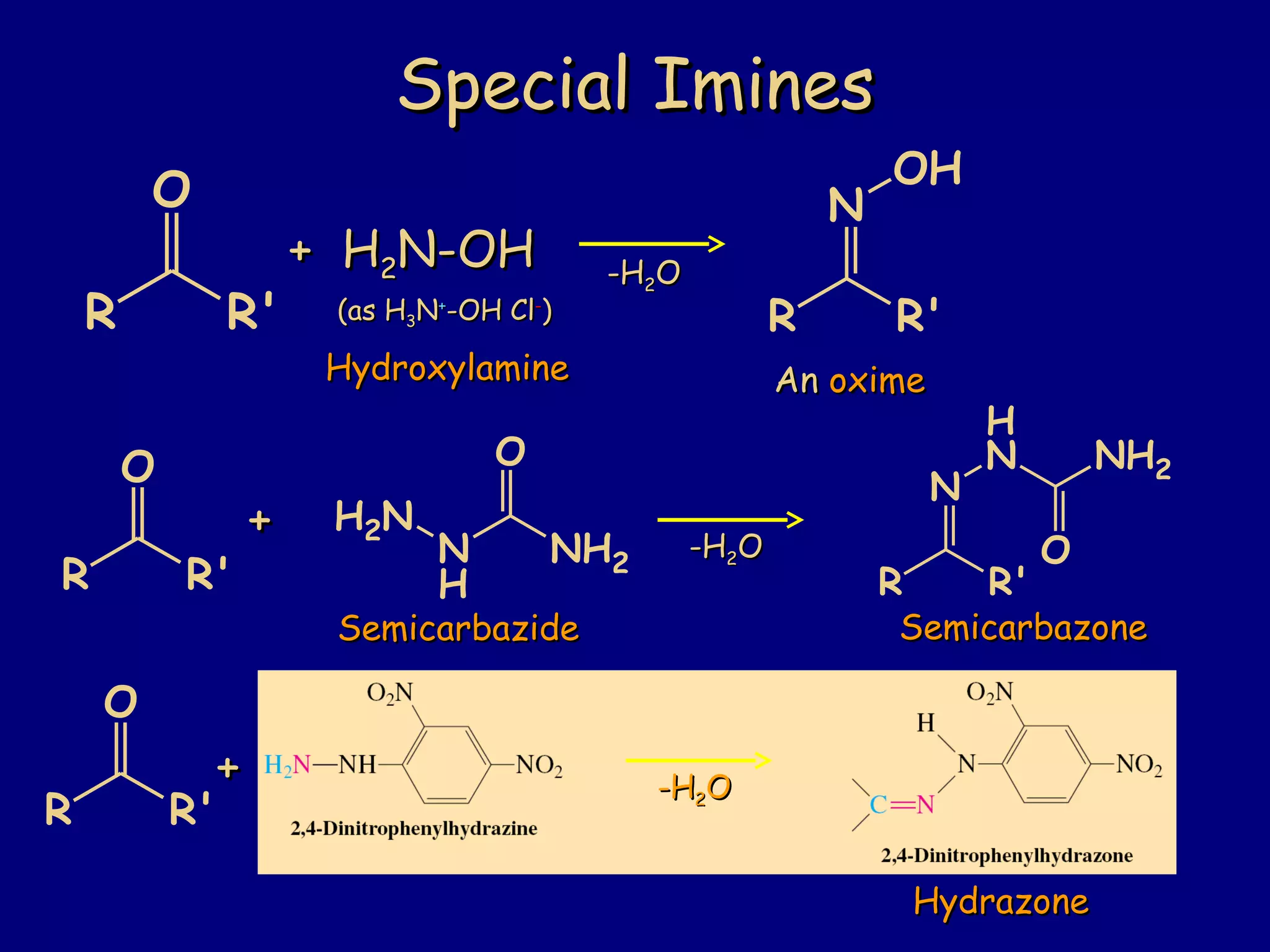
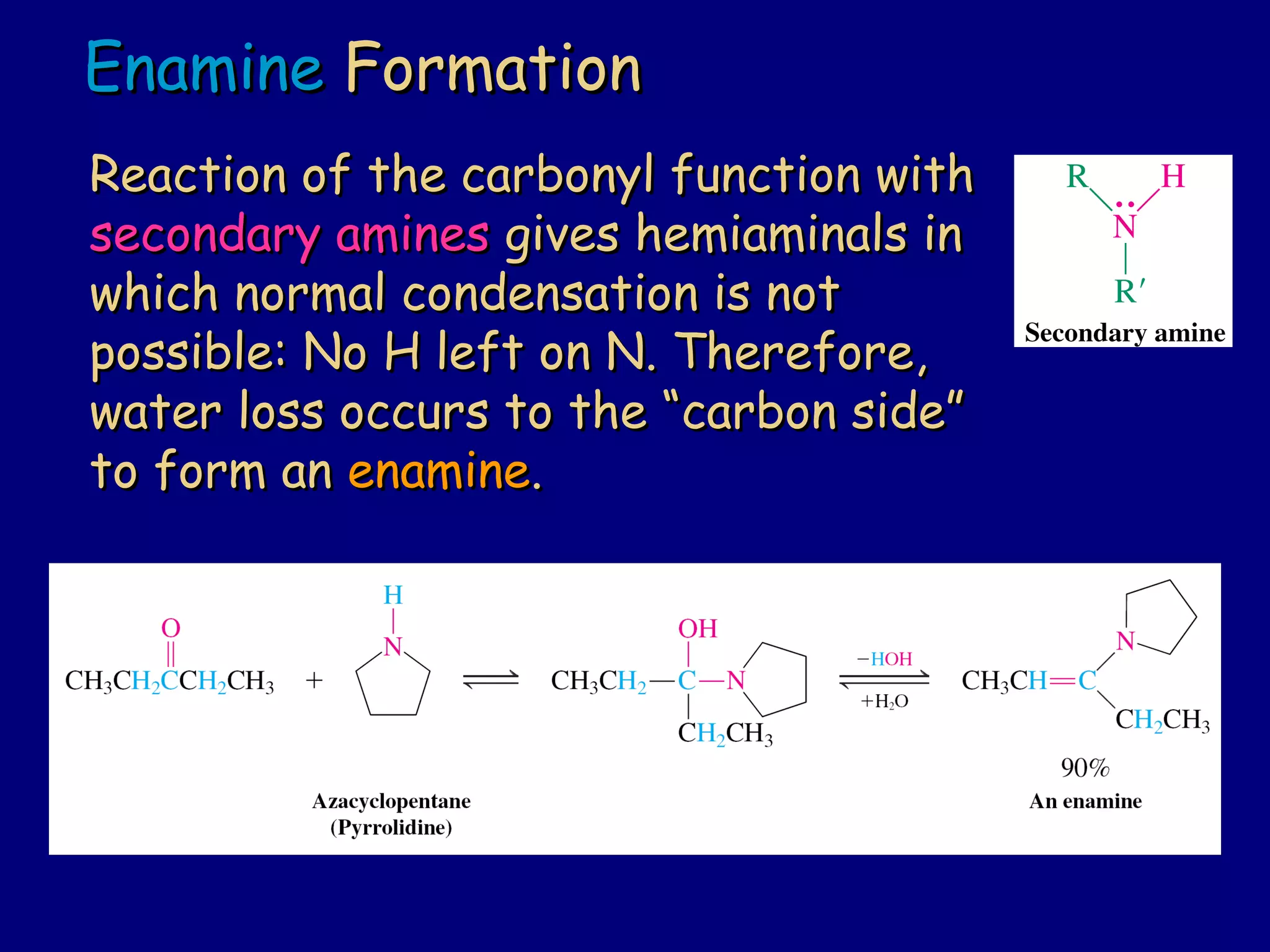
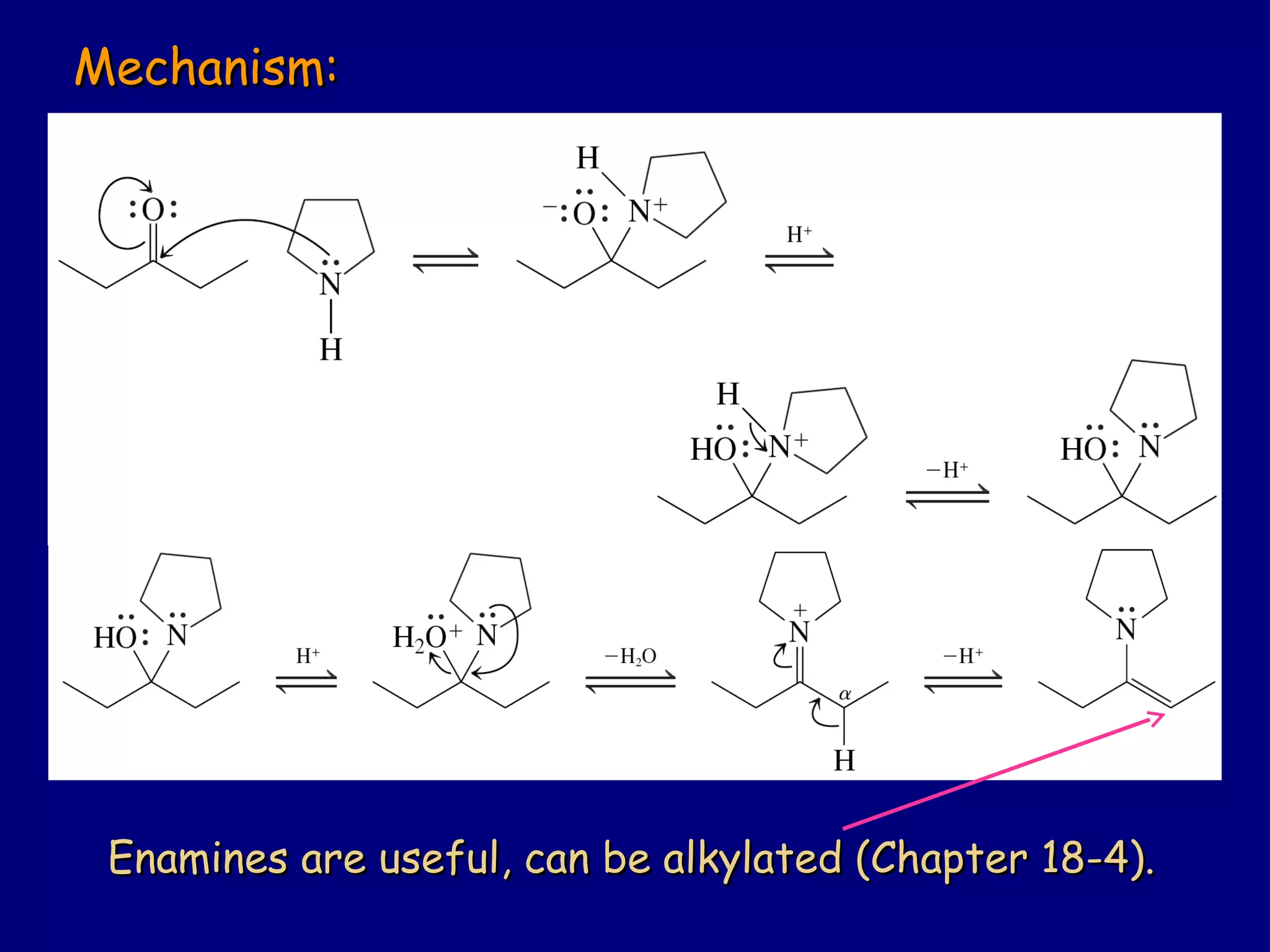
