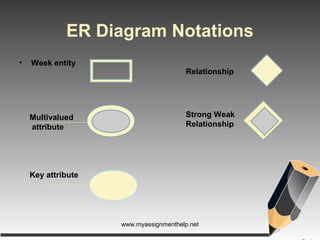
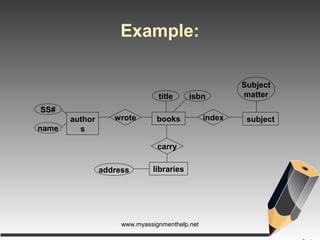
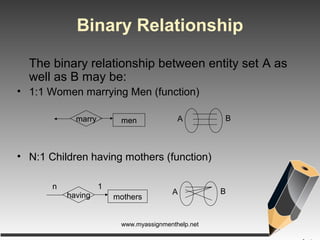
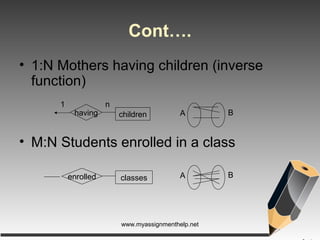
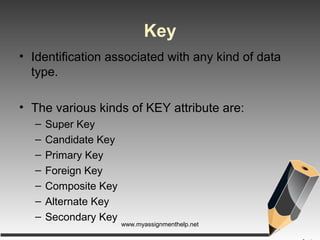
The document describes entity-relationship (E-R) diagrams, detailing entities, attributes, and relationships critical for data representation in organizations. It explains key concepts such as super key, candidate key, primary key, and foreign key, along with their roles in uniquely identifying records in database tables. Various types of relationships, including binary relationships and multi-valued attributes, are also outlined to illustrate data connections.