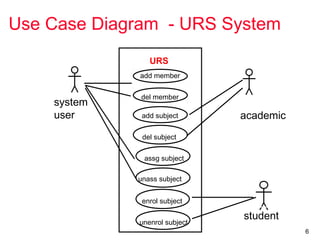
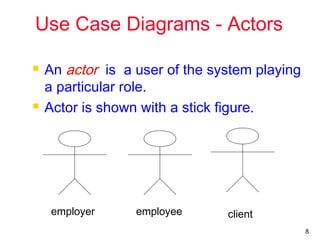
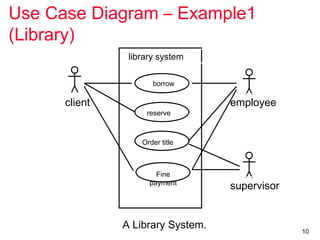
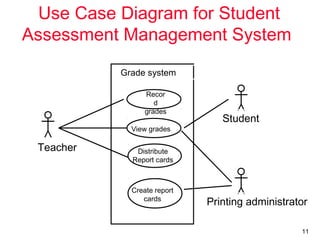
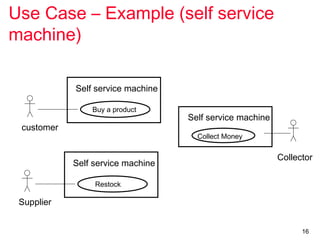
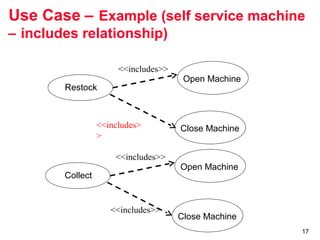
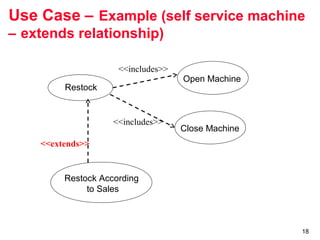
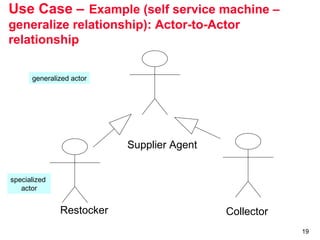
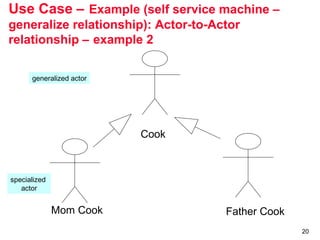
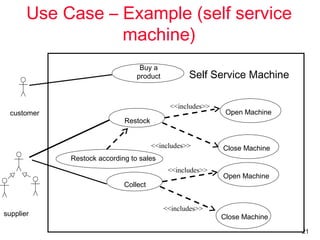
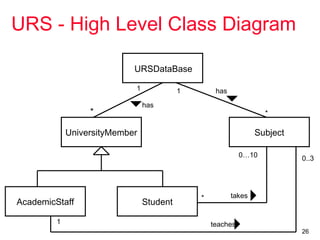
The document outlines the concept of use case diagrams in software modeling, particularly focusing on a University Record System (URS) that manages data about students and academic staff. It details the necessary information for system records, actions supported by the system, and provides examples of use cases and scenarios. Additionally, it discusses the relationships between use cases and the transition from use cases to class identification in the system.