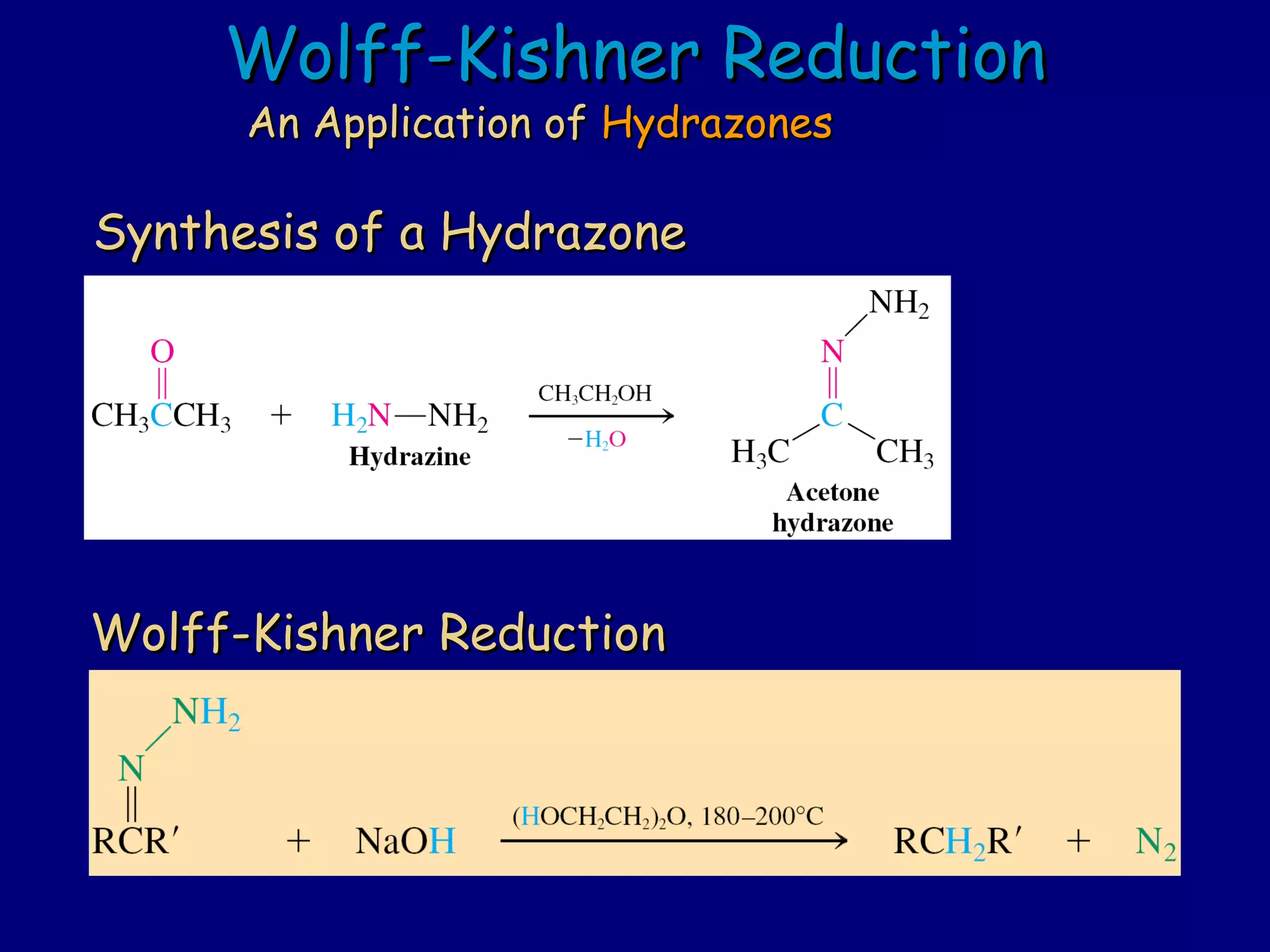
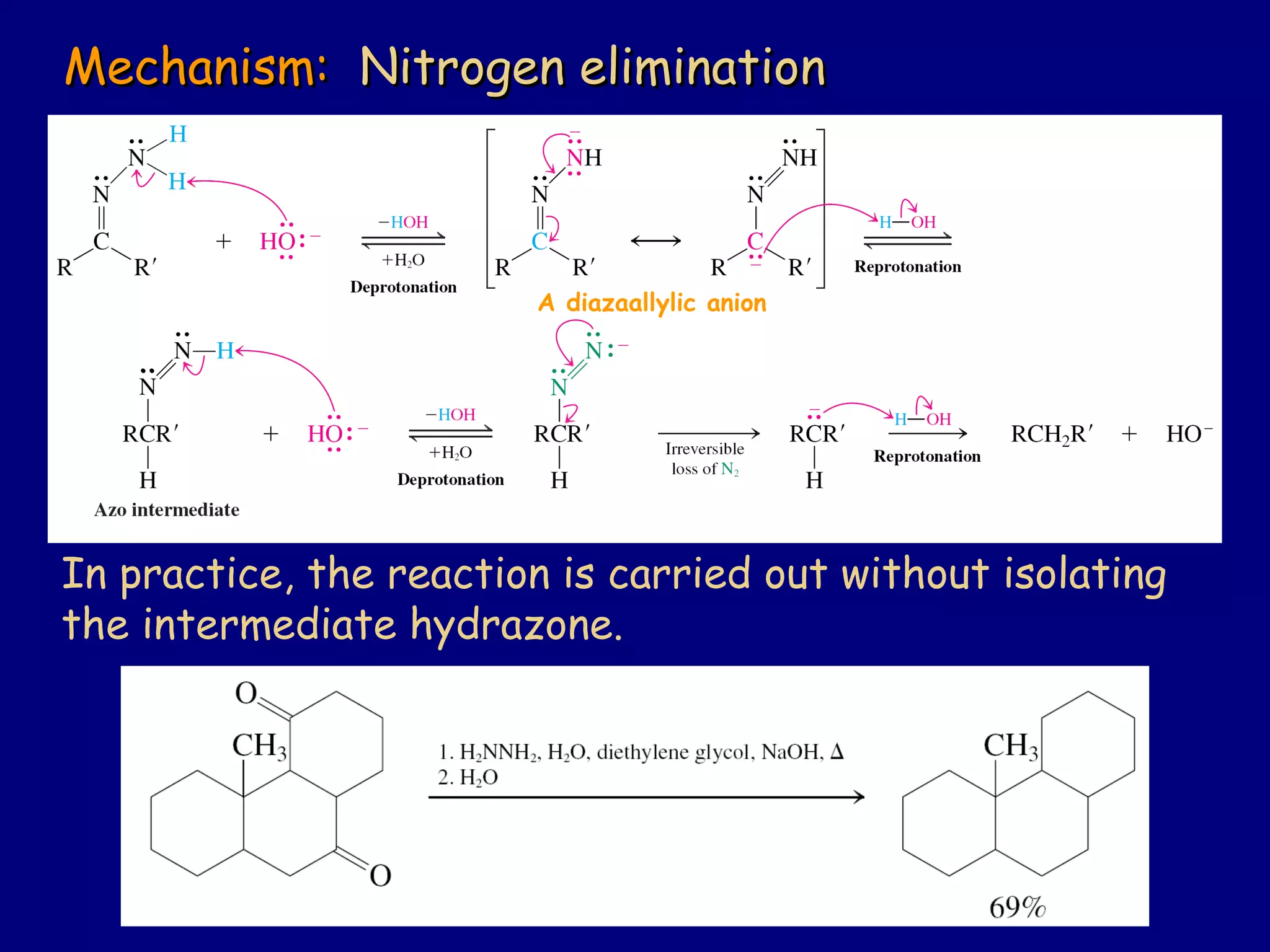
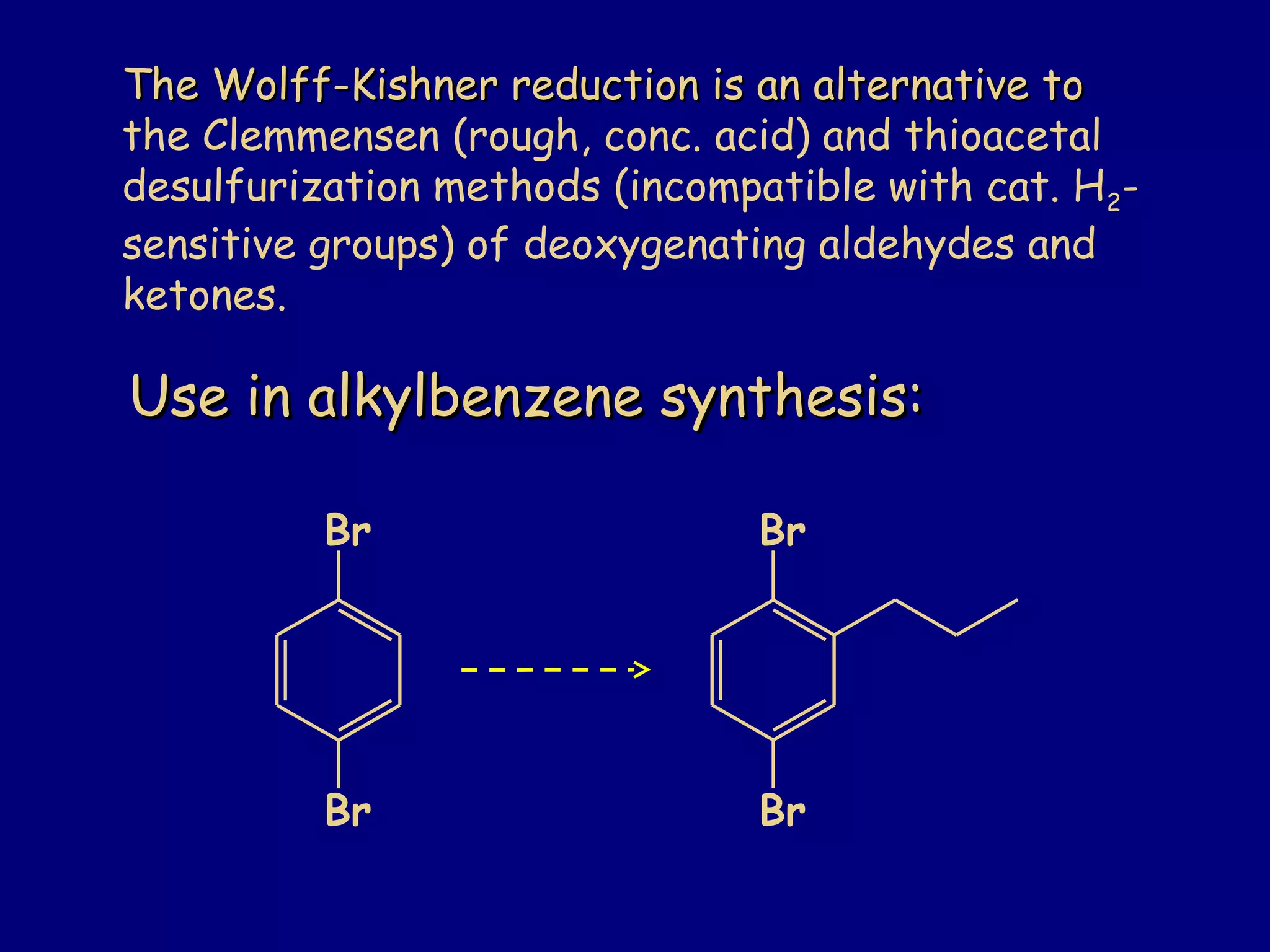
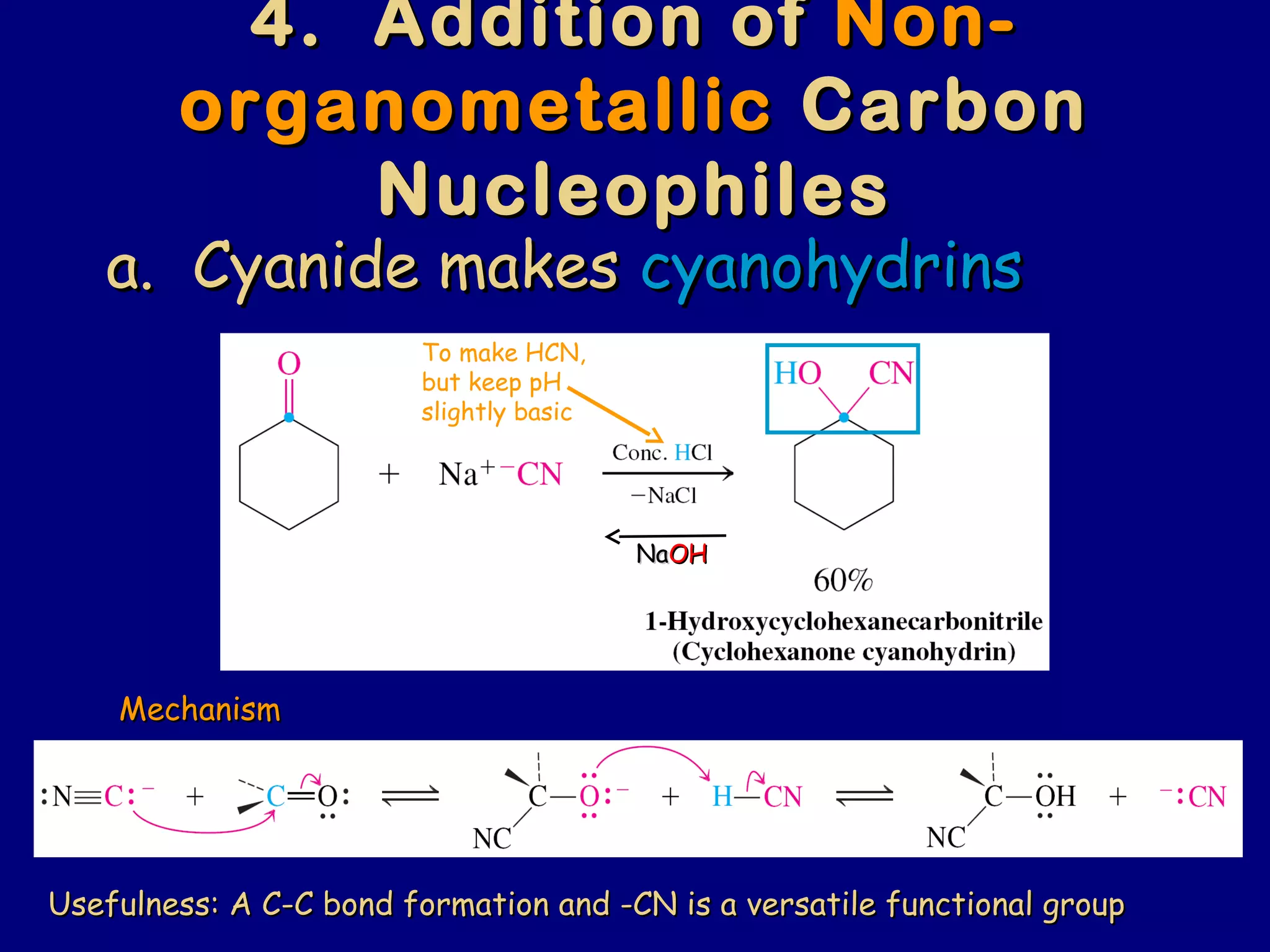
