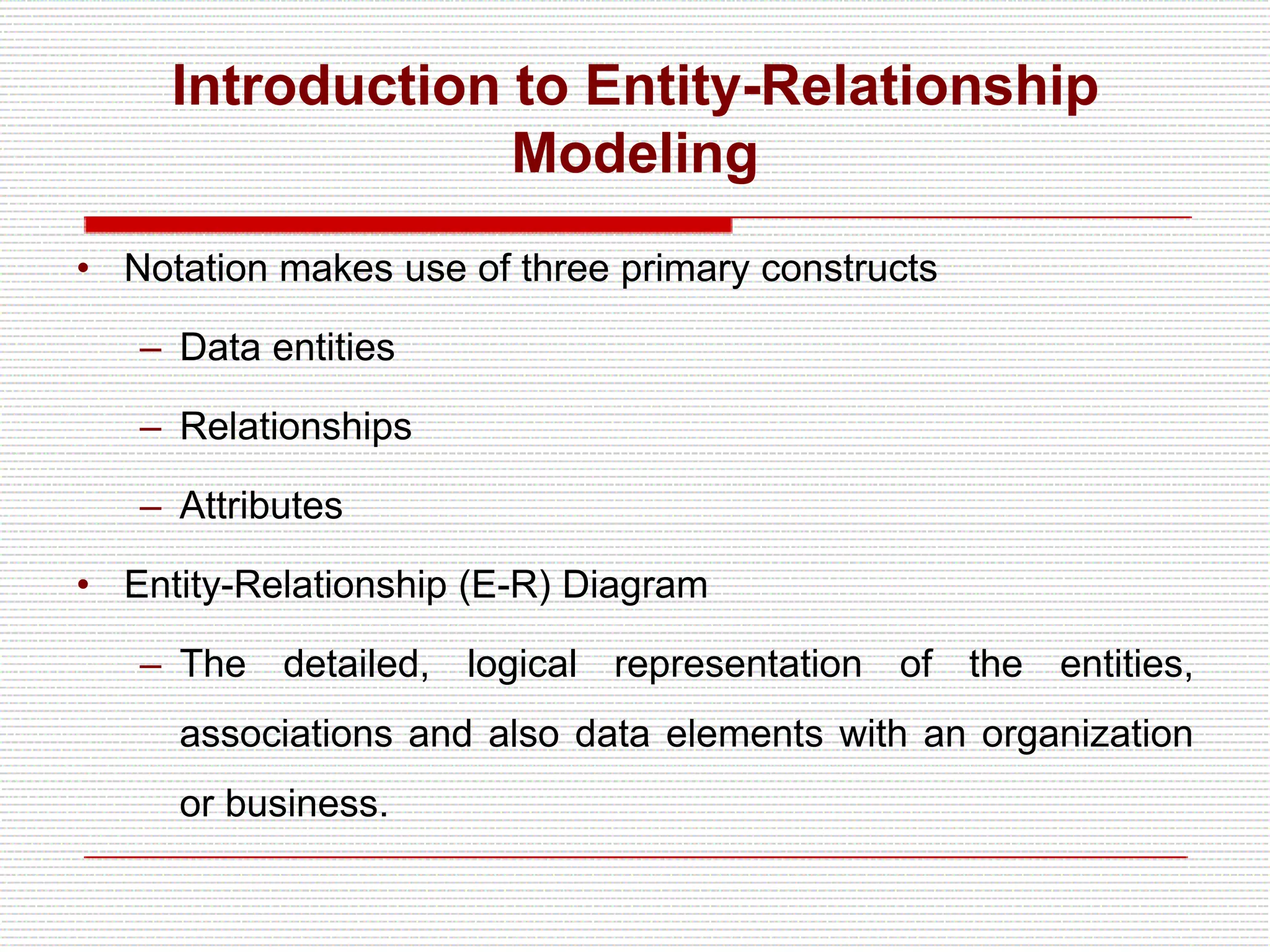
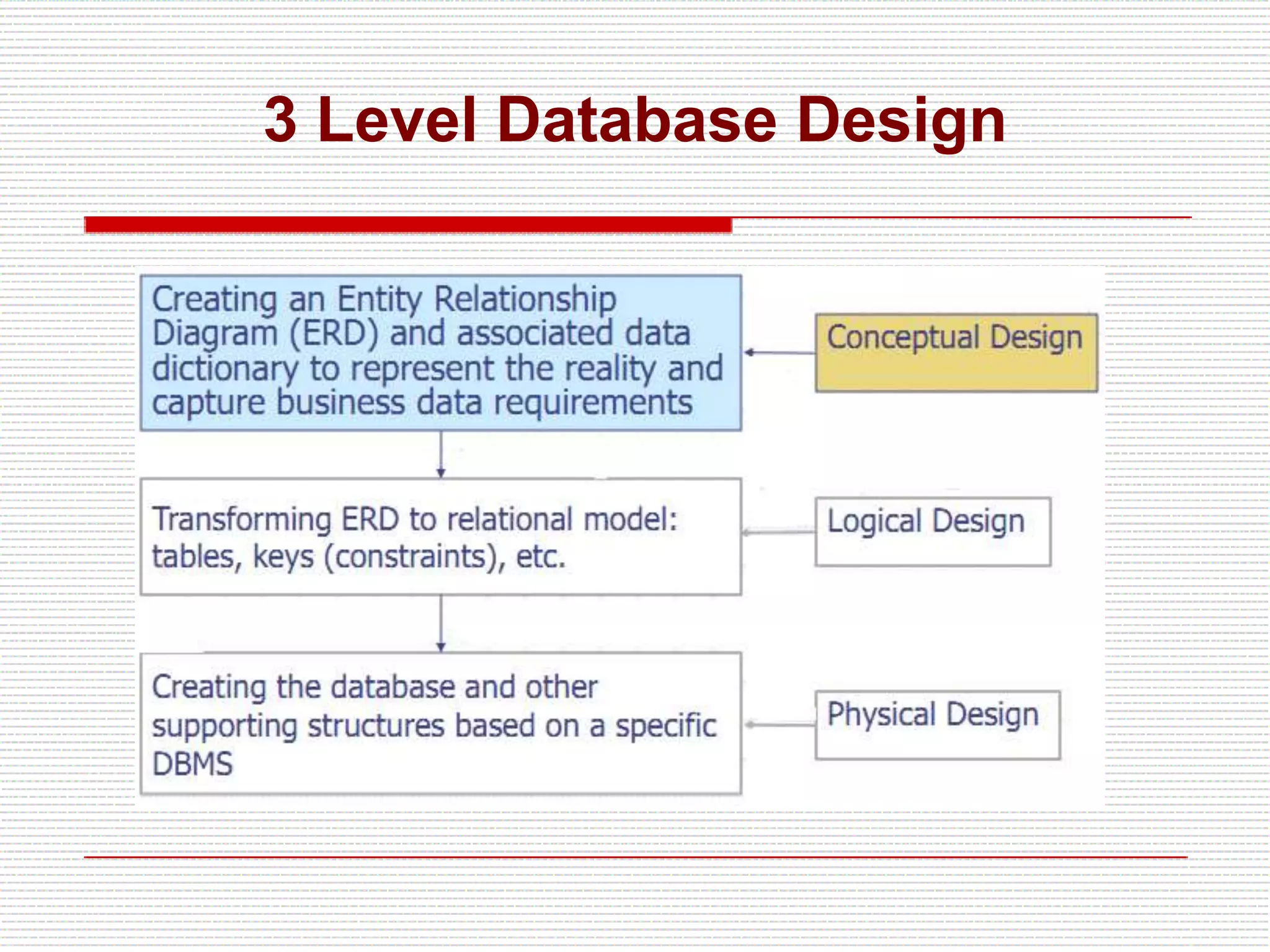
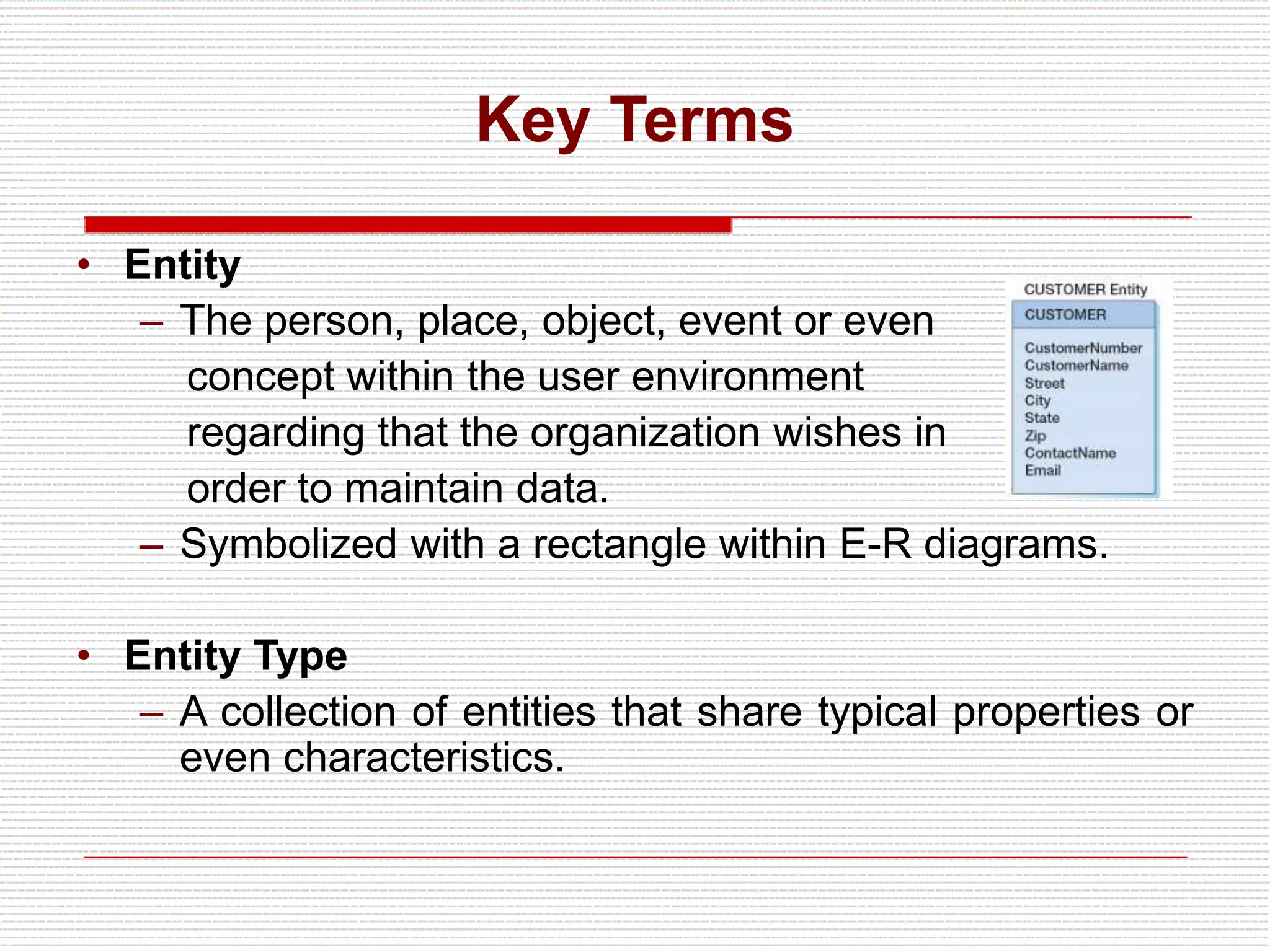
