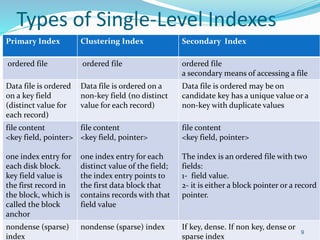
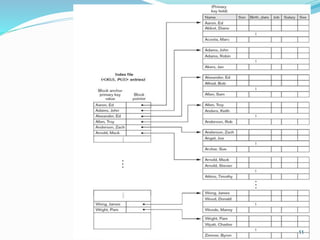
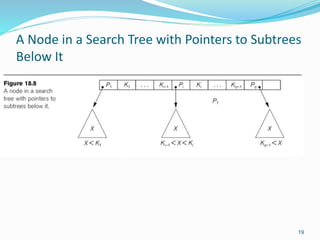
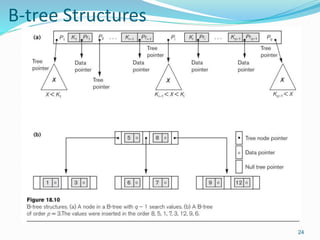
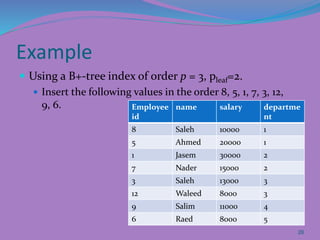
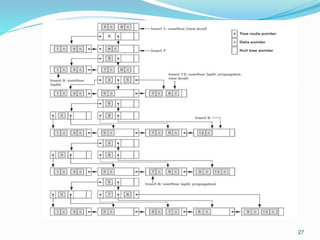
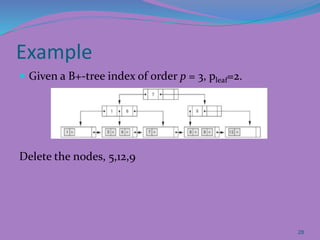
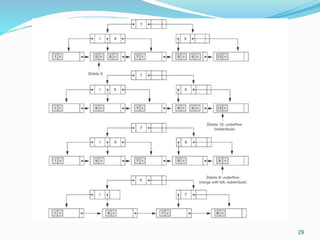
The document discusses different types of indexes that can be used to access data in a database file. It describes single-level indexes including primary indexes, clustering indexes and secondary indexes. It also discusses multi-level indexes and how B-trees and B+-trees can be used as dynamic multi-level indexes that allow efficient insertion and deletion of index entries.