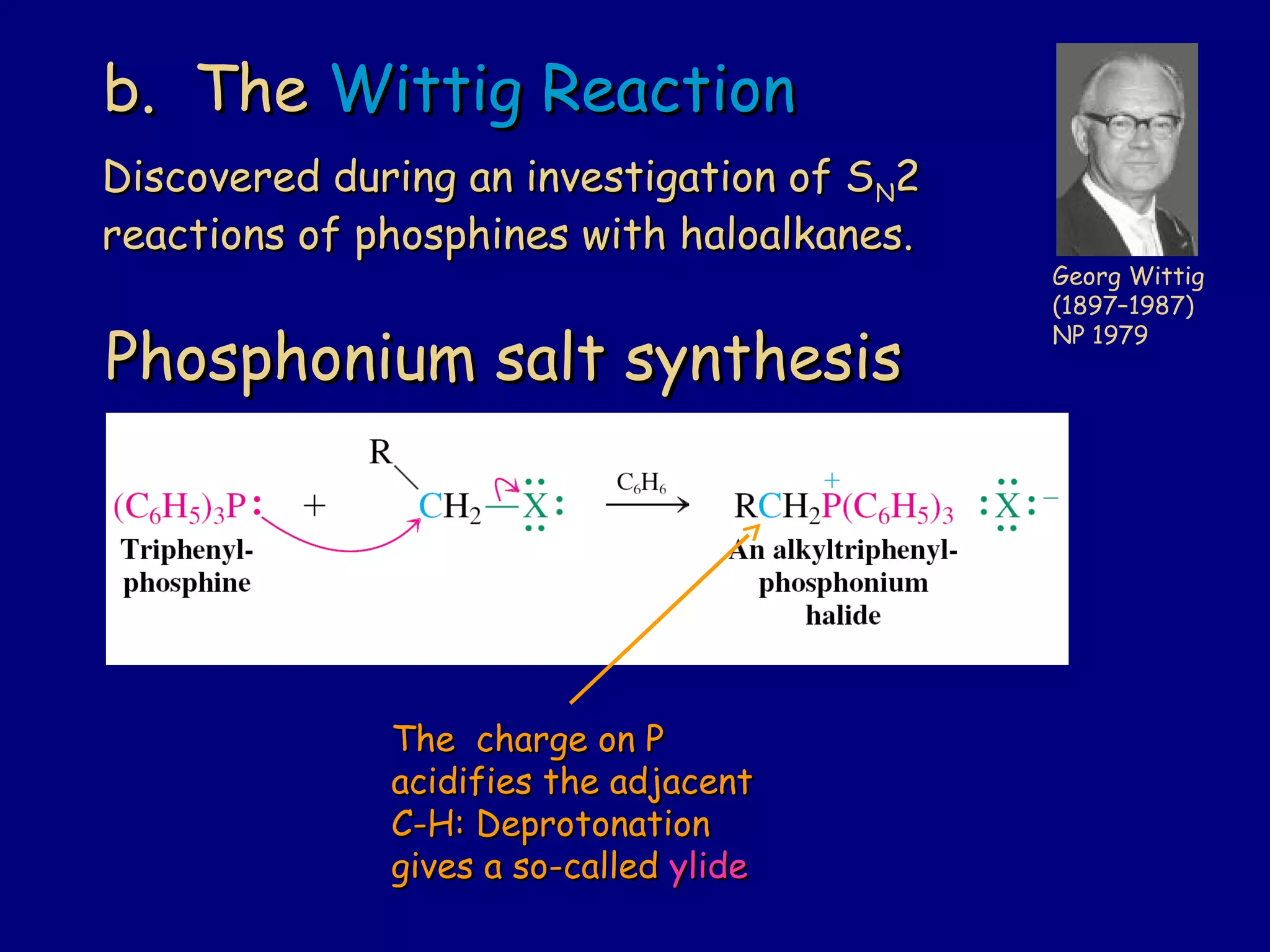
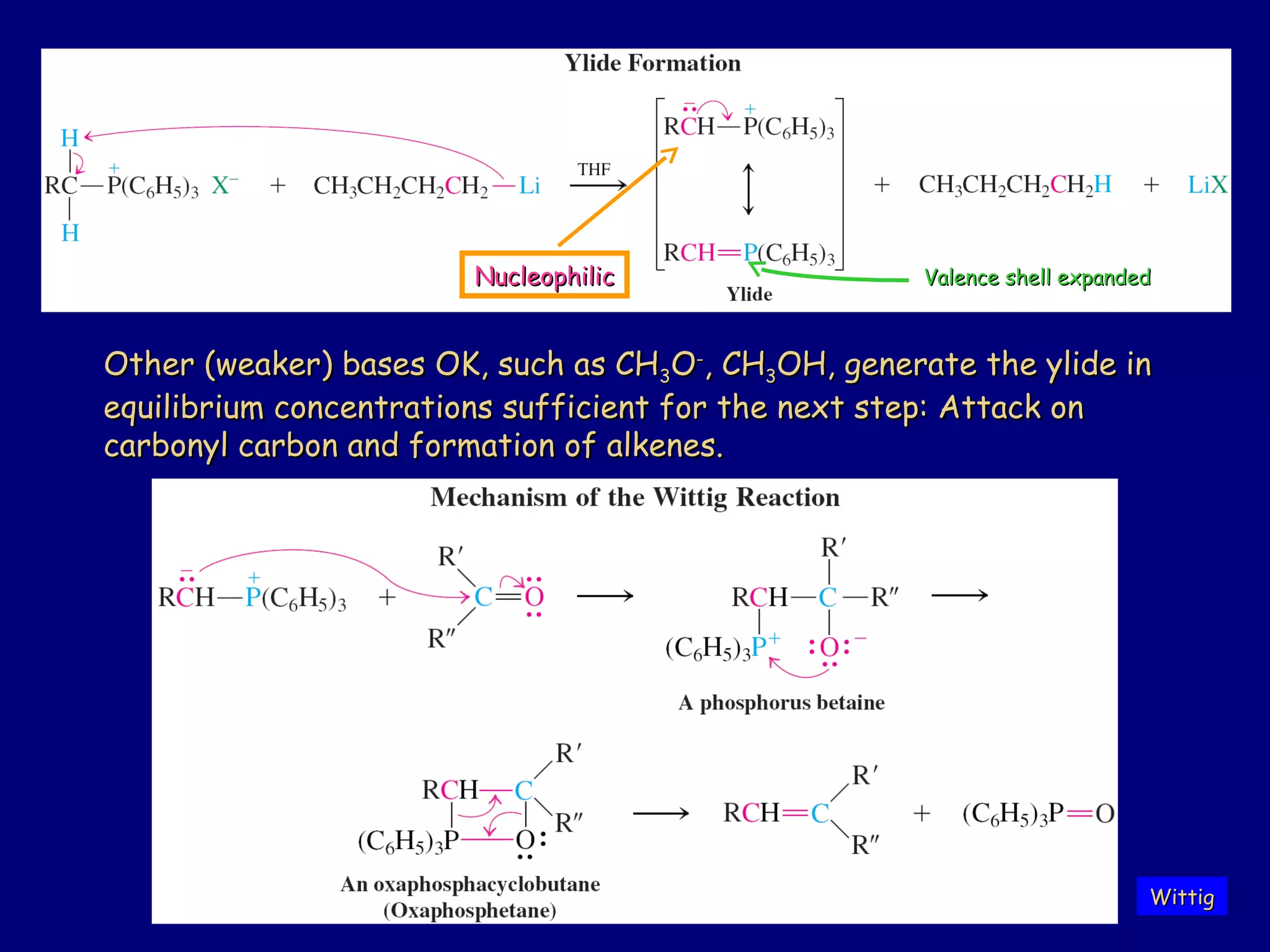
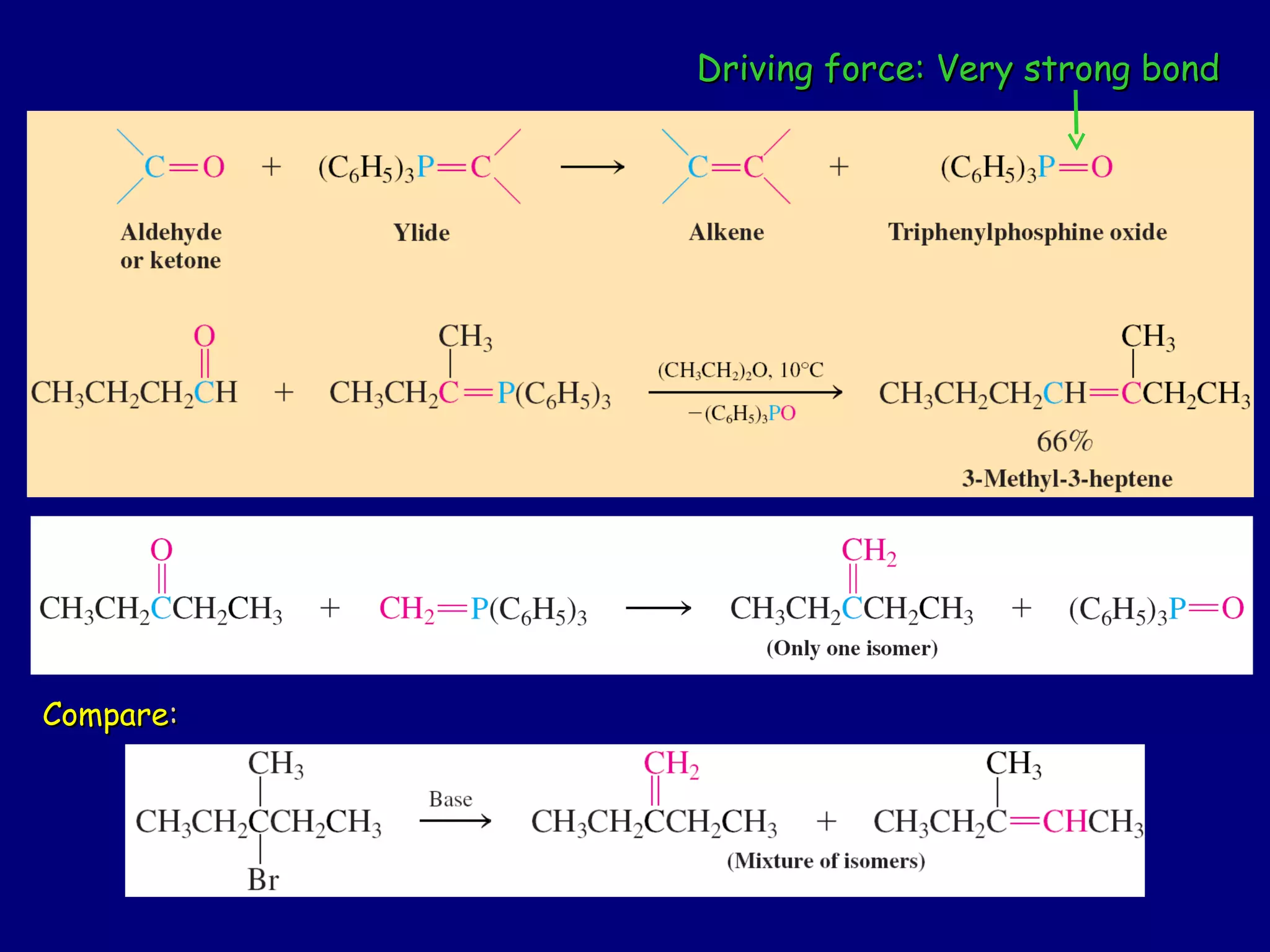