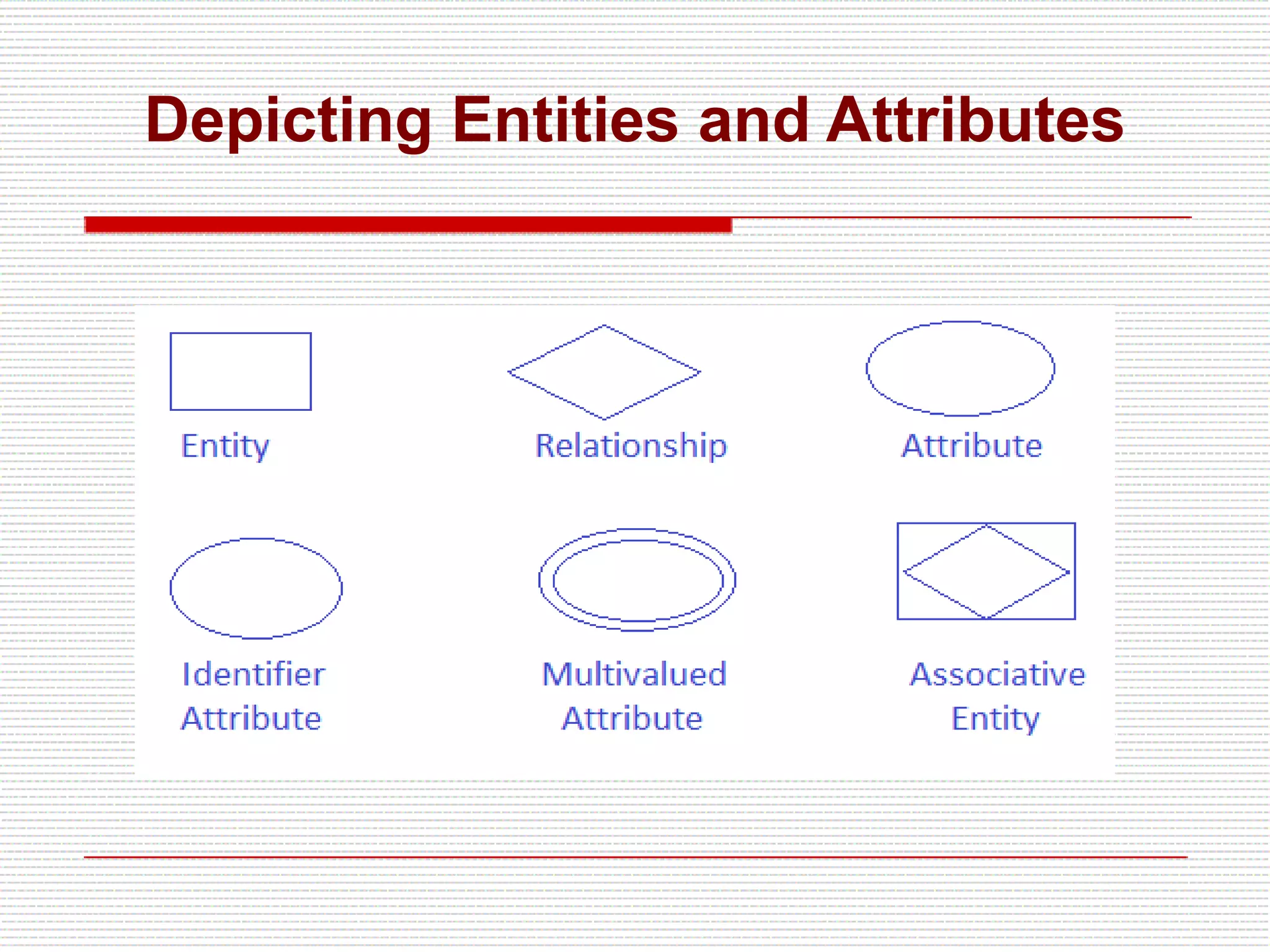
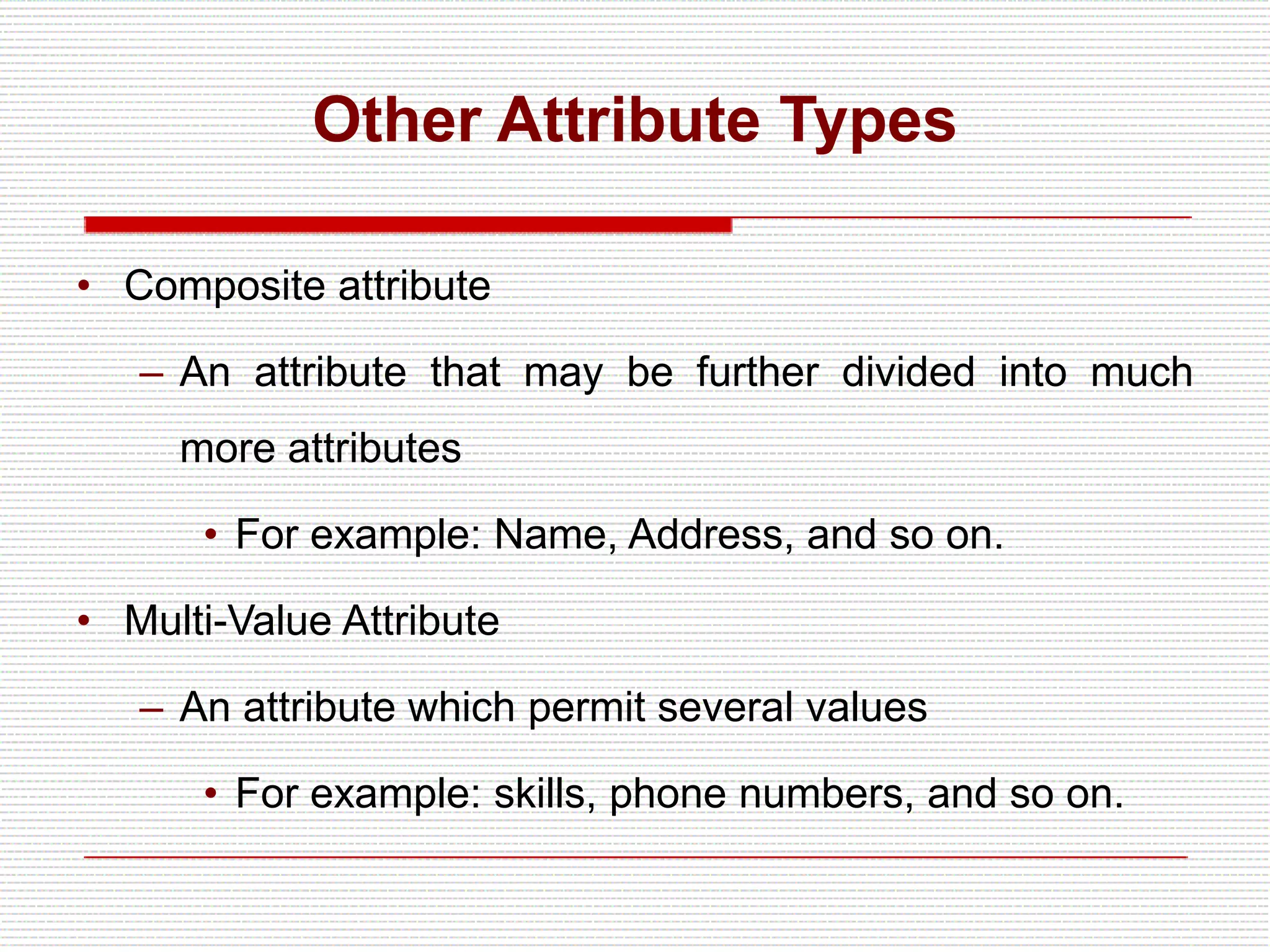
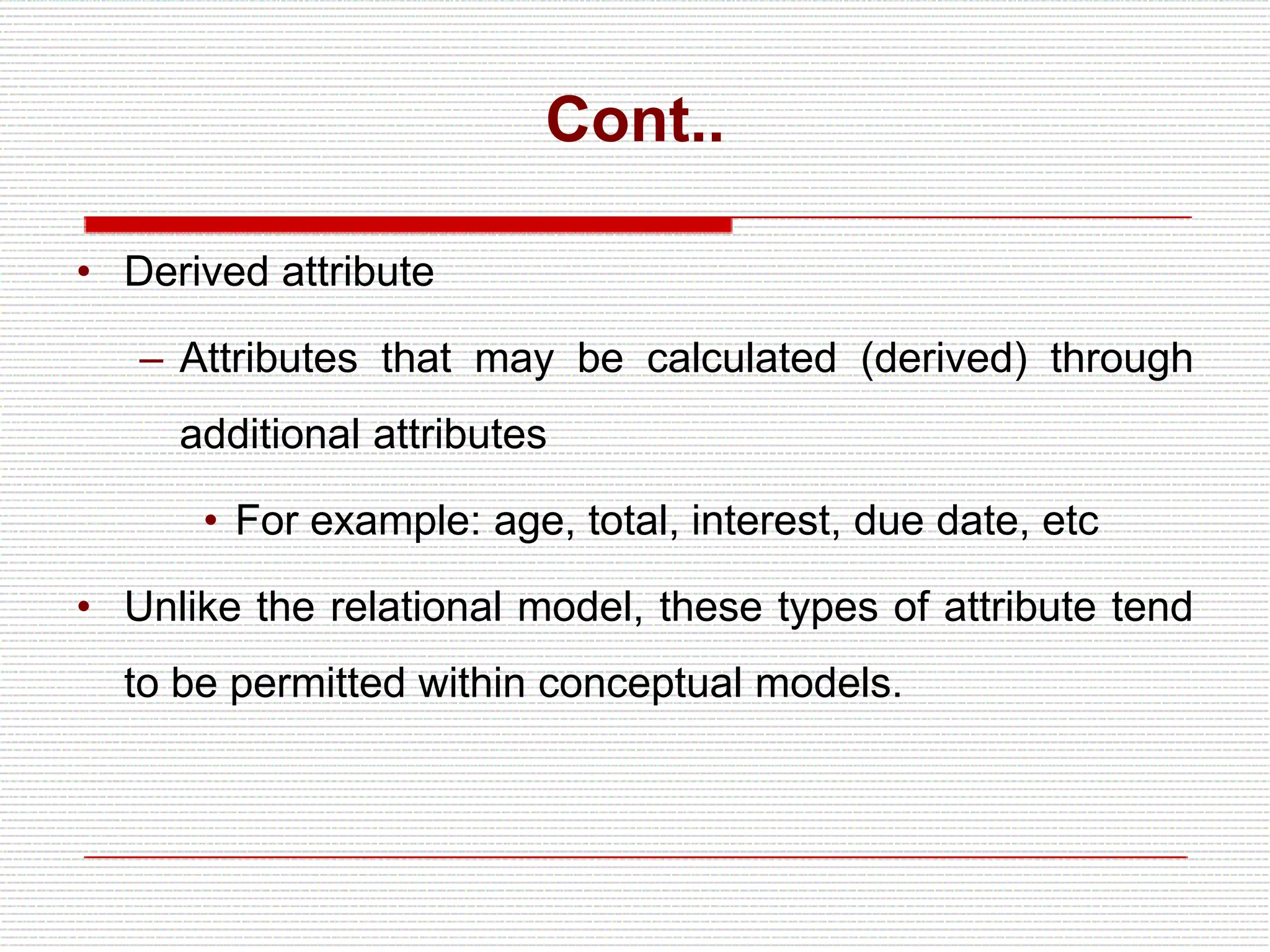
