This document discusses enolate chemistry, including the formation and reactivity of enolates. It describes:
1. How enolates are formed through deprotonation of ketones using bases, and how the pKa values of acidic protons can predict suitable bases.
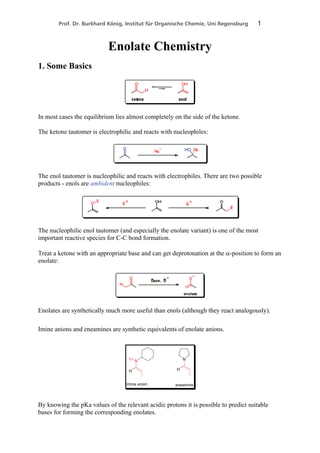
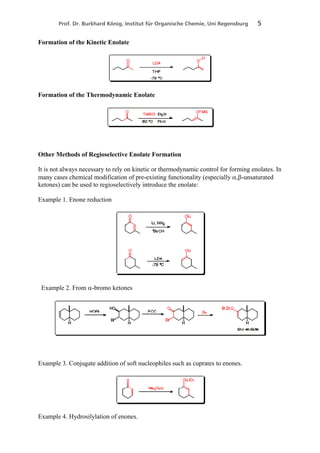
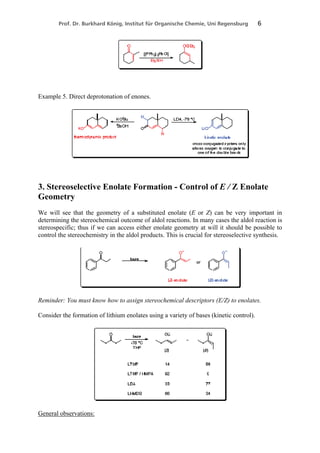
2. Methods for regioselective and stereoselective enolate formation, including kinetic vs thermodynamic control and the factors that influence each.
3. Important reactions of enolates including silyl enol ether formation, alkylation, reactions with enones, and aldol reactions. It highlights the need for regioselective and stereoselective control in aldol reactions.
4. How lithium, bor






![Prof. Dr. Burkhard König, Institut für Organische Chemie, Uni Regensburg 10
Claisen Rearrangement (an example of a [3,3]-sigmatropic shift)
his is an important example of STRATEGIC PATTERN RECOGNITIONT
2 The Crossed Aldol Reaction4.
• One of the most important methods for C-C bond formation.
• Very widely used in organic synthesis.
All the issues previously discussed (1-3) and more (4-6) now become very important:
2. complete or partial enolisation (self vs. cross condensation)
important when chiral aldehydes react with
ral enolates)
of one carbonyl group reacts with the carbonyl group
(usually an aldehyde) of another. To avoid self condensation, the enolate component is
formed beforehand.
1. regioselective enolate formation (kinetic and thermodynamic enolates)
3. stereochemistry of the enolate (E or Z)
4. simple diastereoselection - (syn and anti aldol products)
5. diastereofacial selectivity (this becomes
achiral enolates and when achiral aldehydes react with chi
6. double diastereodifferentiation (reaction of chiral aldehydes with chiral enolates) -
matched and mismatched pairs.
In the crossed aldol reaction, the enolate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/enolatechemistry-08-200405061428/85/Enolate-chemistry-10-320.jpg)