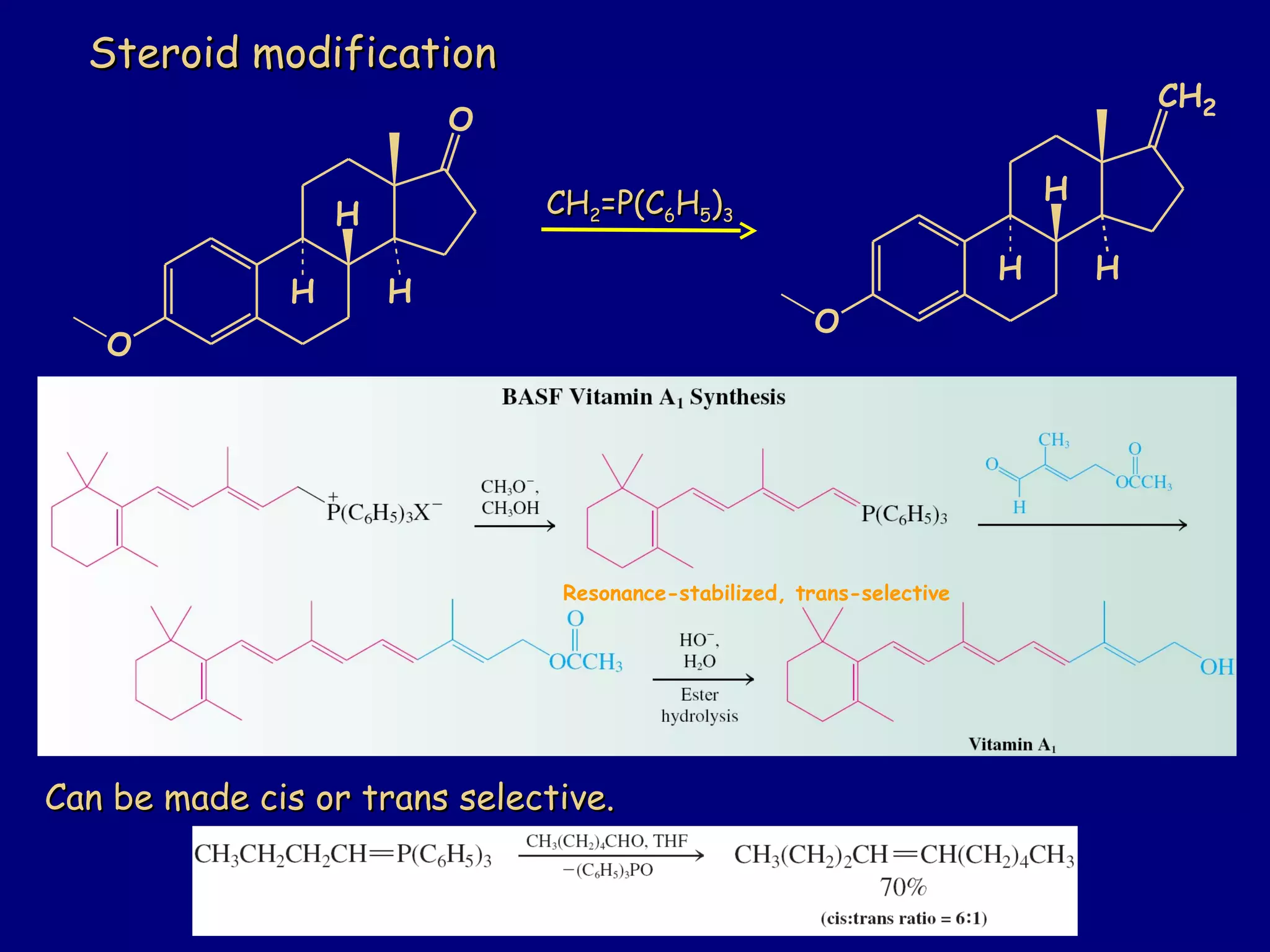
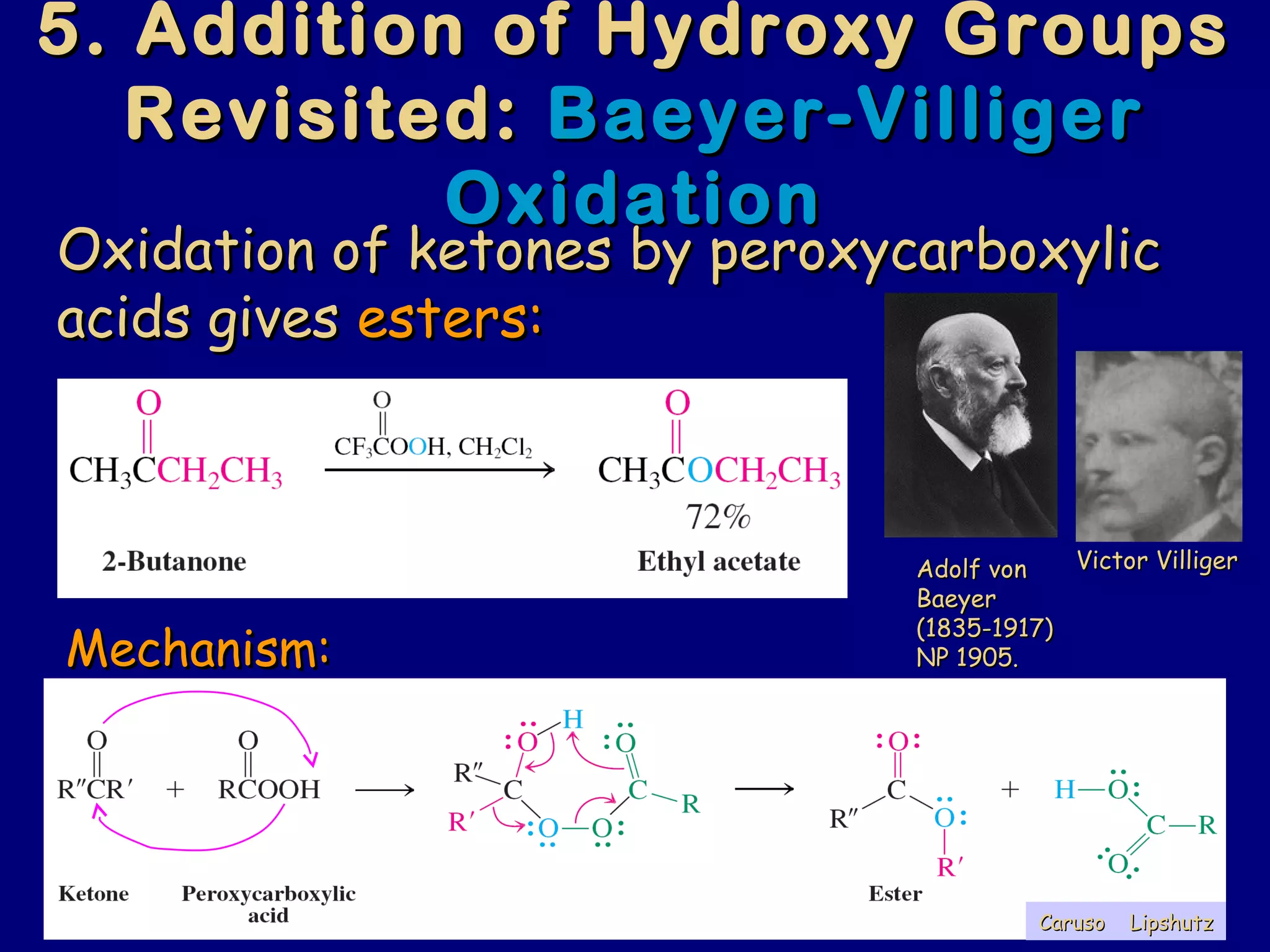
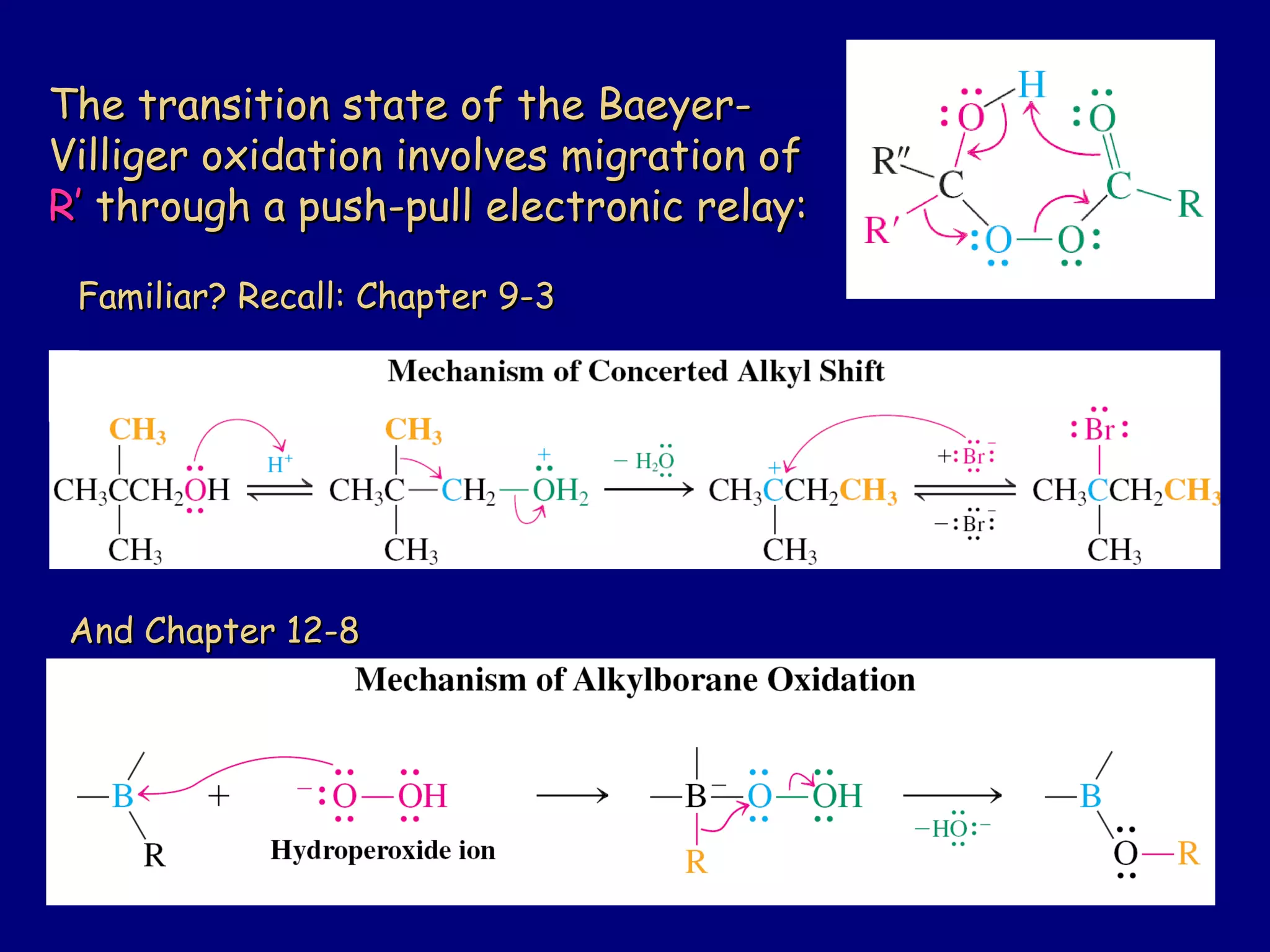
Aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl functional group consisting of a carbon double-bonded to an oxygen. They exhibit characteristic reactivity including nucleophilic addition reactions that form alcohols. Aldehydes and ketones undergo hydration to form geminal diols, addition of alcohols to form hemiacetals and acetals, and addition of amines to form imines through a condensation reaction. Their carbonyl group absorbs strongly in the infrared region and gives deshielded peaks in NMR spectroscopy due to polarization effects.