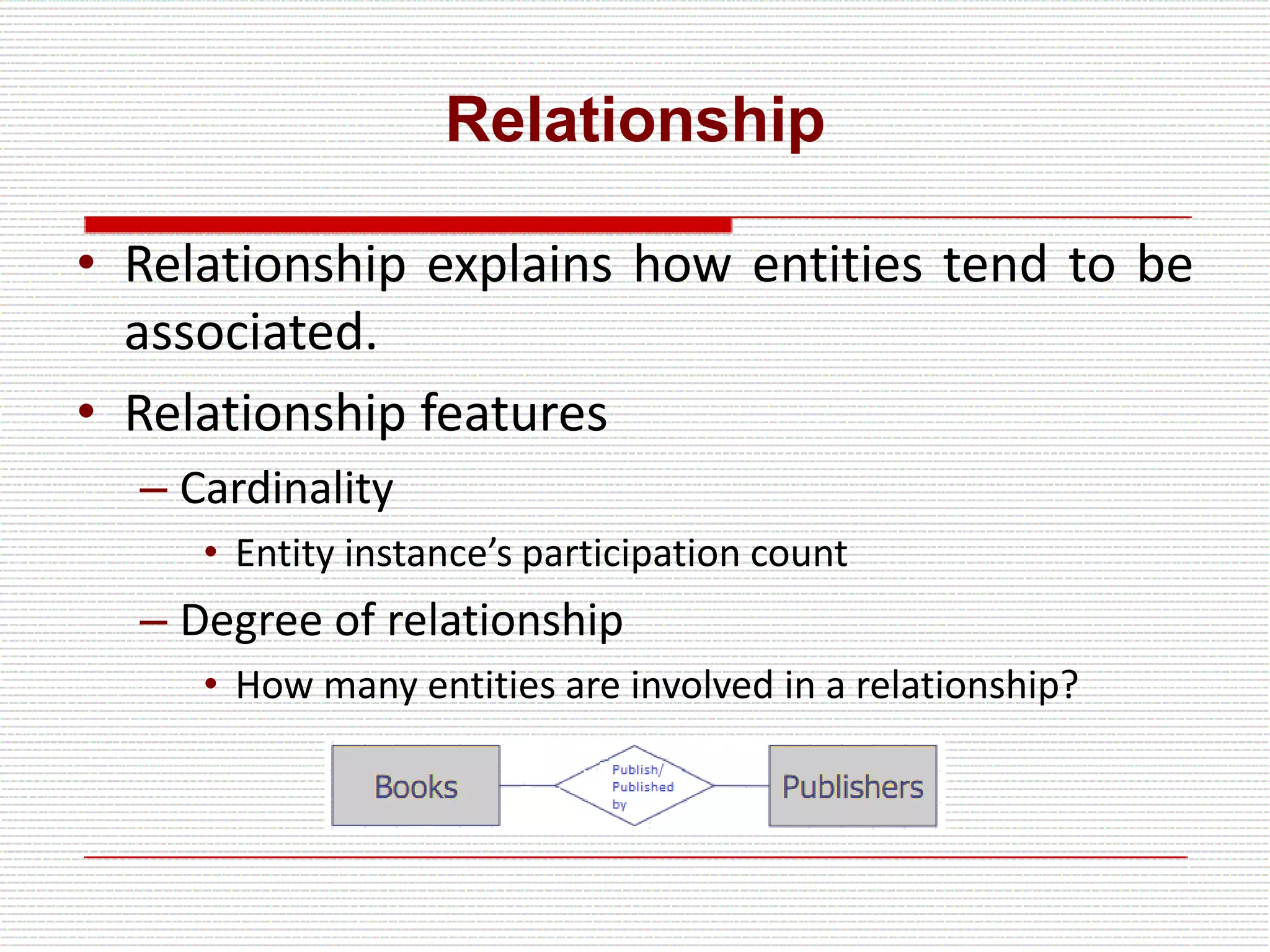
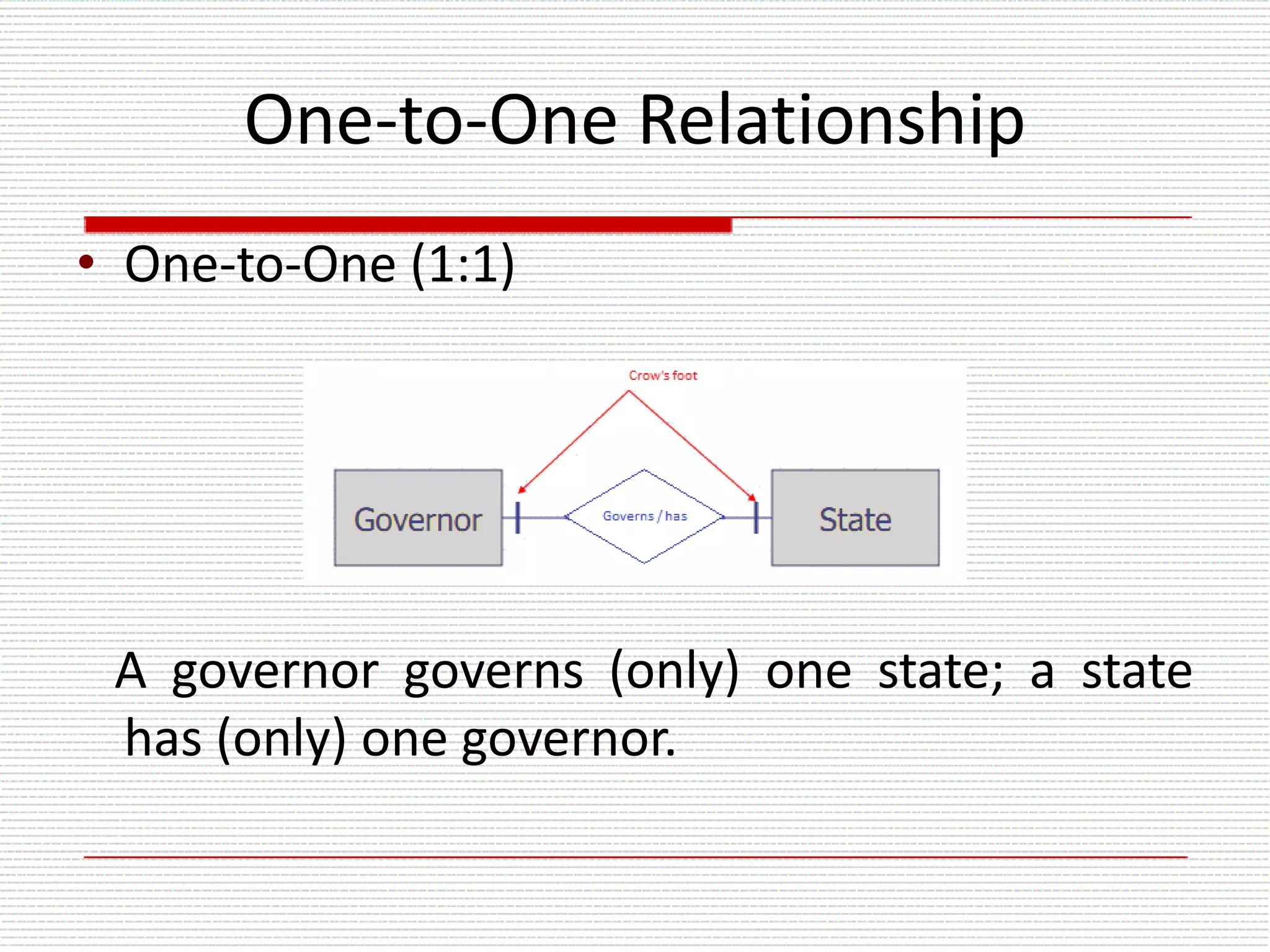
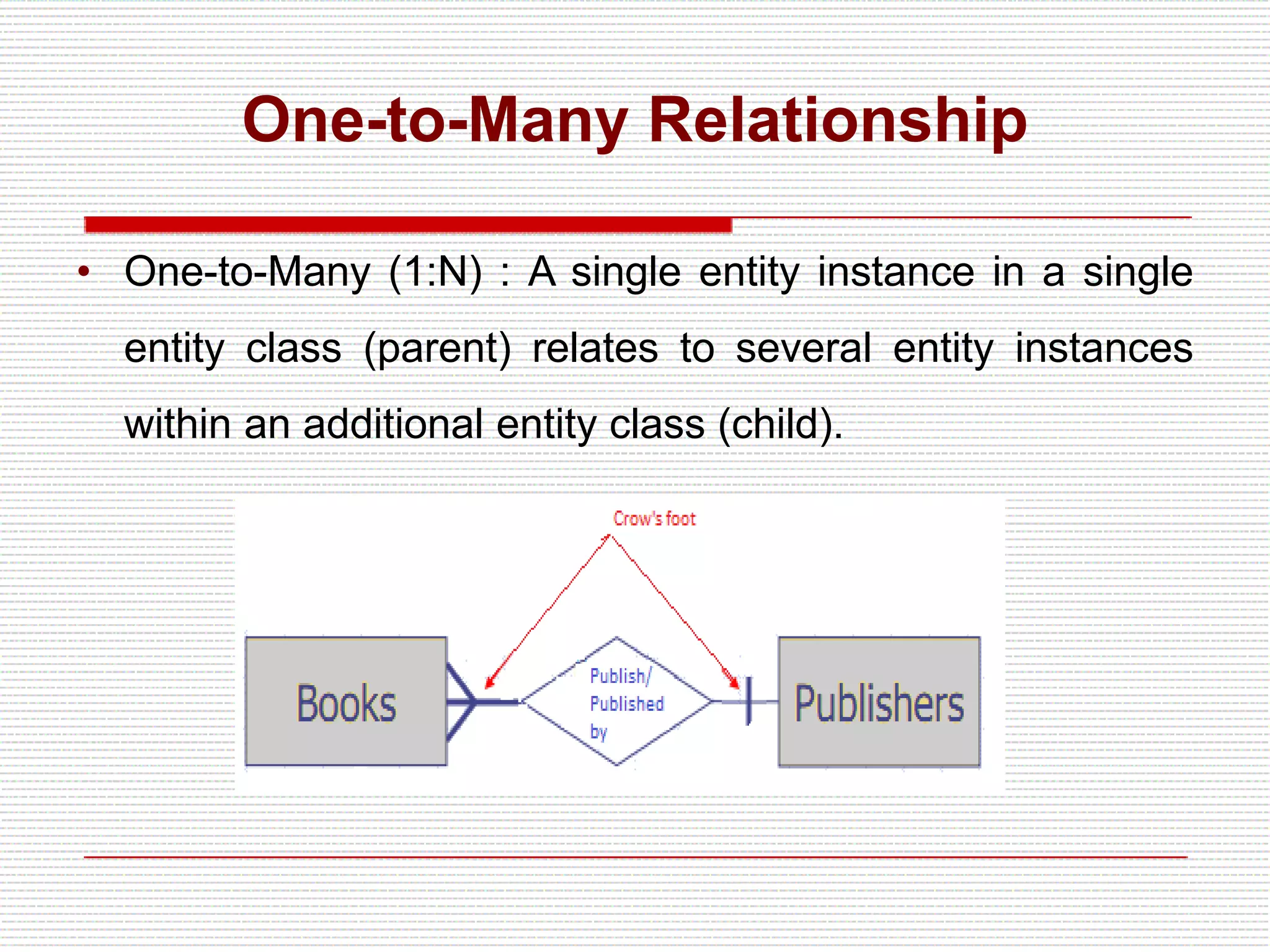
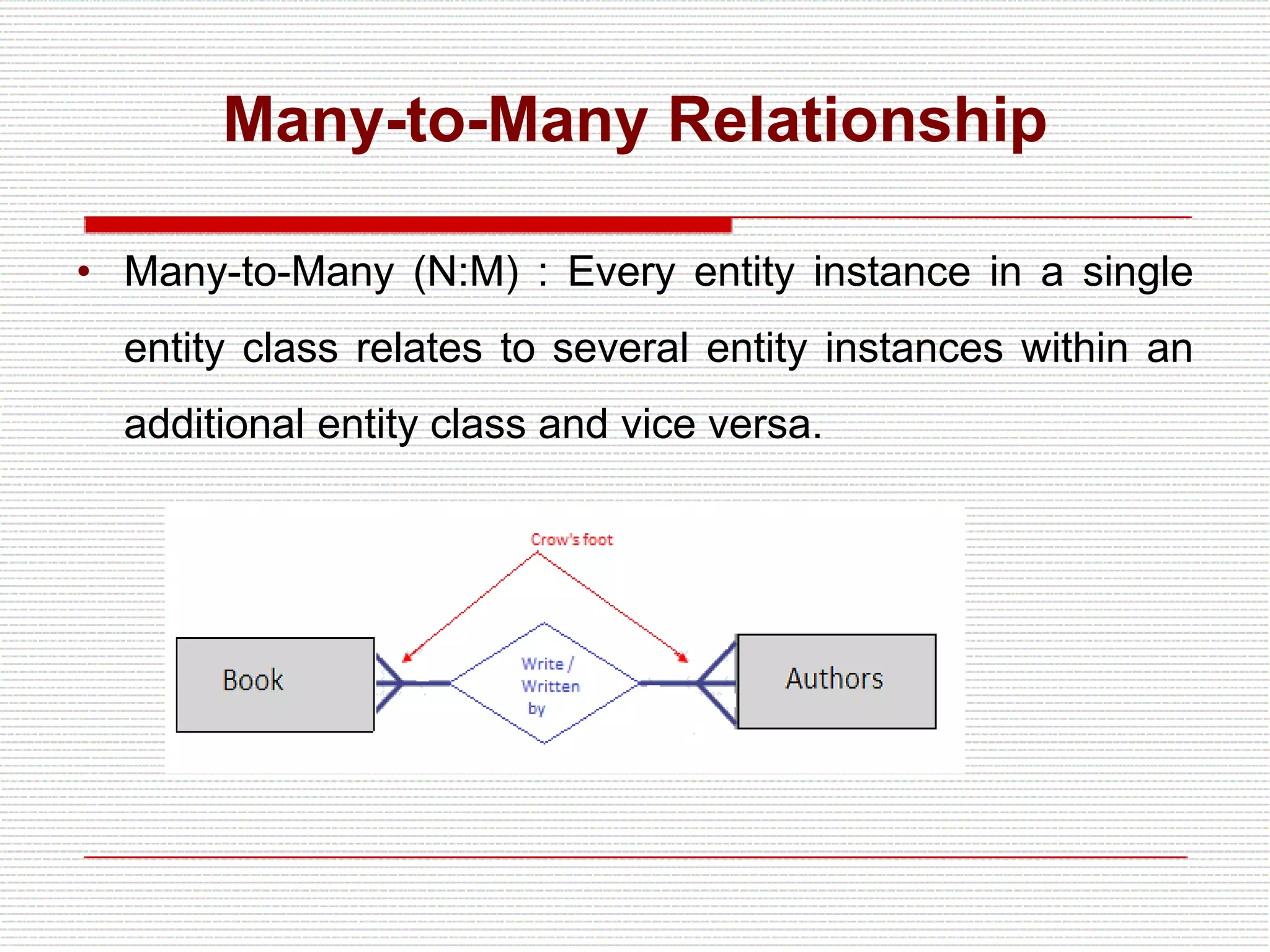
The document provides an introduction to entity-relationship (E-R) diagrams and modeling, emphasizing three primary constructs: entities, relationships, and attributes. It describes various attribute types, such as composite, multi-value, and derived attributes, and outlines how relationships between entities are categorized, including one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many relationships. Additionally, it includes guidelines for naming and defining relationships to ensure clarity and precision in data modeling.